1-Name and describe five types of production tasks that Pro Tools can be used for.
Audio - recording audio, stores as digital file
MIDI - records the performance data
Notation/score - writing music through MIDI score editing window
Mixing/ Automation - panning, signal routing, effects, dynamics
Video/ Post Production - can import video
1-What is the frequency range of human hearing?
20 Hz - 20 kHz
1-What does the frequency of a sound wave affect in terms of how we perceive the sound? How is frequency measured?
How high or low a sound is.
Hertz
1-What does the amplitude of the sound wave affect? How is amplitude measured?
Intensity or loudness of the sound
Decibels
1-How does the sample rate of a system relate to the frequency of audio it can capture? What is the name of the law that specifies the relationship between sample rate and audio frequency?
Sample rate needs to capture the frequency 2 times
Nyquist theorem
1-How does the bit depth of a system relate to the dynamic range of audio it can capture? How can you estimate the dynamic range of a system?
The more bit depth, the greater the dynamic range
Every bit =6 dB so multiply the bit depth by 6
1-What are some common digital connections available on Pro Tools audio interfaces? What type of connector jack does each use? (See “Recording in Digital Format” on page 15.)
AES/EBU - XLR cables
S/PDIF - RCA and Coaxial
1-Name some audio interfaces that are compatible with standard Pro Tools software. (See “Audio Interface Options” beginning on page 16.)
Windows - Any one with an ASIO driver
Mac - Any one with a Core Audio driver
1-Name some Avid audio interfaces that are compatible with Pro Tools | Ultimate software.
HD MADI, MTRX, MTRX studio, HD Omni, HD I/O
1-
HD Madi
1-
HD I/O
1-
HD OMNI
1-
MTRX
1-
MTRX Studio
2-Name some of the folders and files that Pro Tools creates as part of the session hierarchy. Where is the session file (.ptx) stored?
Audio
Bounced file
Backup files
MIDI Files
Wavecache
2-What is the WaveCache.wfm file used for? What happens if the WaveCache file gets deleted or goes missing?
Used to store the sessions waveforms.
It will take longer to load
2-Where are audio files stored in the session hierarchy?
Audio files are stored separately in the audio files folder
2-Where are Pro Tools’ MIDI files normally stored?
In the session folder
2-Which components should you turn on first when powering up a Pro Tools system? Which component should you turn on last?
1st - Anything that needs external power
Last - Audio monitoring device
2-What type of processing does the Hardware Buffer Size affect? What type of processing does it not affect?
Affects - Host based processing
Does NOT affect - DSP processing
2-What kinds of commands can be found under the Pro Tools View menu? How does the View menu differ from the Window menu?
Things that affect the display in widows, tracks, and clips
View affects parts of a window; window affects entire windows
2-What kinds of commands can be found under the Pro Tools Options menu? How does the Options menu differ from the Setup menu
Commands that toggle functions on/off
options toggle on and off where setup affects options to hardware and software
2-Which main Pro Tools window displays audio waveforms and can be used to work directly with audio, MIDI, and video files on tracks?
Edit Window
2-Which Pro Tools window provides access to Pan controls and Volume Faders for each track?
Mix Window
2-
A. Toolbar
B. Track and Clips lists
C. Edit tools
D. Transport controls
2-
A. Insert Selector
B. Sends Selector
C. Input Selector
D. Output Selector
E. Automation
F. Volume Fader
2-
A. Transport Controls
B. Counter
C. MIDI controls
3-What icon is used for the Zoomer tool in the Edit window? How can you use this tool to quickly zoom out, filling the Edit window with the longest track in the session?
It is a magnify glass
Double click on the zoomer tool
3-Which Edit tool is represented by a hand icon? What is this tool used for?
The grabber
For arranging or positioning clips
3-Which tool is active when the Trim, Selector, and Grabber icons are all selected (highlighted in blue) in the Edit window toolbar?
The smart tool
3-What are the four Edit modes in Pro Tools? How can you switch between them?
