How many locations can you place a lens between the object and a screen to create a focused image?
Two
How many different lenses did you use in the lab?
Two: Concave/Convex
Faraday's law of induction tells us that the EMF induced in a circuit is proportional to the:
Rate of change of magnetic flux through the circuit
Lenz's Law tells us that the induced current in the wire loop is such to produce a magnetic field which:
opposes the change in the magnetic source which caused the induced current
In this Lab 3 we will be looking at standing waves on a string, what property are we changing to change the number of nodes in the standing wave?
We change the frequency of the oscillator
In last week's lab we made 3 graphs with period (T) and length (L) of the pendulum. Which graph shows a proportional relationship?
T2 vs L
Which variable had a large effect on the period of a pendulum?
length
Which picture shows a second harmonic standing wave on a string?
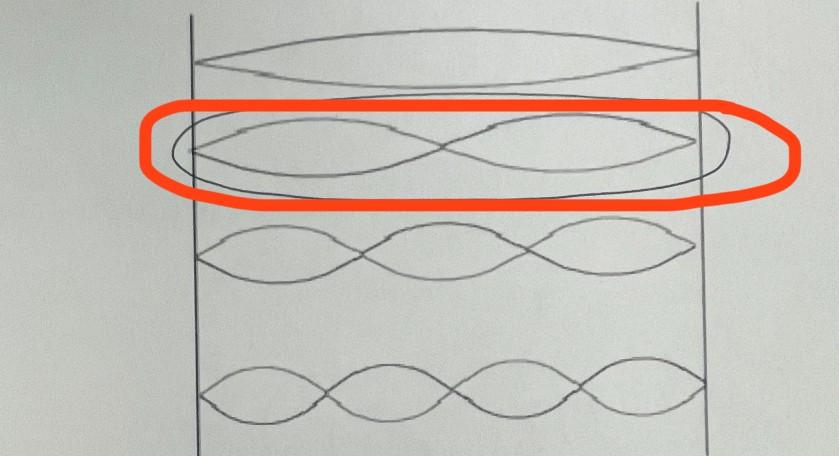
Two loops
Higher frequency sound waves will have __________ velocity compared to lower frequency sound waves.
the same
To measure the wavelength of sound waves we will:
Move the microphone back and forth
In last week's lab (Week 2) when we doubled the tension in the string.
The wave velocity approximately went up by 40%
Other than tension, what determines the speed of a wave on a string?
string density
In today's lab (Week 5) we will investigate electric field-lines and Gauss' Law using:
A computer program
For the Gauss' law part of the lab we will
Count the number of field lines entering and exiting a "loop"
If a pair of charges gets 4 times closer than they were before (say, from 80 cm apart to 20 cm apart), by what factor does the force increase?
16
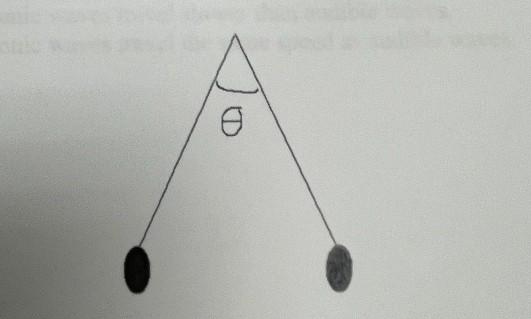
What can you definitely conclude must be true about the charges balls shown in the diagram?
They have like sign charges
According to the lab manual, the prelab will investigate the charge on
Scotch Tape
In the last part of this lab we will test Coulomb's law in a simulation by:
Determining the force between two charged balls
Roughly speaking, how long is the wavelength of a 40 kHz sound wave?
8.5 mm
How does the speed of sound coming out of the 40 kHz transducers differ from the velocity of audible sound frequencies?
The ultrasonic waves travel the same speed as audible waves
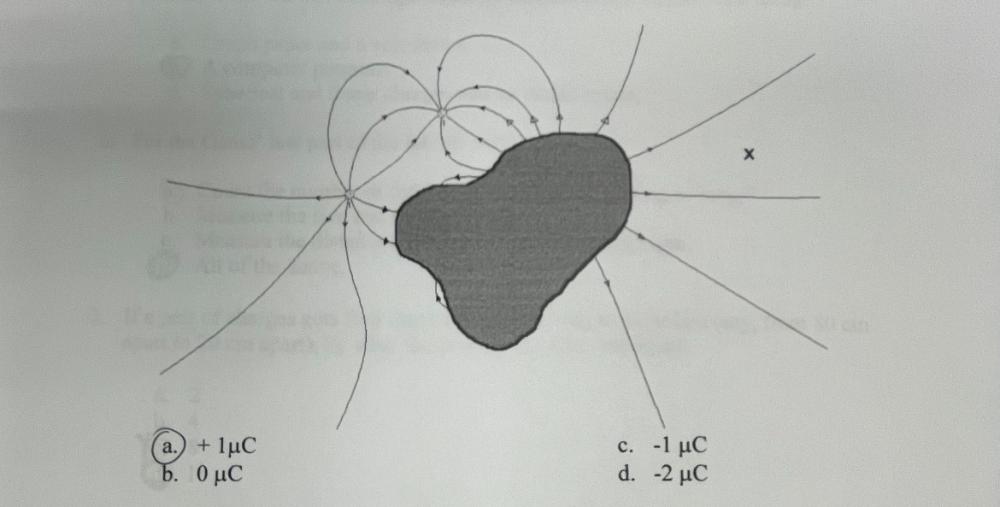
Charges shown have +/- μC of charge. How much charge is hidden behind the locked out region?
+ 1 μC

