The process by which light energy is converted into the stored chemical energy of organic molecules is:
photosynthesis.
What is the correct sequence of wavelengths (beginning with the shortest)?
gamma rays, x-rays, UV, visible light, infrared, microwaves, TV and radio waves
Light behaves not only as waves, but also as particles called:
photons.
By definition, substances that absorb visible light are called:
Pigments.
An electron absorbs a photon of light energy and becomes energized; the electron shifts from a __________ atomic orbital to a __________ atomic orbital.
lower energy; higher energy
Electrons that are excited to a higher energy level may be transferred to an electron acceptor or may return to a ground state. If the latter occurs, energy can be released as an emission of light in a process known as:
fluorescence.
The chlorophyll molecule has a porphyrin ring that contains a single atom of:
magnesium.
Chlorophyll and accessory photosynthetic pigments are associated with the:
thylakoid membranes.
The most important pigment(s) for the process of photosynthesis is(are):
chlorophyll a.
The __________ of a chlorophyll molecule is(are) responsible for absorbing light.
porphyrin ring
A group of thylakoid discs make up:
A granum
In a chloroplast, there is an outer and an inner membrane. The inner membrane encloses a fluid filled region called the:
Stroma
The thylakoid membrane encloses a space called the:
Lumen
Thylakoid membranes are involved in __________ synthesis.
ATP
Chlorophyll:
absorbs red and blue light, and reflects green light.
Which of the following are accessory photosynthetic pigments that expand the spectrum of light that provides energy for photosynthesis:
Both carotenoids and chlorophyll b.
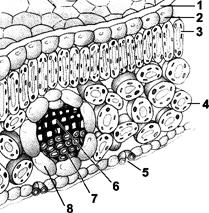
Figure 9-1 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Chloroplasts will be found in the greatest density in the area of Figure 9-1 labeled:
3 and 4

Figure 9-1 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). The primary function of the leaf structure labeled 5 in Figure 9-1 is:
gas exchange
The action spectrum of photosynthesis best matches the absorption spectrum of:
chlorophylls a and b.
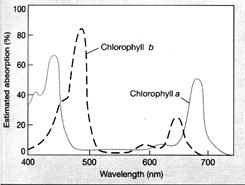
Figure 9-2 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). According to the graph in Figure 9-2, chlorophyll absorbs light most strongly in the:
red and blue wavelengths.

Figure 9-2 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). The graph in Figure 9-2 represents the:
absorption spectra for chlorophylls a and b.
Chlorophyll absorbs primarily __________ and __________ regions of the visible spectrum.
blue; red
Engelmann concluded that chlorophyll in the chloroplasts is responsible for photosynthesis based on the following results:
The action spectrum of photosynthesis matched the maximum production of oxygen by Spirogyra, observed by the greatest accumulation of bacteria in the blue and red regions of the spectrum.
The overall reactions of photosynthesis are best summarized as:
6 CO2 + 12 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O.
During the reactions of photosynthesis, __________ is reduced and __________ is oxidized.
CO2; H2O
In the overall reactions of photosynthesis, it appears that hydrogen atoms are transferred from water to carbon dioxide to form a carbohydrate. This type of reaction is classified as:
a redox reaction
The reactions of photosynthesis are divided into two categories:
light-dependent reactions and carbon fixation reactions.
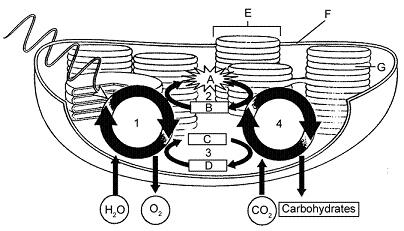
Figure 9-3 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Carbon is fixed in which part of the diagram in Figure 9-3?
4
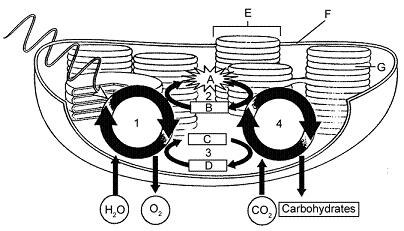
Figure 9-3 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Where in Figure 9-3 is NADPH formed?
3
In photosynthesis, ATP and NADPH are produced during:
the light-dependent phase.
The reactions that occur in the thylakoid membranes are:
the light-dependent reactions.
The reactants of the light-dependent reactions are:
H2O, ADP, and NADP+
The reactants of the Calvin cycle are:
CO2, ATP, and NADPH.
Which of the following is not associated with the thylakoid membranes?
the Calvin cycle
12 H2O + 12 NADP+ + 18 ADP + Pi → 6 O2 + 12 NADPH + 18 ATP summarizes the __________ reactions of photosynthesis.
light-dependent
The electron transport chain of photosynthesis is located in the:
thylakoid membrane.
Reaction center complexes of the light-dependent reactions contain __________ and __________, which receive energy from __________.
chlorophyll; proteins; antenna complexes
How many electrons are needed to reduce one molecule of NADP+ to NADPH?
2
During the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, a constant supply of electrons is provided by:
Water.
The electrons lost by the P680 reactive center are replaced from:
a water molecule.
Oxygen produced by photosynthesis comes directly from:
H2O
Noncyclic electron transport needs a constant supply of electrons. These are obtained from:
H2O
ATP is formed when __________ the thylakoid lumen.
hydrogen ions leave
The synthesis of ATP during photosynthesis or respiration occurs as a result of:
phosphorylation of ADP.
The first step in the Calvin cycle is the attachment of carbon dioxide to:
RuBP (ribulose bisphosphate).
Which of the following is common to both photosynthesis and aerobic respiration?
chemiosmosis
Which of the following is not one of the intermediates or products of the carbon fixation reactions?
NADPH
In C4 plants, reactions that fix CO2 into four-carbon compounds occur in:
mesophyll cells.
Plants, algae, and certain prokaryotes are:
photoautotrophs
Animals, fungi, and many bacteria that use organic molecules as a source of both energy and carbon are:
chemoheterotrophs