Slip, Shuffle, Grid, and Spot
3-Why should you use caution when editing synchronized material in Shuffle mode? When is Shuffle mode useful?
Because it can cause timing issues
It is useful when editing dialog
3-How does editing a clip in Slip mode affect the timing of other clips on the track?
It does not affect the timing of the other tracks
3-When is it helpful to work in Spot mode? When it is helpful to work in Grid mode?
Spot - When you want to place it in a specific place - Dialog box appears
Grid - When you want it to align to the grid based intervals - helpful when needing precise timing.
3-What are some ways to set the Main Time Scale in Pro Tools?
View > Main Counter
From the Main Time scale pop up menu(down arrow next to main counter)
Click on its name on the ruler
3-What are the two types of Rulers available in Pro Tools? What is the difference between them?
Time Based and Conductor
Time base measures time in various ways. Conductor contains events that map out locations, changes, and characteristics.
3-What are some ways to hide Rulers that you do not need displayed in a session?
View > rulers to unselect
Alt click on ruler name
3-Which Pro Tools windows provide access to MIDI controls, such as Wait for Note, Metronome, and MIDI Merge?
Transport window
3-What is the purpose of the Metronome button in the MIDI Controls area? What kind of track must be added to a session for the Metronome button to work?
To provide an audible beat for your musicians
Need a click track
3-What are the two states or modes available for controlling the current session tempo? How can you switch between these modes?
Tempo map mode and manual tempo mode
Switch by clicking the tempo ruler enable button - When active it is in tempo map mode
3-What is displayed by the Tempo field in the MIDI Controls area? What are some ways to set the session tempo using this field?
The current tempo based on the cursor location
You can enter the tempo manually or tap the tempo by pressing T or using a MIDI controller
3-
Trimmer Tool
Selector Tool
Grabber Tool
3-
Smart Tool
3-
A - Wait for note
B - Metronome
C - MIDI Merge
D - Tempo Ruler
4-What are some actions that can be initiated from the Dashboard?
create a session or project
create a session or project from template
open a session of project
4-What is the difference between a session and a project in Pro Tools?
Session is on the local drive
Project is collaborative and is saved on the cloud
4-What is required to create a project document? What are some reasons you might want to create a project instead of a session?
Prevent loss of session if something bad happens to your computer
Ability to access at different locations
Ability to collaborate with people
4-What are some available options for parameter settings in the Dashboard?
Bit depth
sample rate
I/O settings
File type
Interleaved
Save location
4-What audio file types are supported in Pro Tools? What is the default file type?
BWF(WAV) and AIFF
WAV is the default
4-What is the maximum sample rate supported in Pro Tools? What is the maximum bit depth?
Sample rate - 192 kHz
Bit Depth - 32 bit floating
4-What menu command lets you add tracks to your session? What keyboard shortcut can you use to access this command?
Track>New
Ctrl, Shift, N
4-How many tracks can you add to a session at one time?
128
4-Describe some primary track types that are available in Pro Tools. Describe the two types of Folder tracks.
Audio – Used to import, record, and edit audio signals as waveforms
- MIDI – Used to import, record, and edit MIDI & controller data (no audio signal flow)
- Instrument – Combine the functions of MIDI tracks and Aux Input tracks
- Video – Used to add or import video (Pro Tools | Ultimate required for multiple Video tracks)
- Aux Input – Used for effects returns, submixes, and routing live audio (or generating audio from a virtual instrument receiving MIDI input)
- VCA Master – Used to control tracks in a Mix group
- Master Fader – Used to control hardware output levels and bus path levels
- Basic Folder – Used to organize sets of tracks into a collapsible collection
- Routing Folder – Used like a Basic Folder with the added routing functionality of an Aux Input track
4-Which timebase do Audio tracks use by default? Which timebase do MIDI and Instrument tracks use by default?
Audio - Sample based
MIDI - Tick based
4-What happens to the audio and MIDI data on a track when the track gets deleted from your session? Can the Track > Delete command be undone?
