Exercise 10
Be able to recognize examples of protisans and give the taxonomy of each. Give a general characteristic of each example.
Two major characteristics of Kingdom Protist:
Eukaryotic, and aquatic.
Protist means:
A eukaryote that is not a plant, animal or fungus.
Most protists are multi-cellular or unicellular?
Unicellular.
Photoautotrophs:
Organisms make their own food using sunlight as energy.
Heterotrophic:
Obtain food by ingesting other organisms.
Mizotrophs:
They combine photosynthesis and heterotrophic nutrition.
Five clades of Kingdom Protist:
Excavata, Chromalveolata, Rhizaria, Archaeplastida, and Unikonta.
Clade Excavata:
Similar: feeding groove, resembles a "scoop", a flagellum
Clade Chromalveolata:
Marine organisms, usually contain 2 flagella, plankton, Golden and brown algae, evolved from secondary endosymbiosis,
Clade Rhizaria:
Defined by DNA similarities, amoeboid shape, shells
Clade Archaeplastida:
Includes red and green algae, developed from endosymbiotic cyanobacteria, all have plastids in their cells
Clade Unikonta:
Myosin proteins, single flagellum---"uni"konta
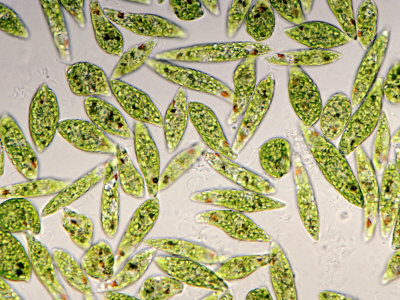
Example of Clade Excavata (Euglena)
Characteristics of Euglena
Found in fresh but polluted waters

Example of Clade Excavata (Trypanosoma)
What causes African Sleeping Sickness?
Trypamosoma
Vector for African Sleeping Sickness
Tsetse fly
Why is African Sleeping sickness difficult to treat?
Surface is covered with multiple copies of a single protein, before the immune system can attack, surface protein switches.

Example of Clade Chromalveolata: Dinoflagellate called (Ceratium)

Example of Clade Chromalveolata (Plasmodium) - causes Malaria
What causes Malaria?
Plasmodium

Example of Clade Chromalveolata (Paramecium caudatum) (slipper shaped) (ciliate)

