Health
- a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being
Wellness
- a lifestyle that enhances our level of health
Lifestyle
- pattern of behaviors
Primary Prevention
- prevent initial development of a disease or poor health
-
ex:
- diet
- exercise
Secondary Prevention
- early detection to halt, reduce, or reverse the effects of a disease or poor health
- manages disease
Essential Nutrients
- body CAN NOT synthesize
- must be obtained from diet
Nonessential Nutrients
- nutrients that the body can synthesize
Dietary Standards
- a guide to adequate nutrient intake levels against which to compare nutrient values of foods consumed
Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA)
- the amount of nutrient and calorie intake per day considered necessary for maintenance of good health
- amount of nutrient needed to satisfy the needs of almost healthy individuals at a life stage or gender study
Estimated Average Requirement (EAR)
- The daily intake of a specific nutrient estimated to meet the requirement in 50% of healthy people in an age- and gender-specific group
Adequate Intake (AI)
- A recommended intake value based on observed or experimentally determined approximations or estimates of nutrient intake by a group of healthy people
- used when recommended allowance is not determined
Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL)
- is the level of nutrient intake that should not be exceeded to prevent adverse health risks
Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR)
- daily percent of calories intake that should come from carbs, lipids, and proteins
daily kcal intake for carbs
- 45-65%
daily kcal intake for saturated fats
- 10% or less
daily kcal intake for lipids/fats
- 20-35%
daily kcal intake for proteins
- 10-35%
Estimated Energy Requirement (EER)
- the DRI for dietary energy intake
Nutrient Density
- ratio comparison of a food's nutrient content with the kcal value that the food contains
- nutrient value vs caloric value
Overnutrition
- consumption of too many nutrients and too much energy in comparison with DRI values
Malnutrition
- condition resulting from an imbalanced nutrient and/or energy intake
Undernutrition
- consumption of not enough energy or nutrients in comparison with DRI values
Four Themes of MyPlate
- Variety
- Proportionality
- Moderation
- Activity
Variety (MyPlate Theme)
- eat foods from all food groups and subgroups
Proportionality (MyPlate Theme)
- eat more of some foods and less of others
Moderation (MyPlate Theme)
- choose types of foods that limit intake of saturated or trans fats, added sugars, cholesterol, salt, and alcohol
Activity (MyPlate Theme)
- be physically active every day
Food Labels
- a way for consumers to see how individual foods fit their nutritional needs
Metabolism
- enzyme mediated chemical reactions
- cells use energy to build and acquire energy from the breakdown of organic molecules
- absorbed nutrients are used by the body for energy and to form and maintain body structures and functions
Anabolism
- process of synthesis from which substances are formed
- uses energy to build organic molecules
- endothermic
Catabolism
- breakdown of food components into smaller molecular particles
- acquires energy breaking down organic molecules
- exothermic
GER (gastroesophagel reflux)
- A backflow of the contents of the stomach into the esophagus, caused by relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter
Strategies to prevent GER
- avoid high-fat meals
- avoid overeating
- avoid laying down after eating
- avoid pressure on stomach
- avoid eating too fast
3 Elements found in Carbohydrates
- Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
Ratio of elements in Carbs
- 1:2:1
Monosaccharides (simple carbohydrates)
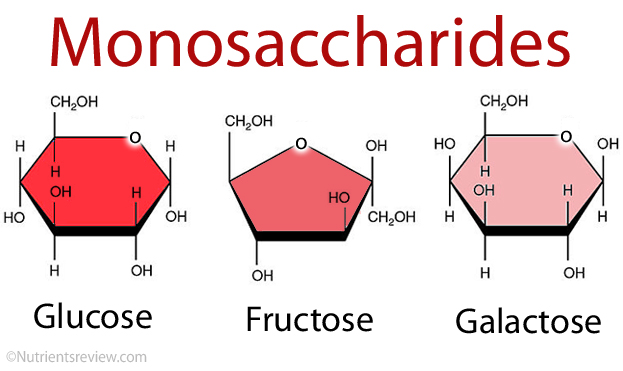
- composed of single carbohydrate units
- ex: glucose, fructose, galactose
Disaccharides (simple carbohydrates)
- consists of two single carbohydrates bound together
- ex: sucrose, maltose, lactose
Polysaccharides (complex carbohydrates)
- consists of many subunits of monosaccharides joined together
- ex: starch, fiber, glycogen
Glycogen
- storage form of carbohydrate energy
- stored in the liver and muscles
- retrieved as needed for energy
Glycogenesis
- the process of converting glucose to glycogen
Carbohydrates
- provides energy (function)
- protein-sparing effect
- If enough carbohydrate is provided to meet the energy needs of the body, protein can be spared or saved to use for specific protein functions
- the CNS functions best from glucose
- the GI tract has the role of digesting carbs into monosaccharides for easy absorption
Blood glucose homeostasis
- between 70 to 100 mg/dL
Glycogenolysis
- the process of converting glycogen back to glucose
Glycolysis