The MIDI and Audio stays in the clip list.
No it cannot be undone
4-Name the two types of cursors available in the Edit window. What is the difference between them?
playback cursor and edit cursor
Playback - Solid blinking line that moves with playback
Edit - Blinking line on the track when you use the selector tool
4-Which tool can be used to set the playback point by clicking directly on a track?
Selector tool
4-What is the Playback Cursor Locator used for? Where will the Playback Cursor Locator appear (in what Ruler)?
It is used to find the playback location when it goes off the screen
It appears in the main time base ruler
4-What is the purpose of the Save As command? Which session will be open after completing the Save As command—the original or the renamed copy?
Save as makes a copy of the session and closes the original so that you can work in the copy. It is useful when wanting to save to a new location or to experiment without affecting the original copy.
4-What is the purpose of the Save As New Version command? What type of Pro Tools document does this command apply to?
To save a copy of a project similar to Save as
Only applies to Projects
4-How can you open a session after locating it in a Workspace browser?
Double click on it
5-How much disk space is consumed per minute by a mono track at a sample rate of 44.1 kHz and a bit depth of 16-bit? What happens to disk space consumption if the sample rate is doubled to 88.2 kHz with the same bit depth?
5 MB
It is doubled - 10MB
5-How can you monitor the storage space available on your system to determine the amount of record time remaining for each mounted drive?
In the Disk Usage window
Window>Disk Usage
5-How can you create a click track for a session? What kind of track is used for a click track?
Track>Create Click Track
Aux input
5-What window(s) can you use to record-enable an Audio track?
Edit or Mix
5-What selector can you use to route a signal from an input on your audio interface to a track for recording?
Audio Input Path Selector
5-How can you adjust the input level going to a record-enabled track? Can you use the Volume Fader to achieve a strong signal going to disk?
Adjust source volume, Microphone placement, Modify signal strength on audio interface
NO
5-How can you place a session in Record Ready mode after record-enabling a track? What modifiers/shortcuts are available to initiate recording without first entering Record Ready mode?
Click record button in transport window or...
Ctrl space or....
F12
5-Where are recorded audio files stored for Pro Tools sessions?
Clips list and tracks playlist
5-What term is used to describe an unedited audio file in Pro Tools? What term is used to describe the smaller, edited pieces of the original sound file?
Whole file clips
Subset clips
5-What types of clips are represented by boldface text in the Clip List? What type is represented by normal (plain) text?
Bold face is Whole file clips
normal is subset clips
5-How do track names affect the default names of the audio files you record in Pro Tools?
The audio files are named the track names and then there is an underscore and the take number. The dash will be the edit number in subset clips
5-Describe two ways to rename an audio file after recording into Pro Tools.
Dbl click on the file or clip(Grabber tool) in edit window or in clip list
Rt click on file or clip in edit window or clip list
Select RENAME
5-How would you go about removing unwanted audio from the Clip List without deleting the files from disk?
CTRL click or click on down arrow on the clip and push CLEAR and the REMOVE
5-How would you go about deleting unused whole-file clips to erase them from your storage drive? Can this action be undone?
CTRL click or click on down arrow on the clip and push DELETE
NOPE
6-What audio file formats can be imported to Pro Tools without requiring conversion?
WAV and AIFF
6-What condition would cause a file in one of Pro Tools’ native formats to require conversion on import?
If the sample rate was not the same
6-Name some common audio file formats that Pro Tools can convert on import.
MP3, AIFC
6-What are some video file formats that can be imported by Pro Tools?
Quicktime and AVID MXF
6-What is the difference between split stereo and interleaved stereo? Which is/are supported for importing into Pro Tools?
Split - Audio files are split into mono files for right and left
Interleaved - Combined into a single file
Both are supported
6-What is the difference between the Add button in the Import Audio dialog box and the Copy button? Which button will force-copy the files into your session’s Audio Files folder?
Add - adds the audio without copying it to the audio file folder. If sample rate is not the same then clip will not play back at correct speed or pitch
Copy - Will copy files into audio file folder - also will change to convert if sample rate does not match.
