Whats the clinical crown
The visible portion if the enamel above the gum thats you can see with your bare eye, not including the deeper enamel, dentin or pulp
Why can't the enamel regenerate after eruption
Because the Ameloblasts are lost/ died as the tooth erupts
How thick is the enamel generally in incisors
In the incisal edge is 2mm thick
How thick is the enamel generally in premolars
In the cusps is 2.3-2.5mm thick
How thick is the enamel generally in molars
In the cusps is 2.5-3mm thick
In which part of the mandibular molars is the enamle the thickest
In the buccal cusps
In which part of the maxillary molars is the enamle the thickest
In the palatal cusps
Whats the organic matrix of enamel made of?
4-12% of water, 1-2% protein
Whats the inorganic part of the enamel made of
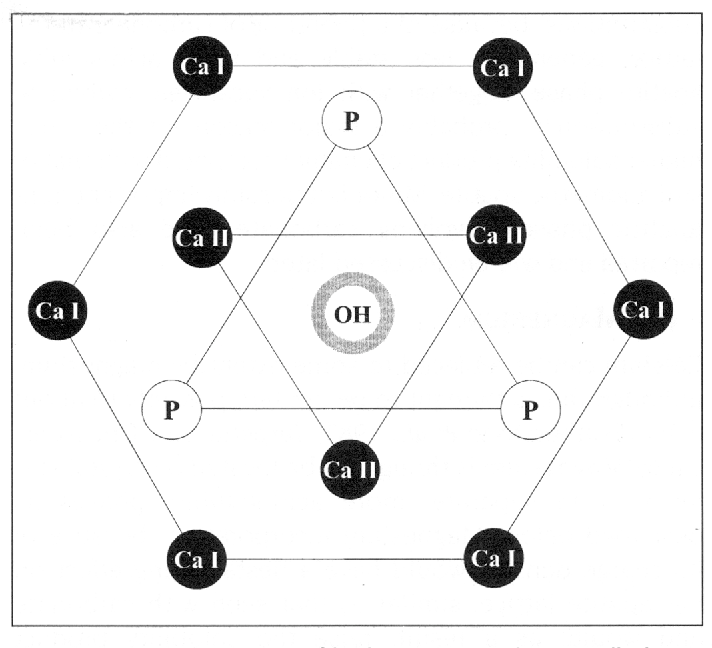
By volume 90-92% Symmetrically repeating Hydroxyapatite(calcium phosphate) crystals
How many rods are there in mandibular incisors
5 million
How many prisms are there in molars
12 million
How big is the diameter of enamel rods near the DEJ
4 microns
How big is the diameter of enamel rods on the surface of enamel
8 microns
What affects the color of the tooth
- Color of the dentin
- thickness of the enamel
- if there are stains in the animal(while developments substances like tetracycline can cause teeth to have a brown band around them bc the Ca binds to the enamel or excess of fluoride can cause Fluorosis) they change how the enamel reflects light
what affects enamel translucency
mineralization and homogeneity of enamel
What enamel structural features act as pain receptors in the enamel
Enamel Spindles
Where do enamel tufts get their names from

from grass tuft
How high can Enamel Tuft get
they can reach as high as the one third(1/3)-half(1/2) the enamel thickness
Why are Enamel Tuft considered weak spots
they're made mostly of proteins and not so much inorganic compounds(hydroxyapetite crystals) which make them easier to break
What role do Enamel Tuft considered play in the enamel
they distribute stress throughout the enamel
What are Enamel lamella
hypominarlized parts of the enamel that contain mostly water and proteins that didn't turn to crystals, they extend throughout the enamel till they reach DEJ, sometimes they even penetrate it
What is Gnarled enamel
they are the twisting of enamel rods around each other to strengthen the enamel especially when they reach the cusps or incisal ridge
What is Hunter-Shreger bands

they are light and dark bands that appear when reflected light hits the enamel, the light bands are bands aligned in one direction while the darker bands are aligned in different directions
What is the Salivary pellicle made from
mucoproteins(proteins that help to make mucus) and sialoproteins (proteins that help to make saliva)
What are Dental plaques made from
Microorganisms that mix with Salivary Plaques
What happens if you don't remove Dental Plaques
after eating the bacteria in the dental plaques metabolize the sugar stuck on the surface of the plaques which results in making acids, that acid with the dental plaques will turn into dental carries and periodontal diseases and the picture(dental calculus(tartar))
What causes mineralization of Enamel
intentional or pathogens
Which part of the enamel is more soluble
the deeper you go the weaker the enamel gets because of less density
How to make the teeth less sensitive to acid attacks
by taking fluoride(F-) whether topically(toothpastes that contain fluoride) or systematically(medications)