How would the total number of field lines entering the blocked out region (that is number entering minus number exiting) change if another positive charge was placed at the position marked with a "X?"
The total number of field lines would remain the same
What analogy is used to describe charge leaving a capacitor in the preliminary questions?
candy in a candy jar
The function that describes the discharge of a capacitor is _______ with time.
exponential
Which analogy was used in the Ohm's Law lab report to describe voltage, current and resistance:
Water flowing through a pipe
What type of relationship does Ohm's Law predict for voltage and current through a resistor?
Proportional
You have 2 capacitors each of which is hooked up to a different resistor. The first capacitor discharges in 5 seconds when hooked up to the first resistor. The second capacitor discharges in 1 second when hooked up the second resistor. Which scenario is NOT possible?
The second resistor is larger and the second capacitor is smaller, τ =Rc
A capacitor is being discharged through a resistor. After one second, half of the charge is left in the capacitor. How much of the charge is left after 2 seconds.
1/4 of it
Which of the following materials is "ohmic" (obeys Ohm's Law), based on your laboratory results?
a resistor
A light bulb heats up as current is passing through it. Compared to its resistance when cold, the resistance when hot is
greater
In this lab, the ultimate objective is to measure the magnetic field of
the Earth
When the magnetic field of the Earth and the coil cancel out, the compass needle will
point halfway between north and south
The horizontal component of the magnetic field of the Earth (what we measured) inside the physics labs is about:
0.25 G
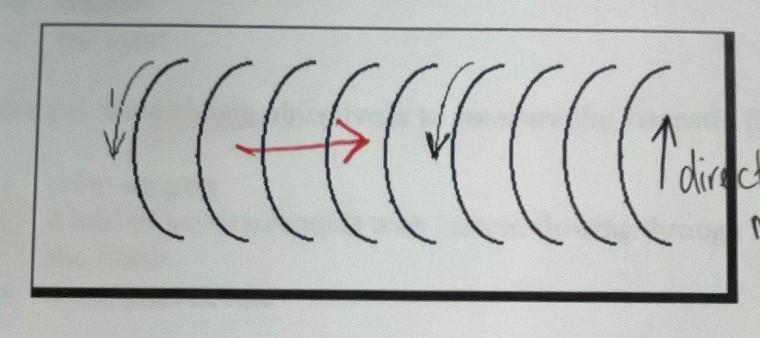
Indicate the direction of the magnetic field inside the solenoid (The heads of the arrows shown below and the part of the circular wires next to them are "closer" to you than the top and bottom parts of the circular wires shown.)

----------->
In today's lab (Week 9) we will study how the magnetic field inside a "long" Slinky depends on: (circle all that apply)
the current in the Slinky
the density of turns in the Slinky
In today's lab (Week 9) we will determine the value of which constant?
μ0
Which law describes only the direction of an induced current?
Lenz's Law
Which law describes the magnitud e of an induced electric potential?
Faraday's Law

According to the textbook the magnetic field inside a slinky is B = μ0 n I. If you take measurements of magnetic field at various turn densities (always using two amperes of current) and get the following graph and fit equation:
What is your experimentally measured μ0 based on the fit equation (y = 0.00224*x + 0.0141)?
1.12 x 10-6 = μ0
Divide the slope of the line (00.224) by the current (2) to find μ0

According to the textbook the magnetic field inside a slinky is B = μ0 n I. Which graph(s) support(s) this claim, based on their slope and intercept values? (Pick as many as you like)

ONLY THE 1 LINEAR GRAPH (top right hand corner)