Example of Clade Chromalveolata (Diatoms)
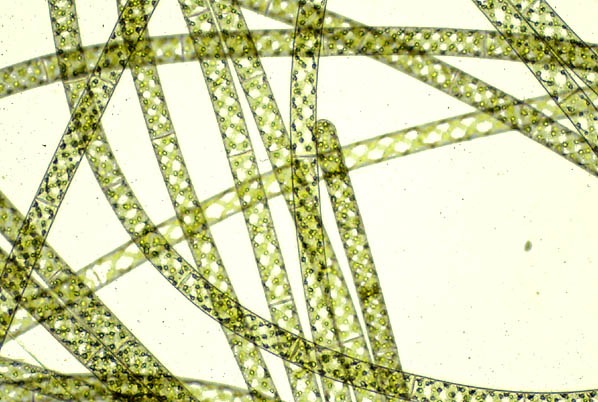
Example of Clade Archaeplastida (Green algae) (Spirogyra)
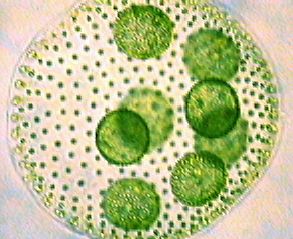
Example of Clade Archaeplastida (green algae) (Volvox)
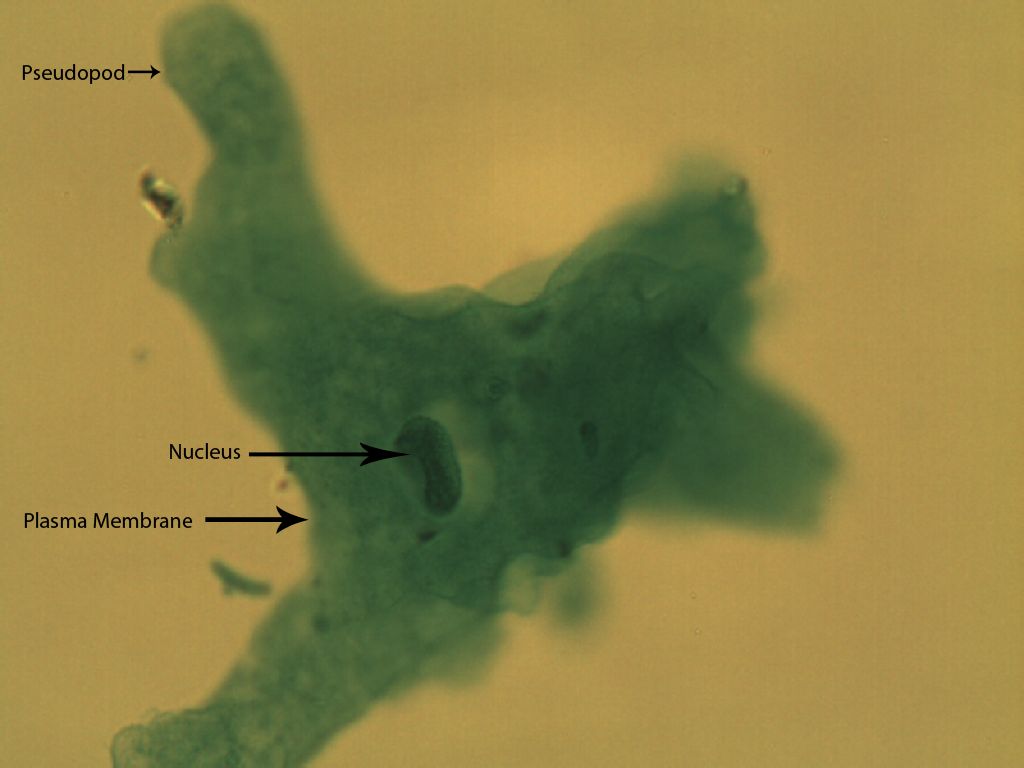
Example of Clade Unikonta (Amoeba Proteus)
What is the cell wall of diatoms made of?
Silica
What is plankton?
bottom of the food chain in marine waters
What is a distinctive feature seen in Paramecium?
2 nuclei, macronucleus and micronuclei
What is a distinctive feature seen in spirogyra?
Spiral shaped chloroplasts.
What kind of algae is Volvox?
Green algae.
How does the amoeba move?
pseudopods
Name the process by which amoeba ingests its food?
Phagocytosis
Why would you expect a fresh water amoeba to be more likely to have a contractile vacuole than a marine amoeba?
A freshwater amoeba lives in a hypotonic environment, water enters by osmosis. Contractile vacuole needed to pump out excess water.
An amoeba in salt water lives hypertonic environment, no need for a contractile vacuole
Exercise 11
Kingdom Animalia: Sponges and Cnidarians
The Animal Kingdom is characterized by:
multicellular, eukaryotic organisms that obtain their nutrients by feeding on other animals, plants or fungi.
Characteristics of Animal Kingdom:
heterotrophic, multicellular organisms
What animal does not have tissues, organs or organ systems?
Sponges
Characteristics of Sponges:
Heterotrophic, filter feeders, asexual reproduction (budding), no tissues, neither protostomes or deuterostomes, sessile, hermaphrodites
What Phylum do sponges belong to?
Porifera (porous body)
What are the classes of sponges?
Calcarea, Hexactinellida, Demospongiae

Class Calcarea (sponge)

Class Hezactinellida (sponge)

