Describe the features and tributaries of the Superior Vena Cava (SVC)

Tributaries from R. and L.Brachiocephalic veins
- Brachiocephalic formed by tributaries of subclavian, internal
jugular and internal thoracic veins
- Subclavian tributary are external jugular veins
Single Azygous vein tributary
Begins in lower border of 1st costal cartilage and descends behind 2nd-3rd intercostal spaces into RA
L.Lateral border is aortic arch and trachea
R.Lateral border is pleura and right upper lobe of lung
Anterior border is thymus and manubrium
Describe the features and tributaries of the Inferior Vena Cava (IVC)
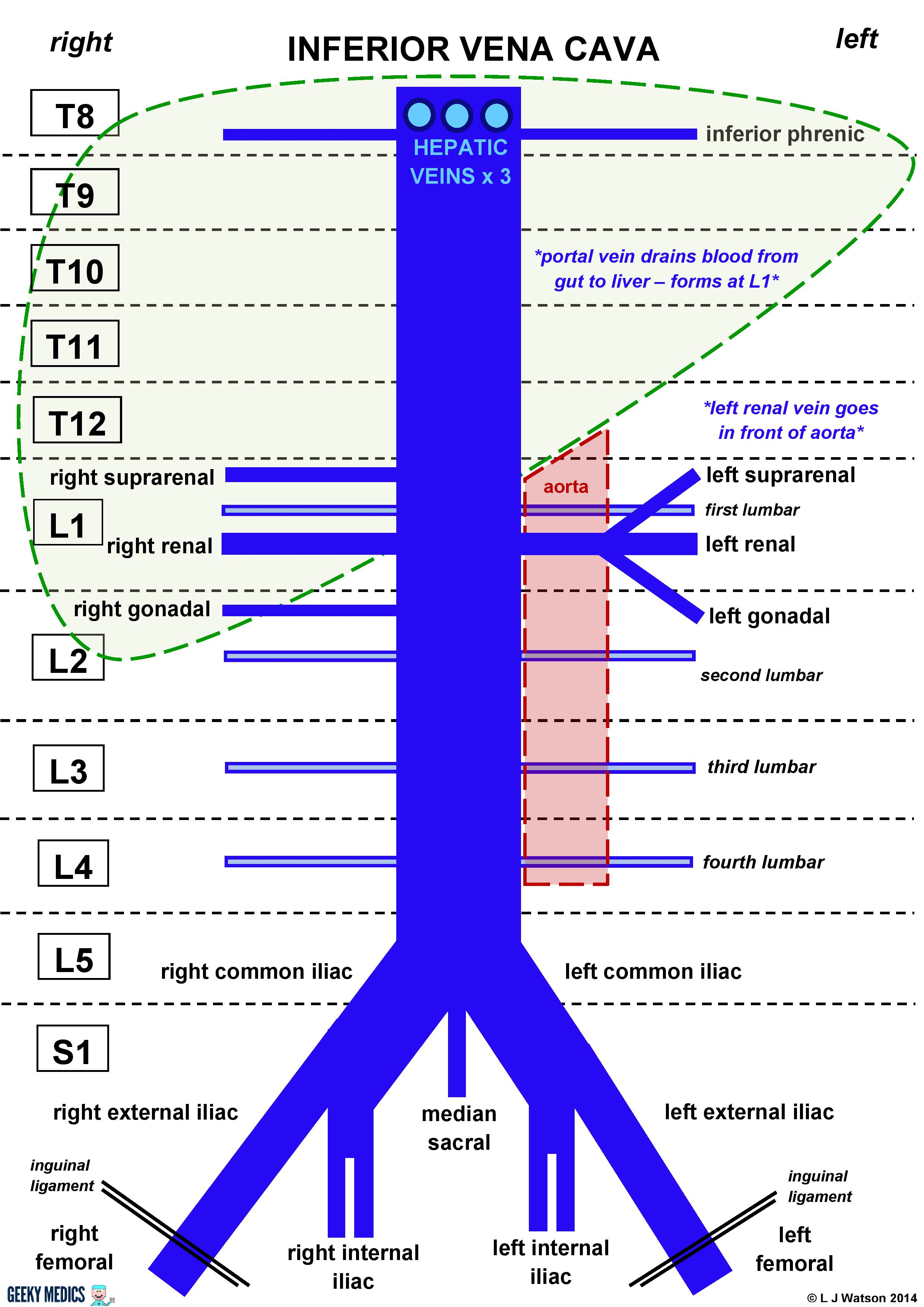
Formed by the joining of the common iliac veins at L5
Is a retroperitoneal structure - Posterior to abdominal cavity next to vertebral colum
Anastomoses the azygous system on the Right side of the vertebral column
Caval opening is at T8
Right side
- Gonadal vein and suprarenal vein drain into IVC
Left side
- Gonadal vein and suprarenal vein drain into renal vein then into IVC
- L.Inferior phrenic veins drain into L.Renal vein
All lumbar and hepatic veins drain into IVC
Tributaries from superior to inferior
- Hepatic - T8
- Inferior phrenic - T8
- 1-2 per side from diaphragm
- R.Suprarenal - L1
- Renal - L1
- R.Gonadal - L2
- Lumbar - L1-5
- Common iliac - L5
- Tributaries of internal and external iliac veins
Describe the epigastric veins, their tributaries and their relationship to the anterior abdominal wall
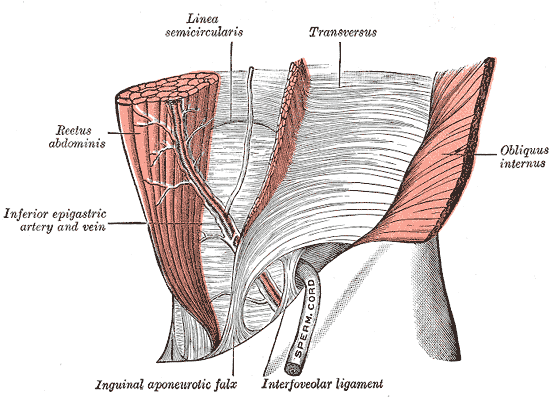
The veins accompany the arteries in the abdominal wall
Superior epigastric
- Drains into internal thoracic vein - inferior to external iliac vein
Both the superior and inferior anastomose with each other at the level of the umbilicus, and with paraumbilical veins
Inferior epigastric vein
- Arises from the superior epigastric vein
- Drains into external iliac vein
Describe the azygous system, its function and the relation to the SVC