- a metabolic process that breaks down carbohydrates through a series of reactions to either pyruvic acid or lactic acid and releases energy for the body in the form of ATP
Gluconeogenesis
- the process of producing glucose from fats or protein
Ketone Bodies
- created when fatty acids are broken down for energy when sufficient carbs are unavailable
Glucose
- simple carbs (monosaccharides)
- blood sugar
- rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream
- food sources: fruits, sweeteners
Fructose
- simple carbs (monosaccharides)
- fruit sugars
- food sources: fruits, honey, syrups, vegetables
Galactose
- simple carbs (monosaccharides)
- food sources: part of lactose, found in milk
Sucrose
- simple carbs (disaccharides)
- glucose + fructose
- table sugar
- food sources: sugarcane, sugar beets, fruits, vegetables
Lactose
- simple carbs (disaccharides)
- milk sugar
- food sources: milk and milk products
- glucose + galactose
Maltose
- simple carbs (disaccharides)
- malt sugar
- food sources: germinating grains
- glucose + glucose
Starches
- complex carbohydrates
- strings of glucose
- storage form of plant carbohydrate
- food sources: grains, legumes, potatoes
Fiber
- roughage
- strings of monosaccharides, usually glucose
- cannot be broken down by human digestive enyzmes
- Insoluble vs Soluble Fiber
- food sources: legumes, whole grains, fruits, vegetables
Blood Glucose
- a source of energy to all cells
Ketoacidosis/Ketosis
- the result build up of ketones leading to acid-base imbalances in the body
Insulin
- hormone
- produced by the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans
- lowers/decrease blood glucose levels by enhancing the conversion of excess glucose to glycogen (glycogenesis)
Glucagon
- hormone
- increases blood glucose levels
- stimulates conversion of liver glycogen to glucose
- assists regulation of blood glucose throughout the night
Somatostatin effect on blood glucose
- hormone
- secreted from the hypothalamus and pancreas
- inhibits the functions of insulin and glucagon
Epinephrine effect on the liver
- hormone
- enhances the fast conversion of liver glycogen to glucose (glycogenolysis)
Steroid Hormones (Insulin Inhibitor)
effect on blood glucose
- functions against insulin
- promotes glucose formation from protein
Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone (ACTH)
effect on blood glucose
- insulin inhibitor
- promotes glucose formation from protein
Thyroid Hormones effect on blood absorption
- affects blood glucose level by enhancing intestinal absorption of glucose and releasing epinephrine
Growth Hormones effect on blood glucose
- insulin inhibitor
- increase gluconeogenesis from protein
Glycemic Index
- rankings of foods according to the level to which a food raises blood glucose levels
- measures a single component of food
Glycemic Load
- considers the total glycemic index effect of a mixed meal of dietary plan
- whole thing
What happens to fructose in the liver?
- liver cels rearrange fructose into glucose
What happens to starch in the digestive tract?
- it is broken down to provide glucose
Insoluble FIber
- fiber that does not dissolve in fluids
Soluble Fiber
- fiber that dissolves in fluids
- thickens substances
- provides structure and protection for plants
Health Effects of Dietary Fiber
- obesity
- constipation
- diverticular disease
- colon cancer
- heart disease
- diabetes control
Since the 1940s ______ grains are generally enriched with niacin, folate, thiamine, riboflavin, and iron.
refined
______/______ grains are sources of magnesium, riboflavin, niacin, thiamin, vitamin B6, zinc, and some protein that are k=lost when refined.
whole/unrefined
Palatibility (Lipids)
- fats make food taste and smell good
Satiety (Lipids)
- hormones released in response to the consumption of fat causes us to feel full and satisfied
Satiation (Lipids)
- increases our desire to eat more fatty food
Emulsifier
- a substance that works by being soluble in water and fat at the same time
Lipoproteins
- carriers or transporters of lipids
Lecithin
- a phospholipid
- extensive role as an emulsifier
- part of lipoproteins
Triglycerides (structure)
- composed of a glycerol and three fatty acids
How can you tell the difference between carbohydrates and triglycerides by looking at the chemical formula?
...
What elements are found in triglycerides?
- carbon
- hydrogen
- oxygen
Physiologic Function of Triglycerides
- stored energy
- organ protection
- temperature regulation
- insulation
Function(s) of Phospholipids
- form part of all cell membrane structure
- serve as emulsifiers to keep fats dispersed in body fluids
Function(s) of Sterols
- provides basic material to make bile, vitamin D, sex hormones, and cells in brain and nerve tissue
What elements are found in fatty acids?
- carbon atoms
Cholesterol
- a vital part of all cell membrane, nerve tissue, and building block for hormones
How many carbons are found in glycerol?