Class Demospongiae (sponge)
Why are sponges so different from other animals in the Kingdom Animalia?
No tissues, organ systems, coelom, or organs.
Phylum Cnidarian
Have true tissues but no organs or organ systems. Radial symmetry. Aquatic.
Characteristics of Phylum Cnidarian:
Radial symmetry, aquatic, three body forms.
The two tissue layers in Phylum Cnidarian?
Epidermis, and inner gastrodermis.
Coelenteron:
The gastrovascular cavity in Phylum Cnidarian.
Cnidocyte:
Cell type in cnidarians, "stinging cell", helps them capture prey.
Two adult forms of Cnidaria?
Polyp and medusa.
hydroid or polyp form:
colonial, not free-moving.
Medusa form:
Free moving,
Are jellyfish medusa or colonial?
Medusa
3 Classes of phylum Cnidaria:
Hydrozoa, Scyphozoa, and Anthozoa.
Examples of Class Hydrozoa:
Hydra, Obelia, and Portugese man of war.
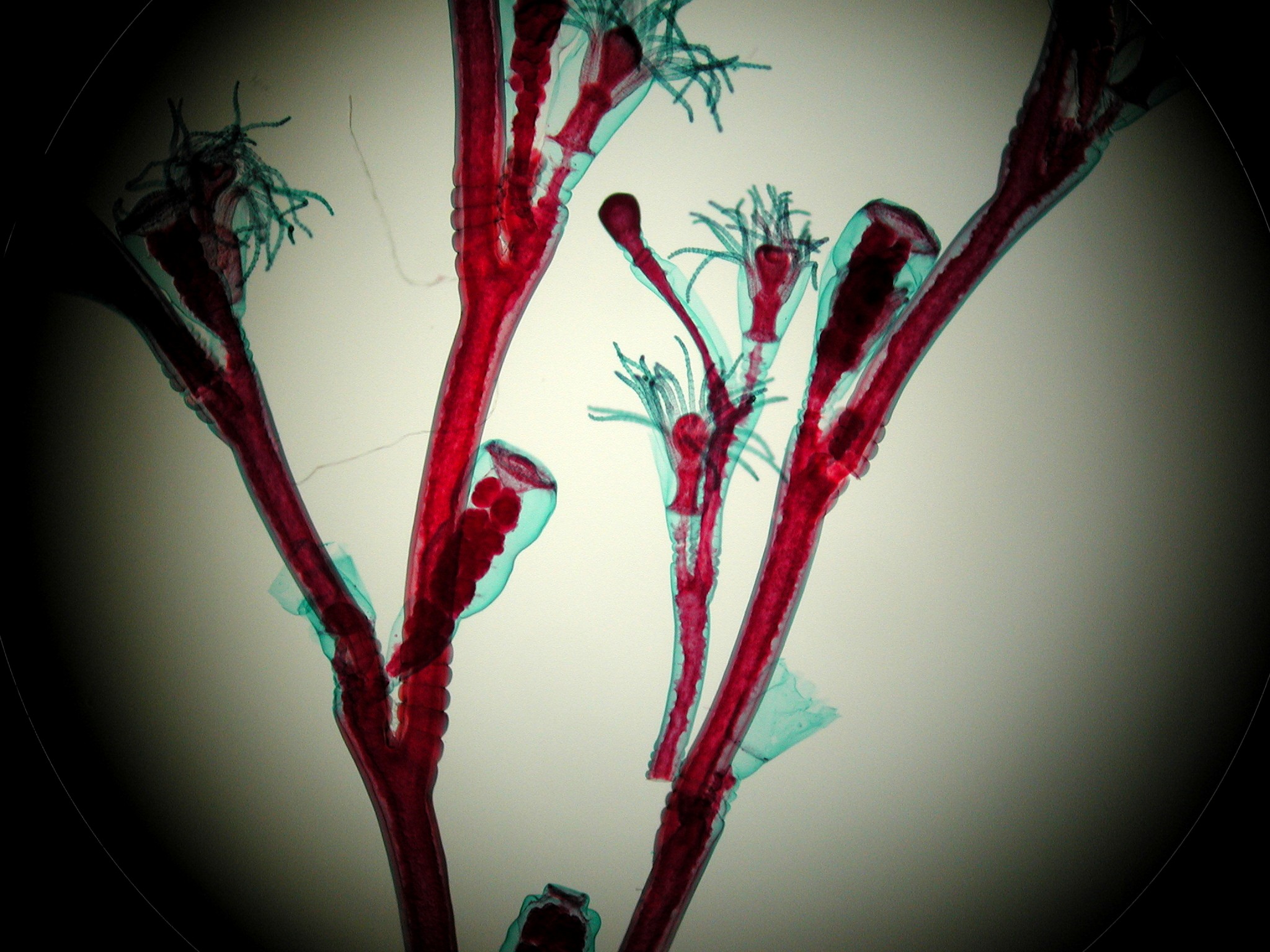
Polyp form of Obelia. (Class Hydrozoa)
Medusa form of Obelia. (Class Hydrozoa)
Is the Portugese man-of war medusa or colonies of individual polyps?
Floating colonies of individual polyps.
Examples of Class Scyphozoa:
Jellyfish (Class Scyphozoa) (always medusa)
Examples of Class Anthozoa:
Corals and sea anemones.
Characteristics of Class Anthozoa:
Display the polyp form and live in colonies.
Which genus in Phylum Cnidaria displays both polyp and medusa adult forms?
Obelia.
What is the name of the class in which jellyfish belong?
Class Scyphozoa.
What is the name of the class to which coral belong?
Class Anthozoa.
Which class of cnidarians always shows the medusa form?
Class Scyphozoa, jellyfish.
Are Cnidarians protostomes or deuterostomes?
Neither.
Exercise 12
Kingdom Animalia Protostomes: Phyla Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, annelida, Mollusca and Arthropoda.
Protostome:
A developmental term that describes the first opening as the forerunner to the animal's mouth. The mouth develops first.
Phylum of Kingdom Animalia Protostomes:
Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, Annelida, Mollusca, Arthropoda.
What phylum are "flat worms" in?
Phylum Platyhelminthes.
Round worms that are unsegmented belong to what Phylum?
Phylum Nematoda.
Segmented round worms belong to what phylum?
Phylum Annelida.
What phylum do mollusks belong to?
Phylum Mollusca.
What phylum to insects and crustaceans belong to?
Phylum Arthropoda.
In what direction are flatworms, flat?
Dorsal-ventral.
Meaning of "Platyhelminthes":
"Platy":flat and "Helminth":worm
Describe the reproductive system of Phylum Platyhelminthes:
Hermaphrodites.
What type of worm is known for being a parasite?
Flat worms.
3 classes of Phylum Platyhelminthes:
Turbelaria, Trematoda, Cestoda.

