What are the requirements for an enzyme with Michaelis-Menten kinetics?
• Steady-state assumption: [ES] remains constant (loss
balances
formation).
• [S] binds [E] to form [ES].
• Product
formation is irreversible
What are the 3 ways of interpreting KM
• Substrate concentration [S] at which at enzyme is at
half its
maximum velocity Vmax (much like KD at half
ligand
saturation).
• Approximation of the dissociation constant.
•
The ratio of the rate constants:
k-1+k2/ k1
What is a turnover number?
• Turn over number: kcat = Vmax/[E]total
The turnover number is
a metric for the rate at which
substrate is converted to product
(turnover) unique to
each enzyme.
What is the catalytic efficiency of an enzyme?
• Catalytic efficiency: kcat/KM
Catalytic efficiency scores an
enzyme based on both its
affinity for substrate and rate of catalysis
Enzyme kinetics seeks to determine the initial and maximal reaction velocity that enzymes can
attain and the binding affinities for substrates and inhibitors
Michaelis-Menten equation has a ______line on a graph
non-linear
Bisubstrate reactions can occur by _____or______mechanisms or by a _______mechanism
ordered, random-sequential, Ping-pong
1st order reactions display a linear plot of the
substrate or product concentration, as a function of time
Rate law is the mathematical relationship
between the reaction rate or velocity, and concentration of reactions (linear)
The amount of A consumed per unit of time
rate, or velocity
Formula for rate law
v=k[A]number in front of letter
Michaelis-Menten formula:
vo=Vmax[S]/ Km+[S]
Vo is equal to
the slope
At low [S], the rate is proportional
as in a first-order reaction
At high [S], the enzyme reaction approaches
zero-order kinetics :Vo=Vmax
Rate of formation of ES is _____, while rate of dissociation is ___.
Rate of product formation is ____
k1, k-1, k2
Catalysis is limiting, because the rate is independent of [S](E is saturated
0th order (when Kmis less than)
Rate is dependent on [S], [S] is limiting
1st order (when Km is greater than)
When above Km, it starts to
plateau due to saturation increasing
Vmax=k2[ET]
...
Km=(k-1+k2)/k1
...
Small Km means
little dissociation (10-6)
Larger Km means
lots of dissociation (10-2)
Kcat, the turnover number, is the number of
substrate molecules converted to product per enzyme molecules, per unit of time, when E is saturated with substrate
Catalytic efficiency formula:
kcat/Km
kcat/Km is approaching
1.0x109
At temperatures are above 50o to 60oC,
enzymes typically decline in activity
The two classes of single-displacement:
random and ordered
Random single displacement where either
substrate may bind first, followed by the other substrate
Ordered single displacement where a
leading substrate binds first, followed by the other substrate
Double displacement (Ping-Pong) reactions
involves a covalent intermediate
In single displacement, high concentrations the
y-intercept is lower
Random, single-displacement reaction is formed rapidly and reversibly when
enzyme is added to a reaction mixture containing A,B,P, and Q
Ordered, single-displacement reaction leading substrate (A) must
bind first, followed by B. And for the products, P and Q
Double-displacement has a formation
of a covalently modified enzyme intermediate, E'
Reversible inhibitor may bind
at the active site or at some other site
Four types of reversible enzyme inhibitors:
-competitive
-noncompetitive
-mixed noncompetitive
-uncompetitive
Competitive inhibition
only time where inhibitor can be competed by the substrates
Increases the apparent Km but
no effect on Vmax
Noncompetitive inhibitor
decreases Vmax with no change in Km
Mixed noncompetitive alters
both Km and Vmax
Uncompetitive inhibition alters
both Km and Vmax but with same slope Km/Vmax
Uncompetetive inhibition only observed
in enzyme having two or more substrates
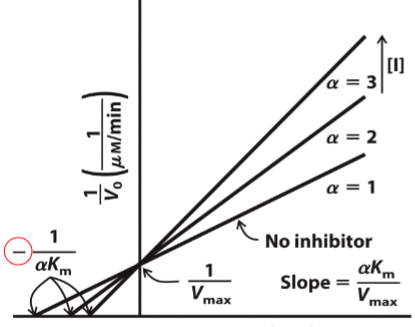
What type of reversible inhibitor is this?
Competitive Inhibition
Competitive inhibition______apparent Km but______on Vmax
increases, no effect
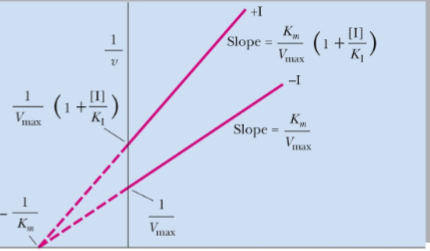
What type of reversible inhibitor is this?
Pure noncompetitive inhibition
Pure noncompetitive inhibition____Vmax with ____in Km
decreases, no change
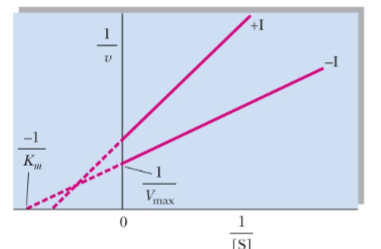
What type of reversible inhibitor is this?
Mixed noncompetitive inhibition
Mixed noncompetitive inhibition alters Km and Vmax by _____
decreasing
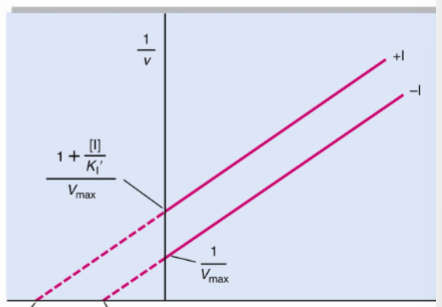
What type of reversible inhibitor is this?
Uncompetitive inhibition
Uncompetitive inhibition alters both Km and Vmax but have ______
the same slope, Km/Vmax