6-What happens when you use the Workspace browser to import audio that is not compatible with your session’s parameters (audio that requires conversion)? What happens when you import audio that does not require conversion?
It will automatically convert and copy audio files
If no conversion is necessary then they will be referenced and not copied.
6-What steps are required to conduct a search for an audio file using the Workspace browser?
WINDOW>NEW WORKSPACE>DEFAULT
ADVANCED SEARCH(magnify with +)
SEARCH - KIND
FILE TYPE-AUDIO
6-How would you go about importing a QuickTime movie file to Pro Tools while simultaneously importing the audio embedded in the file?
SETUP>PLAYBACK ENGINE>ENABLE
FILE>IMPORT>VIDEO
Click Open
If you want Audio then click the import audio box
6-How many video files can be associated with a standard Pro Tools session at once?
1
7-What does the term MIDI stand for? How is MIDI data different from the data stored in an audio file?
Musical Instrument Digital Interface
MIDI is data that is transmitted as a data about a performance not as waveforms
7-How many channels of MIDI information can be sent over a single MIDI cable?
16
7-What two types of tracks does Pro Tools provide for working with MIDI data? What is the difference between the two track types?
MIDI and Instrument
MIDI will not play audio - you will need to route it to Aux
Instrument will play audio
7-How many ticks are in a quarter note in Pro Tools?
960
7-Describe three ways to set the Main Time Scale to Bars|Beats.
bars/beats of ruler area
View>main counter> bars/beats
Main counter selector
7-What is the default meter in Pro Tools? How would you go about changing the meter?
4/4 - click on ADD METER CHANGE button(+) sign
7-What is the default tempo in Pro Tools?
120
7-What physical connections can you use to connect a MIDI controller to your system for recording on a MIDI or Instrument track?
MIDI interface or USB
7-Give some examples of virtual instrument plug-ins that are installed as standard components of Pro Tools. On which track types are virtual instrument plug-ins typically placed?
Xpand 2, Boom, Falcon
Instrument or Aux Input
7-How many parts can be included in an Xpand!2 patch? How can each part be turned on/off?
4
the power button next to the letter
7-What kind of virtual instrument is Boom? What does the Boom Matrix Display show?
Drum sequencer
the drum pattern
7-What track views are available for MIDI data in the Edit window? Which view allows you to scroll up or down to see notes at different pitches?
Notes view, clips view, velocity view
Notes view
7-What track types can display data in MIDI Editor windows?
Instrument, MIDI, Aux input
7-What is the Notation Display Enable button used for in the MIDI Editor window?
toggle between notes view and notation view
8 - What does the Universe view display? How can you use this view to scroll in the Edit window?
Shows an overview of the entire session
click in the Universe view display
8-What are the Timeline Selection In/Out Points? How can you use them to adjust a selection?
The start and end of a selection
You can click and drag them
8-How can you make an edit selection using the Grabber tool?
You click on the clip in that you would like. This can be in playlist or on the track itself
8-Describe two ways to make an edit selection using the Selector tool. How can the Selector tool be used to easily select an entire clip?
Click and drag or click then push down shift and click
double click
8-How can you make a selection across adjacent tracks using the Selector tool? How can you extend a selection to a nonadjacent track?
click and drag across the tracks
Shift and then click on the track
8-What does the Link Track and Edit Selection setting do?
shares edit selections across tracks
8-How does the Tab key affect the cursor position when working in a track? How does this behavior change when the Tab to Transients button is active in the Edit window?
It goes to the boundaries of the clips
It will go to the start of each transient
8-How can the track height be adjusted for a track? How can all tracks be set to the same height?
Tack options menu or the amplitude bar
Option and click the amplitude bar
8-Describe three ways to change the order of tracks in Pro Tools.
click and drag on name plate it edit window
click and drag in mix window
Click and drag in track list
8 - Describe the button in the Edit window that activates Zoom Toggle. What does the Zoom Toggle function do?