Example of Class Turbelaria:
Planaria.
Example of Class Trematoda:
Clonorchis sinesis. (Chinese liver fluke)
How to identify the Chinese liver fluke?
oral sucker
The three hosts of the Chinese Liver fluke:
Human, snail, and fish.
Life-cycle of a chinese liver fluke?
1. Human eats raw or undercooked fish, that contains immature flukes.
2. Flukes mature in the bile ducts of the liver, where they produce eggs.
3. Eggs pass out through feces.
4. Miracidia are eaten by snails, invade tissues and develop into sporocysts.
5. Sporocysts develop into free-swimming cercariae and leave the snail.
6. Cercariae invade fish muscle and form protective cysts and develop into metacercariae.
Example of Class Cestoda:
Tapeworms.
Scientific name for tapeworm?
Dipylidium caninum.
Proglottids:
Repeating units in a tapeworm.
Scolex
Head of a tapeworm
Can a tapeworm regenerate?
Yes because of its proglottids.
Lifecycle of a tapeworm:
1. Human eats undercooked pork that contains tapeworm cysts. 2. Cysts attatch to intestinal wall. 3. Eggs from tapeworm pass in feces. 4. Pig eats infected food. 5. Pig's muscles are filled with larvae cysts.
What part of a tapeworm attaches to a dog's intestinal wall?
Scolex.
Classes in Phylum Nematoda:
Polychaeta, Hirudinea, and Oligochaeta.
Phylum Nematoda consists of:
Round, unsegmented worms with bilateral symmetry.
How do you tell male from female worm?
Female is bigger and male has a hook at the end.

