Pulmonary Circuit

-carries blood to and from the gas exchange surfaces of the lungs
-begins and ends at the heart
Systemic Circuit

-carries blood to and from the body
-begins and ends at the heart
Arteries/Efferent Vessels

-carry blood AWAY from the heart
Veins/Afferent Vessels

carry blood TO the heart
Capillaries/Exchange Vessels
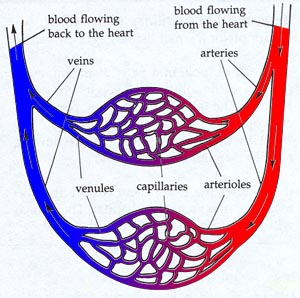
-microscopic thin-walled vessels
-interconnect the smallest arteries and veins
- exchange materials between blood and tissues (b/c of thin walls)
-materials include dissolved gases, nutrients, and waste products
Each day the heart pumps about _____ liters of blood.
8000
The heart is about the size of a clenched _____.
fist
Four Chambers of the Heart

1.Right Atrium
2.Right Ventricle
3.Left Atrium
4.Left Ventricle
Right Atrium
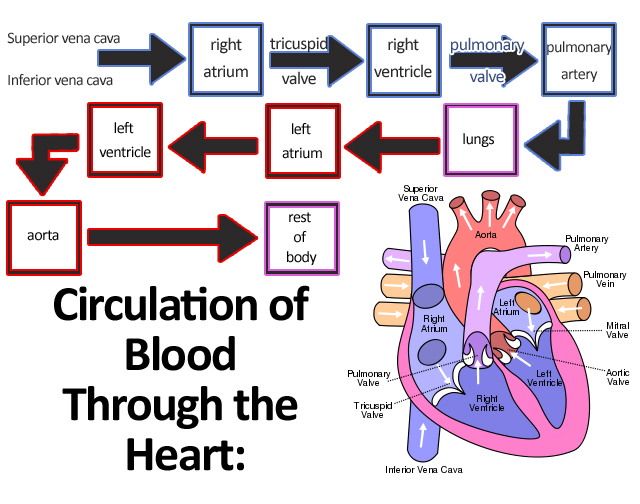
-receives blood from the systemic circuit and then passes through right ventricle
Right Ventricle

-pumps blood to the pulmonary circuit
Left Atrium

-collects blood from the pulmonary circuit and empties it into the left ventricle
Left Ventricle

pumps blood to the systemic circuit
When the heart beats, first the _____ contract, and then the ______ contract.
Atria; Ventricles
The heart is located near the ________ chest wall, directly posterior to the ______.

anterior; sternum
Apex

inferior, pointed tip of the heart
Pericardial Sac/Fibrous Pericardium
-surrounds the heart
-consists of a dense network of collagen fibers
-stabilizes the the position of the heart
Pericardium
-double lining of the pericardial cavity
1)visceral pericardium (epicardium)
2)parietal pericardium
Pericardial Cavity

-the space between the visceral and parietal pericardium
-contains 15-50 mL of pericardial fluid
Pericardial Fluid

acts as a lubricant, reducing friction between the opposing surfaces as the heart beats
Coronary Sulcus

-a deep groove that marks the border between the atria and ventricles
Anterior Interventricular Sulcus and Posterior interventricular sulcus

shallow depressions that mark the boundary between the left and right ventricles
Epicardium

-covers the outer surface of the heart
Myocardium

-muscular wall of the heart
-consists of concentric layers of cardiac muscle tissue
Endocardium

-covers the inner surface of the heart
-simple squamous epithelium
Characteristics of Muscle Cells

-interconnected by intercalated discs
-small
-single nuclei
-branching interconnections between cells
Intercalated Discs

-transfer the force of contraction from cell to cell and propagate action potentials