
Which of the following pressures must remain negative to prevent lung collapse?
atmospheric pressure
intrapulmonary pressure
intrapleural pressure
transpulmonary pressure
Intrapleural pressure
Which of the following maintains the patency (openness) of the trachea?
surface tension of water
surfactant production
pseudostratified ciliated epithelium
C-shaped cartilage rings
C_Shaped cartilage rings
Which of the disorders below is characterized by destruction of the walls of the alveoli producing abnormally large air spaces that remain filled with air during exhalation?
pneumonia
coryza
emphysema
tuberculosis
Emphysema
True and False :
The lungs are perfused by two circulations: the pulmonary and the bronchial. The pulmonary circulation is for oxygenation of blood. The bronchial circulation supplies blood to the lung structures (tissue).
True
The nose serves all the following functions except ________.
as a passageway for air movement
warming and humidifying the
air
as the direct initiator of the cough reflex
cleansing
the air
As the direct initiator of the cough reflex

Which of the following respiratory rates illustrates eupnea for an average, healthy adult at rest?
60 breaths per minute
120 breaths per minute
15 breaths
per minute
25 breaths per minute
15 breaths per minute
Which of the following qualifies as a fully saturated hemoglobin molecule?
hemoglobin is transporting three oxygen molecules
hemoglobin is transporting two oxygen molecules
hemoglobin is transporting one oxygen molecule
hemoglobin is transporting four oxygen molecules
Hemoglobin is transporting four oxygen molecules
Surfactant helps to prevent the alveoli from collapsing by ________.
humidifying the air before it enters
interfering with the cohesiveness of water molecules, thereby reducing the surface tension of alveolar fluid
protecting the surface of alveoli from dehydration and other environmental variations
warming the air before it enters
interfering with the cohesiveness of water molecules, thereby reducing the surface tension of alveolar fluid

Where does gas exchange occur in the respiratory system?
terminal bronchioles
alveoli
lobar (secondary)
bronchi
trachea
Alveoli
Which of the choices below determines the direction of respiratory gas movement?
partial pressure gradient
the temperature
solubility in
water
molecular weight and size of the gas molecule
Partial pressure gradient
The erythrocyte count increases after a while when an individual goes from a low to a high altitude because the ________.
temperature is lower at higher altitudes
concentration of oxygen and/or total atmospheric pressure is higher at higher altitudes
basal metabolic rate is higher at high altitudes
concentration of oxygen and/or total atmospheric pressure is lower at high altitudes
concentration of oxygen and/or total atmospheric pressure is lower at high altitudes
Tidal volume is air ________.
inhaled after normal inspiration
forcibly expelled after
normal expiration
exchanged during normal breathing
remaining in the lungs after forced expiration
exchanged during normal breathing
What determines the respiratory rhythm in the body?
medullary respiratory centers
pontine respiratory
centers
oxygen levels in the blood
Hering-Breuer stretch reflexes
Medullary respiratory centers
Which of the choices below describes the forces that act to pull the lungs away from the thorax wall and thus collapse the lungs?
compliance and transpulmonary pressures
compliance and the surface tension of the alveolar fluid
the natural tendency for the lungs to recoil and transpulmonary pressures
the natural tendency for the lungs to recoil and the surface tension of the alveolar fluid
the natural tendency for the lungs to recoil and the surface tension of the alveolar fluid
Hypoxia can be caused by ______.
hyposecretion of erythropoietin
having a fever
slightly
elevated level of lactic acid in the blood
All of the listed
responses are correct.
Hyposecretion of erythropoietin
The __________ is also known as the "guardian of the airways."
larynx
vestibular folds
epiglottis
glottis
Epiglottis
In the plasma, the quantity of oxygen in solution is ________.
not present except where it is combined with carrier molecules
about equal to the oxygen combined with hemoglobin
greater than the oxygen combined with hemoglobin
only about 1.5% of the oxygen carried in blood
only about 1.5% of the oxygen carried in blood
Respiratory control centers are located in the ________.
upper spinal cord and medulla
medulla and pons
midbrain
and medulla
pons and midbrain
Medulla and pons
Which of the following is not an event necessary to supply the body with O2 and dispose of CO2?
internal respiration
pulmonary ventilation
external
respiration
blood pH adjustment
Blood pH adjustment
Which parts of the respiratory system function as the main sites of gas exchange?
primary bronchi
terminal bronchioles
alveoli
trachea
Alveoli

What is the volume of the total amount of exchangeable air for a healthy, young adult male?
2400 ml
3600 ml
6000 ml
4800 ml
4800 ml

Since mucus-producing cells and cilia are sparse in the bronchioles and alveoli, how does the body remove microorganisms that make their way into the respiratory zone?
type II alveolar cells secrete a substance called surfactant
type I alveolar cells produce antimicrobial proteins
alveolar macrophages crawl freely along internal alveolar surfaces
the pleurae produce pleural fluid
alveolar macrophages crawl freely along internal alveolar surfaces