Arrows to the left of zoomer
goes between current zoom and zoomed in
8- What is the function of the buttons numbered 1 through 5 beneath the Zoom buttons?
They are zoom presets
8-What are the two main types of memory locations provided in Pro Tools? How many memory locations can you add to a session?
Markers and selections
999
8-How can you add a marker at the current cursor location? How can you add markers on the fly during playback?
Click the + button on marker ruler
Press enter on numeric keyboard
8 - Describe three ways to recall a memory location.
Click the marker symbol
In the memory locations window
on numeric keypad . # .
9 - What does the Loop Playback option do? What is the minimum loop length required for loop playback?
Allows you to listen to a section repeatedly
At least 0.5 seconds
9 - What happens when you delete a clip from between two existing clips in Shuffle mode? What happens when you do the same thing in Slip mode?
They'll move to the left to close up the space
There is no effect on subsequent clips
9- What happens when you move a clip whose start point falls between Grid lines in Absolute Grid mode? What happens when you do the same thing in Relative Grid mode?
It will snap its start time to the nearest grid line
The clip will move in grid increments preserving the offset from the grid.
9 - How can you configure the size of the Grid increments used in Grid mode? How can you display or hide the Grid lines in the Edit window?
Grid Value Pop-Up in Toolbar > Choose appropriate Time Scale > Click Grid Value pop-up selector again and choose corresponding grid size. (Available options vary depending on time scale)
Click main Timebase Ruler or click Grid Indicator in Toolbar
9 - Name some common editing commands provided in Pro Tools.
Cut, Copy, Paste, Clear, Duplicate, Repeat, Separate, Heal
9 - What are some operations that the Separate Clip command can be used for?
Split clip into two separate clips at insertion
Separate selection from larger clip / material on other side
Slice up clip at Grid Lines or transient locations
9 - What happens when you click on a clip with the Grabber tool in Spot mode?
The Spot dialog box will appear
9 - What is the Trim tool used for? What modifier can you use to reverse the direction of the Trim tool?
Dynamically adjusting length of clips
Option (Mac) / Alt (Windows) before trimming
9 - What is the Nudge value used for? In what Edit modes can the Nudge function be used?
To adjust placement in small, precise increments
All Edit modes
9 - What keys are used to nudge a clip or selection earlier or later on a track?
Plus (+) and Minus (-) on the numeric keypad
9 - How would you go about creating a fade-out at the end of a clip? How would you go about creating a crossfade between two adjacent clips?
Select end of clip > Command + F
Highlight boundary between clips > Command + F
9 - How many levels of operations can you undo in Pro Tools? What are some operations that cannot be undone?
64 levels
Deleting tracks
Closing Session / Quitting ProTools
Clearing audio from Clip List
Recording in Destructive Record Mode
9 - How can you display the Undo History window? What are some actions available in this window?
Window > Undo History
Multiple simultaneous undos / redos
Undo all
Redo all
Clear the queue
9 - What are some available options for undoing changes that are no longer available in the Undo History window? When would each option apply?
File > Revert to Saved (Goes back to last save point of your session)
File > Open Session > Choose Backup Folder (Goes back to specific date and time)
10-What term is used to describe an audio patch point that applies a signal processor directly into the signal path on a track? How many of these patch points does Pro Tools provide on each track?
insert
10
10-What term is used to describe a signal path carrying a mix output of one or more tracks routed for parallel processing? How can this signal be returned to the sending device?
send
10
10- What menu would you use to display or hide the Mix window? What keyboard shortcut can you use to toggle between the Mix and Edit windows?
Window
Command + =
10-What menu command can you use to display or hide an Inserts or Sends view area in the Mix window?
view>mix window
10-What type of plug-in provides real-time processing? What type provides non-real-time processing?
AAX - file based = real time
audiosuite = not real time
10-What are some commonly used plug-in options for EQ and dynamics processing in Pro Tools?