- there are three carbon atoms in glycerol
- tri = 3
Saturated Fatty Acid

- has a single-bonded carbon chain
- fully saturated b/c hydrogen atoms are attached to all available bonding sites
- contained in meats, butterfat, shortening, and vegetable oils
Monounsaturated Fatty Acid (MUFA)
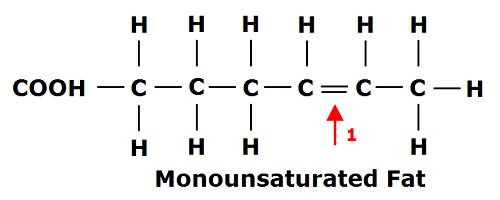
- a carbon chain has only one unsaturated double bond
- dietary sources: olive oil, peanuts, and canola oil
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid (PUFA)
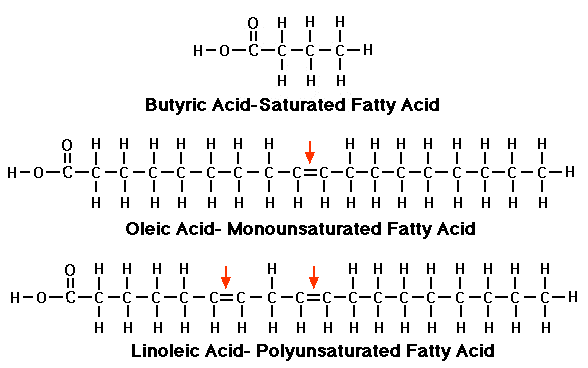
- a carbon chain has two or more unsaturated double bonds
- characterized by the location of the unsaturation in the molecular structure
- dietary sources: vegetable oils, fish, and margarine
What two categories of polyunsaturated fatty acids are essential?
- omega-3 (linolenic)
- omega-6 (linoleic)
Americans consume a large amount of Omega-____.
omega-6 (linoleic)
Americans consumption of Omega-___ is low.
omega-3 (linolenic)
Types of Omega-_ help prevents heart disease.
omega-3 (linolenic)
Rich sources of Omega-__ are deep water fish such as salmon, tuna, sardines, and herring. Omega-__ can also be obtained from plant sources such as canola oil, some nuts such as walnuts, soybean and soybean oils, and extra virgin or virgin oils.
omega-3; omega-3
Hydrogenation
- process which forces hydrogen atoms to break a double bond and attach to the carbons
- creates saturated fat
- makes fats more solid/stable
Dietary Sources of Saturated Fatty Acids
- meats
- butterfat
- shortening
- vegetable oils
- beef
- poultry
- pork
- lamb
- egg yolks
- dairy products
Catabolism of Lipids
- involves the hydrolysis of triglycerides into two-carbon units that become part of acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA)
Acetyl CoA (Lipids)
- an intermediate byproduct in metabolism
- formed from the breakdown of glucose, fatty acids, and certain amino acids
- enters the TCA cycle
Lipogenesis
- synthesis of lipids
- results in the formation of triglycerides, phospholipids, cholesterol, and prostaglandins
When found in excess, glucose and amino acids are converted to what form of lipid?
- triglycerides and phosphates
Lipid metabolism is primarily regulated by _______, ____ _____, and ______ ______ ______.
insulin; growth hormones; adrenal cortex hormones
Role of Bile Emulsification (Lipids)
- bile emulsifies fat to facilitate digestion
Chylomicrons
- the first lipoproteins formed after the absorption of lipids from food
- transport fats from the intestinal wall to the liver cells
Most Americans consume between _______ and _______ % of total energy as fat. How does this compare to the suggested ADMR?
- 35 to 40%
- it exceeds the ADMR for fat which is 20-35%
Very Low-Density Lipoproteins (VLDL)
- large lipoproteins rich in triglycerides;
- VLDLs circulate through the blood giving up their triglycerides to fat and muscle tissue until the VLDL remnants are modified and converted into LDL
- leaves the liver cells full of fats and lipid components to transfer newly made triglycerides to the cells
Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL)
- a lipoprotein that t ransports cholesterol in the blood; composed of moderate amount of protein and a large amount of cholesterol;
- high levels are thought to be associated with increased risk of coronary heart disease and atherosclerosis
Protease
- protein enzymes
- secreted in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine
Amino Acids (20)
- organic compounds
- contain carbon, hyrdrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen
Essential Amino Acids (9)
- must be eaten in food
Nonessential Amino Acids (11)
- liver can create as long as the structural components (including nitrogen) are available
Amino Acid Pool
- a collection of amino acids that is constantly resupplied with EAAs and NEAAs
- allows cells to build proteins easily
Functions of Proteins
- growth and maintenance
- All growth depends on a sufficient supply of amino acids. The amino acids are needed to make the proteins required to support muscle, tissue, bone formation, and the cells themselves
- creation of communicators and catalysts
- immune system response
- fluid anf electrolyte balance
- acid-base balance
- transportation
Complete Protein
- contains all nine EAAs in sufficient quantities that best support growth and maintenance
Incomplete Protein
- lacks one or more of the nine essential amino acids
Protein Energy Malnutrition (PEM)
...