What part of the larynx covers the laryngeal inlet during swallowing to keep food out of the lower respiratory passages?
epiglottis
glottis
vocal folds
thyroid cartilage
Epiglottis
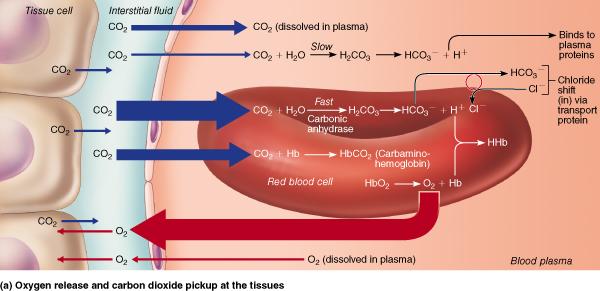
Which form of CO2 transport accounts for the least amount of CO2 transported in blood?
dissolved in plasma
chemically bound to hemoglobin
as
bicarbonate ion in plasma
as carbon monoxide in plasma
Dissolved in plasma

Which muscles are activated during normal quiet inspiration?
scalenes, sternocleidomastoid, and pectoralis minor muscles
oblique and transversus muscles
diaphragm and external intercostal muscles
diaphragm and internal intercostal muscles
diaphragm and external intercostal muscles
What is the most powerful respiratory stimulant in a healthy person?
oxygen needs of cells
arterial blood pH
arterial blood
carbon dioxide level
arterial blood oxygen level
Arterial blood carbon dioxide level
True and False:
The olfactory mucosal lining of the nasal cavity contains the receptors for the sense of smell.
True
True or False:
Although lung cancer is difficult to cure, it is highly preventable.
True

What is the tidal volume of an average adult male?
500 ml
3100 ml
1200 ml
4800 ml
500 ml
Possible causes of hypoxia include ________.
too little oxygen in the atmosphere
getting very cold
taking several rapid deep breaths
obstruction of the esophagus
too little oxygen in the atmosphere

Which of the following conditions or scenarios increases the respiratory rate?
acidosis
increasing partial pressure of oxygen
hypocapnia
alkalosis
Acidosis
Emphysema can result in an ______.
increased level of carbaminohemoglobin
increased level of
deoxyhemoglobin
increased likelihood of the skin of Caucasians
developing a slightly blue coloration
All of the listed
responses are correct.
All of the listed responses are correct
The local matching of blood flow with ventilation is ________.
ventilation-perfusion coupling
the Bohr effect
chloride
shifting
the Haldane effect
Ventilation-perfusion coupling
Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in the lungs and through all cell membranes by ________.
filtration
active transport
diffusion
osmosis
Diffusion
Which of the following gives the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas?
Haldane effect
Boyle's law
Henry's law
Dalton's
law of partial pressures
Boyle's law

What is the most common method of carbon dioxide transport?
as bicarbonate ions in the plasma
chemically bound to hemoglobin as carbaminohemoglobin
dissolved in the plasma
chemically bound to hemoglobin as oxyhemoglobin
as bicarbonate ions in the plasma
True and False:
Emphysema is distinguished by permanent shrinkage of the alveoli.
False
Intrapulmonary pressure is the ________.
difference between atmospheric pressure and respiratory
pressure
pressure within the pleural cavity
pressure
within the alveoli of the lungs
negative pressure in the
intrapleural space
pressure within the alveoli of the lungs
In babies born prematurely, pulmonary surfactant may not be present in adequate amounts ______.
in the conducting zone structures of the lungs
due to insufficient exocytosis in the type II alveolar cells
to permit adequate surface tension in the alveoli
because the presence of collapsed alveoli prevents surfactant production
due to insufficient exocytosis in the type II alveolar cells
True or False:
The parietal pleura lines the thoracic wall.
True

Which volumes are combined to provide the inspiratory capacity?
tidal volume (TV) + inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) + expiratory reserve volume (ERV) + residual volume (RV)
expiratory reserve volume (ERV) + residual volume (RV)
tidal volume (TV) + inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
tidal volume (TV) + inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) + expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
tidal volume (TV) + inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
True or False:
Intrapleural pressure is normally about 4 mm Hg less than the pressure in the alveoli.
True
True or False:
During normal quiet breathing, approximately 750 ml of air moves into and out of the lungs with each breath.
False
The major nonelastic source of resistance to air flow in the respiratory passageways is ________.
friction
air pressure
surfactant
surface tension
Friction
Which of the following is NOT a function of the larynx?
to assist in taste sensation
stimulation of the "cough" reflex
voice production
to provide a patent airway
to act as a switching mechanism to route air and food into the proper channels
to assist in taste sensation

