cleavage
(1) The process of cytokinesis in animal cells, characterized by pinching of the plasma membrane. (2) The succession of rapid cell divisions without significant growth during early embryonic development that converts the zygote to a ball of cells.

blastula
A hollow ball of cells that marks the end of the cleavage stage during early embryonic development in animals.

gastrulation
In animal development, a series of cell and tissue movements in which the blastula-stage embryo folds inward, producing a three-layered embryo, the gastrula.

gastrula
An embryonic stage in animal development encompassing the formation of three layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
larva
A free-living, sexually immature form in some animal life cycles that may differ from the adult animal in morphology, nutrition, and habitat.
metamorphosis
A developmental transformation that turns an animal larva into either an adult or an adult-like stage that is not yet sexually mature.
Ediacaran biota
An early group of soft-bodied, multicellular eukaryotes known from fossils that range in age from 565 million to 550 million years old.
Cambrian explosion
A relatively brief time in geologic history when many present-day phyla of animals first appeared in the fossil record. This burst of evolutionary change occurred about 535–525 million years ago and saw the emergence of the first large, hard-bodied animals.
body plan
In multicellular eukaryotes, a set of morphological and developmental traits that are integrated into a functional whole—the living organism.
radial symmetry
Symmetry in which the body is shaped like a pie or barrel (lacking a left side and a right side) and can be divided into mirror-imaged halves by any plane through its central axis.
bilateral symmetry
Body symmetry in which a central longitudinal plane divides the body into two equal but opposite halves.
dorsal
Pertaining to the top of an animal with radial or bilateral symmetry.
ventral
Pertaining to the underside, or bottom, of an animal with radial or bilateral symmetry.
anterior
Pertaining to the front, or head, of a bilaterally symmetrical animal.
posterior
Pertaining to the rear, or tail end, of a bilaterally symmetrical animal.
cephalization
An evolutionary trend toward the concentration of sensory equipment at the anterior end of the body.
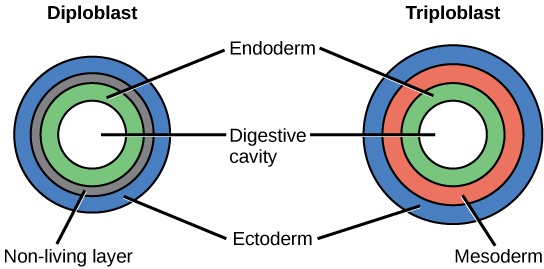
ectoderm
The outermost of the three primary germ layers in animal embryos; gives rise to the outer covering and, in some phyla, the nervous system, inner ear, and lens of the eye.

endoderm
The innermost of the three primary germ layers in animal embryos; lines the archenteron and gives rise to the liver, pancreas, lungs, and the lining of the digestive tract in species that have these structures.

diploblastic
Having two germ layers.

triploblastic
Possessing three germ layers: the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. Most eumetazoans are triploblastic.

mesoderm
The middle primary layer in a triploblastic animal embryo; develops into the notochord, the lining of the coelom, muscles, skeleton, gonads, kidneys, and most of the circulatory system in species that have these structures.
body cavity
A fluid- or air-filled space between the digestive tract and the body wall.
coelom
A body cavity lined by tissue derived only from mesoderm.

coelomate
An animal that possesses a true coelom (a body cavity lined by tissue completely derived from mesoderm).

pseudocoelomate
An animal whose body cavity is lined by tissue derived from mesoderm and endoderm.

acoelomate
A solid-bodied animal lacking a cavity between the gut and outer body wall.
protostome development
In animals, a developmental mode distinguished by the development of the mouth from the blastopore; often also characterized by spiral cleavage and by the body cavity forming when solid masses of mesoderm split.
deuterostome development
In animals, a developmental mode distinguished by the development of the anus from the blastopore; often also characterized by radial cleavage and by the body cavity forming as outpockets of mesodermal tissue.

spiral cleavage
A type of embryonic development in protostomes in which the planes of cell division that transform the zygote into a ball of cells are diagonal to the vertical axis of the embryo. As a result, the cells of each tier sit in the grooves between cells of adjacent tiers.
determinate cleavage
A type of embryonic development in protostomes that rigidly casts the developmental fate of each embryonic cell very early.

radial cleavage
A type of embryonic development in deuterostomes in which the planes of cell division that transform the zygote into a ball of cells are either parallel or perpendicular to the vertical axis of the embryo, thereby aligning tiers of cells one above the other.

archenteron
The endoderm-lined cavity, formed during gastrulation, that develops into the digestive tract of an animal.

blastopore
In a gastrula, the opening of the archenteron that typically develops into the anus in deuterostomes and the mouth in protostomes.
Eumetazoans
Member of a clade of animals with true tissues. All animals except sponges and a few other groups are this.
Bilaterians
Member of a clade of animals with bilateral symmetry and three germ layers.
Ecdysozoans
Member of a group of animal phyla identified as a clade by molecular evidence. Many are molting animals.
Lophotrochozoans
Member of a group of animal phyla identified as a clade by molecular evidence. They include organisms that have lophophores or trochophore larvae.
lophophore
In some lophotrochozoan animals, including brachiopods, a crown of ciliated tentacles that surround the mouth and function in feeding.
trochophore larva
Distinctive larval stage observed in some lophotrochozoan animals, including some annelids and molluscs.