Ascaris (Nematoda)

Trichinella spiralis (nematoda)
How do you get Trichinella spiralis?
Eat under cooked pork.
Phylum Annelida consists of:
Round, segmented worms with bilateral symmetry.
What worm phylum has a true coelom?
Phylum Annelida
Classes in Phylum Annelida:
Polychaeta, Hirudinea, Oligochaeta.
Look at Earthworm dissection picture and website:
http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/BL_14/BL_14.html
Examples of Class Polychaeta:
Sandworms, and marine worms.

Sand worm
Example of Class Hirudinea:
Leeches
Example of Class Oligochaeta:
Earthworm
What Class do earthworms belong to?
Oligochaeta
Phylum Mollusca:
Soft bodied animals, many with outer shells and a bilaterally symmetrical body plan with three areas called foot, mantle, and visceral mass. Animals live in land or water.
5 classes of Phylum MolluscaL:
Polyplacophora, Bivalvia, Gastropoda, Cephalopoda, Scaphopoda, and Arthropoda.
Class Polyplacophora:
Chitons, lives in intertidal regions. (sea rollie-pollie)
Class Bivalvia:
Clams, oysters, mussels, and scallops. Two shells connected together at a hinge joint.
Class Gastropoda:
Snails, slugs, welks and conchs.
Class Cephalopoda:
Squid, octopus, and the nautilus shell.
Siphon (squid):
Helps the squid propel itself backwards

Tusk shells. (Class Scaphopoda)
Class Scaphopoda:
Tusk shells
Phylum Arthropoda:
Insects and crustaceans.
What are exoskeletons made of?
Chitin.
Go back and write characteristics of each phylum and class.
...
The 3 body regions of Arthropoda:
Head, Thorax, and abdomen.
Cephalothorax:
When the head and thorax are fused together.
The 3 subphylum of Phyla Arthropoda:
Chelicerata, Crustacea and Uniramia
Two classes in Sub-Phylum Chelicerata:
Merostomata (horseshoecrab), and Arachnida (spiders).
Class Merostomata:
Horseshoecrab
The horseshoecrab belongs to which Class?
Merostomata
Class Arachnida:
Spiders
Sub-phylum Crustacea:
Barnacles, and all crustaceans
Carapace:
Outer covering on custacean.
Telson:
Tail on a horseshoecrab
3 classes in sub-phylum Uniramia:
Insecta, Chilopoda, and Diplopoda.
Class insecta:
Insects
Class Chilopoda:
Centepedes
Class Diplopoda:
Millipedes.
Earth Worm dissection:
...
EWD: Clitellum:
Un-segmented, smooth section, 1/3 down the worm. Where eggs are shed, functions as a cocoon.
EWD: Prostomium
Mouth and overhanging "lip" on an Earth worm.
EWD:Setae
Tony bristles that cover an earth worm.
EWD: Septum, or septa
Segmented section of earth worm body.
EWD:The gastrointestinal tract is referred to as the...
Alimentary canal
EWD:What are earth worm "hearts"?
five enlarged arteries that contract and relax
EWD: What are the two major blood vessels?
Dorsal and ventral
Squid dissection:
...
SD: Mantle:
the outer covering of the body of the squid
Phylum Arthropoda:
...