Which of the following pressures rises and falls with the phases of breathing, but eventually equalizes with the atmospheric pressure?
intrapulmonary pressure
intrapleural pressure
transpulmonary pressure
atmospheric pressure
Intrapulmonary pressure
Which of the following structures would be the LEAST vulnerable to damage caused by oxygen toxicity?
brain
spleen
muscles
costal cartilages
costal cartilages

Which of the following initiates inspiration?
ventral respiratory group (VRG)
diencephalon
pontine respiratory centers
dorsal respiratory group (DRG)
ventral respiratory group (VRG)
True or False:
The paired lungs occupy all of the thoracic cavity.
False
What is the most immediate driving force behind pulmonary ventilation?
smooth muscle contraction
environmental stimuli
air sac
contraction
intrapulmonary pressure change
Intrapulmonary pressure change
The respiratory membrane is a combination of ________.
respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts
alveolar and
capillary walls and their fused basement membranes
atria and
alveolar sacs
respiratory bronchioles and alveolar sacs
Alveolar and capillary walls and their fused basement membranes

What type of epithelial tissue forms the walls of the alveoli?
simple squamous epithelium
simple cuboidal epithelium
stratified squamous epithelium
pseudostratified ciliated
columnar epithelium
Simple squamous epithelium
Which of the following stimuli is the most powerful respiratory stimulant to increase respiration?
arterial pH
a rise in body temperature
an increase in
blood pH
rising carbon dioxide levels
Rising carbon dioxide levels
During pneumonia, the lungs become "waterlogged"; this means that within the alveoli there is an abnormal accumulation of ______.
blood
blood plasma
interstitial fluid
water
Interstitial fluid
True and False:
Changes in arterial pH can modify respiration rate and rhythm even when carbon dioxide and oxygen levels are normal.
True
Which of the following is not a stimulus for breathing?
rising blood pressure
acidosis resulting from CO2
retention
rising carbon dioxide levels
arterial Po2 below
60 mm Hg
Rising blood pressure
True or False:
Oxygenated hemoglobin releases oxygen more readily when the pH is more basic.
False
True or False :
Labored breathing is termed dyspnea.
True
__________, the difference between the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures, prevents the lungs from collapsing.
Intraalveolar pressure
Atmospheric pressure
Transthoracic pressure
Transpulmonary pressure
Transpulmonary pressure
What is ventilation-perfusion coupling?
matching the amount of blood flow through the body to the amount of oxygen in the air sacs
matching the amount of gas reaching the alveoli to the blood flow in pulmonary capillaries
matching the amount of oxygen exchanged for carbon dioxide in the alveoli to the exchange at the tissue level
matching the amount of gas reaching the alveoli to pO2 and pCO2 values in the blood
matching the amount of gas reaching the alveoli to the blood flow in pulmonary capillaries
Gas emboli may occur because a ________.
person holds his breath too long
person breathes pure oxygen
in a pressurized chamber
diver holds his breath upon
ascent
pilot holds her breath upon descent
Diver holds his breath upon ascent
True and False:
The structures within the respiratory system's conducting zone include the trachea and the paranasal sinuses.
True
Which center is located in the pons?
pontine respirator group (PRG)
inspiratory center
expiratory center
pacemaker neuron center
pontine respirator group (PRG)
Which of the choices below is not a role of the pleura?
helps divide the thoracic cavity into three chambers
aids in blood flow to and from the heart because the heart sits between the lungs
allows the lungs to inflate and deflate without friction
helps limit the spread of local infections
Aids in blood flow to and from the heart because the heart sits between the lungs
True or False:
Increased temperature results in decreased O2 unloading from hemoglobin.
False
True or False:
Tracheal obstruction is life threatening.
True
The statement, "in a mixture of gases, the total pressure is the sum of the individual partial pressures of gases in the mixture" paraphrases ________.
Henry's law
Dalton's law
Boyle's law
Charles' law
Dalton's law
How is the bulk of carbon dioxide carried in blood?
as carbonic acid in the plasma
chemically combined with the amino acids of hemoglobin as carbaminohemoglobin in the red blood cells
chemically combined with the heme portion of hemoglobin
as the bicarbonate ion in the plasma after first entering the red blood cells
as the bicarbonate ion in the plasma after first entering the red blood cells
Which of the choices below is not a factor that promotes oxygen binding to and dissociation from hemoglobin?
number of red blood cells
partial pressure of carbon
dioxide
partial pressure of oxygen
temperature
number of red blood cells
Because the lungs are filled with fluid during fetal life, which of the following statements is true regarding respiratory exchange?
Respiratory exchanges are made through the ductus arteriosus.
Because the lungs develop later in gestation, fetuses do not need a mechanism for respiratory exchange.
Respiratory exchanges are not necessary.
Respiratory exchanges are made through the placenta.
Respiratory exchanges are made through the placenta.