The azygous or hemiazygous vein arise from the ascending lumbar vein from the lumbar veins and lateral sacral vein that come from the common iliac vein
- When these ascending lumbar veins cross the subcostal vein (vein along the bottom of the 12th rib) it becomes the azygous or hemiazygous
Comprises the azygous, hemiazygous, accessory hemiazygous and the L.superior intercostal vein
Function
- Drain the posterior abdominal wall, thoracic wall and the upper lumbar region via the lumbar and posterior intercostal veins
Azygous
- Arises from the union of the R.ascending lumbar and the R.subcostal vein ~T12
- Drains the R.lower 8 posterior intercostal veins and the R.bronchial veins
- Enters thorax via aortic hiatus
- Ascends along vertebral column on the RHS within the posterior mediastinum
- Arches over R.main bronchus T5-6
- Enters SVC at T4 or can enter into R.Brachiocephalic or R.subclavian
- Tributaries
- Hemiazygous joins at T8 as it crosses from L. to R.
- R.superior intercostal vein joins superiorly
Hemiazygous
- May or may not be present
- Arises from the L.ascending lumbar vein
- Passes through L.crus of diaphragm
- Drains L.9-11 posterior intercostal veins and L.subcostal vein
- Crosses vertebral column from L. to R. at T8 where it anastomoses with the azygous
Accessory hemiazygous
- Not always present
- On the LHS
- Arises from the 4th-8th L.posterior intercostal veins
- Drains L.bronchial vein
- Crosses behind the oesophagus at T8 to anastomose with the azygous or can anastomose superiorly to the L.brachiocephalic vein to join into the SVC
List all of the veins and their tributaries of the trunk (abdomen, thorax and neck region)

- SVC
- L. and R. Brachiocephalic
- Internal Jugular
- External Jugular
- Subclavian
- IVC
- Hepatic veins
- R. Suprarenal
- R. gonadal
- R. Renal
- L. Suprarenal
- L. Renal
- L. Gonadal
- Common iliac
- Internal iliac
- External iliac
- Femoral
- R.Ascending lumbar vein
- Azygous
- Hemiazygous
- Accessory Hemiazygous
- L.Ascending lumbar
Describe in brief the major drainage vessels of the 3 section of the gut (fore, mid and hind) via the hepatic portal system

Foregut ~ oesophagus, duodenum, stomach
- Drained by splenic vein
- Supplied by coeliac trunk
Midgut ~ Small intestine
- Drained by superior mesenteric vein
- Supplied by superior mesenteric artery
Hindgut ~ Large intestine
- Drained by inferior mesenteric vein
- Supplied by inferior mesenteric artery
Describe the relationship between surface/cross sectional anatomy and that truncal venous system
R.1st costal cartilage = Brachiocephalic veins become SVC
Manubriosternal joint = Azygous terminates at SVC
Transpyloric plane = Confluence of superior mesenteric and splenic veins
L5 = Common iliac veins joint o form IVC