Avid EQIII
Avid dynamics III
Avid Channel Strip
10-Which Pro Tools automation mode discussed in this lesson records changes to track controls in real time when playing back the session?
write
10-What is the difference between Read mode and Off mode? Which mode allows you to play back existing automation on the track?
Read - Will play the automation
Off - will not play the automation
read mode
10-What track control can you use to display an automation playlist? What window are automation playlists displayed in?
track view selector
edit
10-What tool can you use to add, move, or delete automation breakpoints? What modifier can you use to delete a breakpoint by clicking on it?
grabber
Option
10-Why is it important to back up your Pro Tools sessions? What are some ways in which your Pro Tools work can be lost accidentally?
So you dont lose your work
Virus, Corruption, accidental deletion
10-.How is the Save Copy In command different from the Save As command, in terms of the files that are saved?
Save as - only session file
Save copy in- all files are copied
10-Which session will be open after completing a Save Copy In operation: the original or the copy? How is this different from the Save As operation?
The original will be open with save copy in
The copy with save copy as
10-What command can you use to save a session with a different sample rate or bit depth?
save copy in
10-What are some considerations for bouncing audio in Pro Tools? How is the bounce affected by soloed or muted tracks? How is it affected by the active selection?
make sure it is routed correctly
based on timeline selection
only the audio that you can hear will be bounced, if something is muted it will not be bounced
10-What command lets you mix your entire session directly to a stereo file? What file types are supported for the bounce file with this command?
Bounce to disk
WAV, AIFF, MP3, MXF
10-What bit depth and sample rate should you use when bouncing if you plan to burn the file to CD without further processing?
16 bit, 44.1kHz
10-How can you add audio files to iTunes for use in burning a CD??
click interleaved and add to itunes in the bounce window
Which companies have played a direct role in developing Pro Tools software?
A Aldus Corporation
B Digidesign
C Avid Technology
D Both A and B
E Both B and C
E
The maximum dynamic range of 16-bit audio is __________.
A 24dB
B 48dB
C 64dB
D 96dB
E 144dB
D
What unit of measurement is used to indicate the amplitude of a sound?
A Hertz
B Decibel
C Ohm
D Farad
E Volt
B
Why is the sample rate of a digital recording important?
A It determines how many levels of undo are possible when editing the recorded file
B It determines the available dynamic range that can be captured in the recording
C It determines the range of frequencies that can be captured in the recording
D It affects the size of the recorded file
E Both C and D
E
Which of the following connection types is/are common on audio interfaces for making digital transfers?
A S/PDIF
B AES/EBU
C RF
D Both A and B
E Both A and C
D
The differences between a standard Pro Tools system with a USB interface and a Pro Tools|HDX system with dedicated DSP hardware include:
A Standard Pro Tools systems are Mac-only; Pro Tools|HDX systems are Windows-only.
B Standard Pro Tools systems use a different file format than Pro Tools|HDX systems.
C Standard Pro Tools systems are not available through a subscription, whereas Pro Tools|HDX systems are subscription-only.
D Standard Pro Tools systems do not support plug-ins.
E Standard Pro Tools systems are host-based; Pro Tools|HDX systems are not.
E
When working in a session document, where are recorded audio files stored by default?
A Inside the session file
B Inside the Audio Files folder
C Inside the Recorded Files folder
D In your Avid Cloud storage
E In the Bounced Files folder
B
What is the purpose of the Session File Backups folder inside the Pro Tools session folder?
A Tracks storage locations used with the Save As command
B Stores session backup files created by the Auto Backup function
C Stores a document map for use with Avid Cloud storage
D Contains exported media for archival purposes
E Stores the Last Used I/O Settings file
B
The _____ ________ window provides access to pan controls and volume faders for your tracks.
A Mix
B Transport
C MIDI Editor
D Score Editor
E Soundbase
A
The __________ window lets you view, edit, arrange, and print MIDI data as music notation.
A Mix
B MIDI Event
C Transport
D Score Editor
E Universe
D
What dialog box lets you choose the audio device to use for Pro Tools playback/recording (such as a USB microphone, an audio interface, or your computer's built-in speakers)?
