1
Emerging Diseases
- one that has appeared in a population for the first time
- or one that previously existed but is rapidly increasing in incidence
2
Pathogens

- any agent that causes a disease
- usually virus, bacterium, fungus, protozoan, or helminth
3
Bioremediation
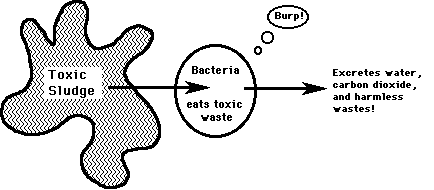
- decomposition of harmful chemicals by microbes or consortia of microbes
4
Genetic Engineering

- a field involving deliberate alterations of the genomes of microbes, plants, and animals through special technological processes
5
Algae
- photosynthetic, plantlike organ that generally lack the complex structure of plants
- they may be single-celled or multicellular
- inhabits diverse habitats
6
Macroscopic
- visible to the naked eye
7
Adapitibility
- the adjustment of bacterial physiology to a new environment
8
Immunology

- the study of the system of body defenses that protect against infection
9
Epidemiology

- the study of the factors affecting the prevalence and spread of disease within a community
10
Biotechnology
- the use of microbes or their products in the commercial or industrial realm
11
Infectious

- capable of cause an infection
12
Prokaryote

- a single celled organism that does not have special structures such as a nucleus or membranous organelles
-
includes:
- bacteria
- archea
13
Eukaryote
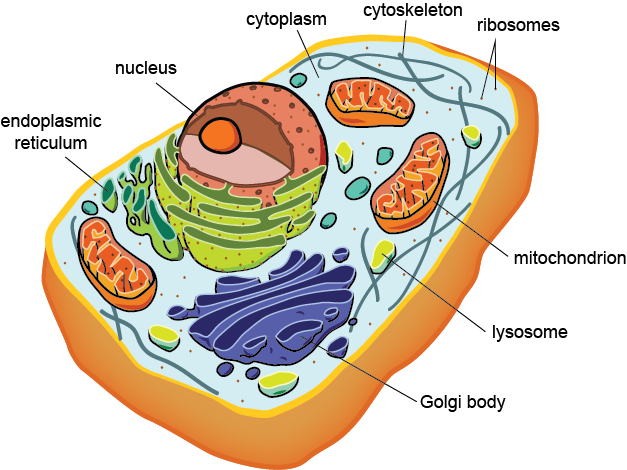
- a member of the domain Eukarya
- cells have a well-defined nucleus and membranous organelles
-
includes:
- plants
- animals
- fungi
- protozoa
- algae
14
Parasites

- an organism that lives on or within another organism from which it obtains nutrients and enjoys protection
- produces harm to the host
15
Hosts
- organism in which smaller organisms or viruses live, feed, and reproduce
16
Spontaneous Generation
- early belief that living things arose from vital forces present in nonliving or decomposing matter
17
Abiogenesis
- the belief in spontaneous generation as a source of life
18
Biogenesis
- belief that living things can only arise from others of the same kind