All of the following are functions of the cell membrane EXCEPT:
being freely permeable to all substances.
Which of the following statements concerning phospholipids is FALSE?
They contain three fatty acids chains.
In a lipid bilayer, __________ fatty acid tails face each other within the bilayer and form a region that excludes water.
hydrophobic
If phospholipids form a spherical structure when placed in water, then which of the following is the most logical conclusion about those phosopholipid molecules?
They are cone-shaped.
A key discovery that weakened the Davson-Danielle "sandwich" model of cell membranes was that:
membrane proteins were not uniform and did not form flattened sheets.
Who proposed the fluid mosaic model of cell membrane structure in 1972?
Singer and Nicholson.
What is meant by the term “fluid mosaic model”?
It is the movement of proteins within the phospholipid bilayer.
In the experiment in which Frye and Edidin fused the plasma membranes of a mouse and a human cell, what happened to the membrane proteins?
They moved laterally across the cell surface.
Vegetable oil is different from animal fat in that the phospholipids in vegetable oil have fatty acid tails that:
bend at each double bond.
Cholesterol within membranes functions as a(n) __________ through its interactions with both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts of phospholipids.
fluidity buffer
Which of the following statements about lipid bilayers is FALSE?
They are inflexible.
Integral proteins:
are amphipathic.
A transmembrane protein differs from other membrane proteins because it:
completely extends through the membrane.
Peripheral proteins are linked to either surface of the plasma membrane by:
bonding to integral proteins through noncovalent interactions.
Integral proteins are:
made by ribosomes located on the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Biological membranes are normally permeable to:
small, hydrophobic molecules.
Which of the following molecules is least likely to cross a cellular membrane by simple diffusion?
potassium ion
An ABC transporter:
uses the energy of ATP to transport solutes.
Which of the following is not a characteristic of aquaporins?
They cause dehydration.
A bottle of perfume is opened on the opposite side of the room and within minutes you begin to smell the perfume. This phenomenon is a classic example of:
simple diffusion.
The passive movement of a substance along its concentration gradient is termed:
diffusion.
Simple diffusion may involve the movement of __________ through the plasma membrane down a concentration gradient.
small nonpolar molecules.
Which of the following membrane activities does NOT require the expenditure of energy by the cell?
osmosis
If the concentration of solutes in a cell is less than the concentration of solutes in the surrounding fluid, then the extracellular fluid is said to be:
hypertonic.
The higher the concentration of solute in a solution, the __________ the effective water concentration and the __________ the osmotic pressure.
lower; higher
Consider a U-tube that initially contains pure water on one side of a selectively permeable membrane and water plus solute on the other side. Which of the following best describes what will happen next?
Some water molecules become "bound up" with solute molecules and do not diffuse freely.
Solutions that are isotonic:
have equal concentrations of solute and water.
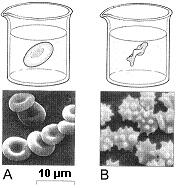
Figure 5-1 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Refer to Figure 5-1. Which of the following statements about the red blood cells in Figure B is true?
These red blood cells have shrunken in response to a hypertonic external solution.

Figure 5-1 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). Refer to Figure 5-1. Which of the following statements about the red blood cells in Figure A is true?
There has been no net water movement.
A patient who has had a severe hemorrhage accidentally receives a large transfusion of distilled water directly into a major blood vessel. You would expect this mistake to:
have serious, perhaps fatal consequences because the red blood cells could swell and burst.
A plant cell placed in a hypertonic solution will:
undergo plasmolysis.
Penicillin is toxic to certain dividing bacterial cells because it prevents cell wall formation, causing the cells to burst. This indicates that the bacteria live in:
a hypotonic medium.
A wilted flower placed in a vase of water for several hours became stiff and stood erect. When a fresh flower was placed in a salt solution, it wilted. From this information we can say that:
the fresh water is hypotonic and the salt solution is hypertonic to the cells of the flower.
Facilitated diffusion:
requires a specific transport protein.
Carrier proteins are involved in:
Both facilitated diffusion and active transport.
Although glucose molecules constantly diffuse into a cell along their concentration gradient, equilibrium is never reached and glucose continues to enter the cell. This is a direct result of:
the rapid and continuous formation of glucose phosphates within the cell.
Studies of glucose transport in liposomes have revealed that:
glucose binds to the carrier protein causing the carrier protein to change its shape during the transport process.
Even though a bacterium contains a higher concentration of sodium ions than in the surrounding pond water, the sodium ions continue to enter the bacterium. Evidently, sodium ions are entering the cell by:
active transport.
Which of the following describes how facilitated diffusion is powered?
Energy is required to do the work of establishing and maintaining a concentration gradient.
Which of the following statements about the sodium-potassium pump is true?
It transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell in exchange for 2 potassium ions into the cell.
In the cotransport of glucose and sodium ions:
sodium ions are transported down their concentration gradient.
A human white blood cell engulfs a bacterial cell by:
phagocytosis.
Pinocytosis:
is the nonspecific uptake of fluids by pinching inward of the plasma membrane.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis:
occurs when specific molecules combine with receptor proteins in the plasma membrane.
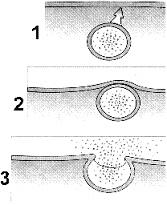
Figure 5-2 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). The process illustrated in Figure 5-2 is called:
exocytosis
Figure 5-2 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). The process illustrated in Figure 5-2 would most likely be used to transport:
hormones.
Select the receptor mediated endocytosis events that are in the correct (before, after) order:
Ligand binds to receptors; coated vesicle forms by endocytosis
In cells that are constantly involved in secretion, an equivalent amount of membrane must be returned to the interior of the cell for each vesicle that fuses with the plasma membrane; if this does not occur, then what would happen?
The cell surface will keep expanding.
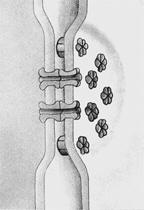
The structures in this figure:
allow the transport of small molecules and ions between adjacent cells.
Plasmodesmata of plant cells are functionally equivalent to __________ of animal cells.
gap junctions