A The Playback Engine dialog box
B The Click/Countoff Options dialog box
C The Preferences dialog box
D The New Tracks dialog box
E The Import Audio dialog box
A
Which of the following functions are available under the Edit menu in Pro Tools?
A Cut, Copy, and Paste
B Import and Export
C Create New Track
D Open Session
E Preferences
A
What is the purpose of the Bounced Files folder inside the Pro Tools session folder?
A it is the default location for recorded audio files
B It is the default location for rejected audio files
C It is the default location for files created using the Bounce to Disk function
D It is the default location for Elastic Audio files
E It is the default location for recorded MIDI files
C
Where are the Pro Tools Edit tools located
A In the Mix window side column
B In an Edit window side column
C In the Edit window toolbar
D In the Transport window
E In Workspace browsers
C
TRUE or FALSE? Standard Pro Tools software does not include any plug-ins; all plug-in bundles require a separate purchase or Pro Tools | Ultimate software.
A True
B False
B
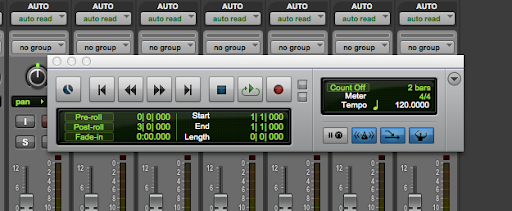
The Transport window (shown below) can be accessed from the _______ menu.
A File
B Edit
C View
D Options
E Window
E
Which of the following is affected by the Hardware Buffer Size setting?
A Monitoring latency during recording on Native systems
B DSP processing on Pro Tools|HDX systems
C Bit-depth conversion for imported audio files
D Sample rate conversion for imported audio files
E C and D only
A
Lesson 3
Which of the following is a type of Ruler available in Pro Tools?
A Bars|Beats
B Min:Secs
C Timecode
D All of the above
E A and B only
D
How can you quickly zoom out to get a full track view that fills the Edit window with the longest visible track in the session?
A Shift-click on the Zoomer tool.
B Double-click on the Zoomer tool.
C Shift-click on the Selector tool.
D Double-click on the Selector tool.
E Click on any track with the Zoomer tool in Single Zoom mode.
B
Which of the following methods can be used to hide a ruler in the Edit window?
A Choose Edit > Ruler > Hide and select a ruler name
B Choose View > Rulers and select a checked ruler
C Option-click (Mac) or Alt-Click (Windows) on a ruler name in the Timeline display area
D Both A and B
E Both B and C
E
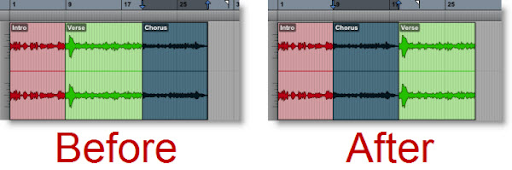
Refer to the image. Which Edit mode should you use if you want clips to swap positions on a track when dragged on top of one another, without overlapping?
A Shuffle
B Slip
C Spot
D Grid
E Grab
A
Which Edit mode should you use if you want to place a clip by specifying a precise numeric location in a dialog box (as shown below)?
A Shuffle
B Slip
C Spot
D Absolute Grid
E Relative Grid
C
TRUE or FALSE? The Sub Time Scale determines the timebase units used in the Start, End, and Length fields in the Edit window.
A True
B False
B
TRUE or FALSE? The Main Time Scale determines the timebase units used in the Main Counter in the Edit window.
A True
B False
A
Refer to the image. What is the purpose of the Metronome button in the MIDI Controls section of the Transport window?
A To set the playback tempo
B To turn the click on or off
C To turn Elastic Audio on or off
D To set the grid value
E To open the MIDI Editor window
B
Which Edit mode should you use if you want the clip start to "snap" to Grid boundaries ?
A Shuffle
B Slip
C Spot
D Absolute Grid
E Relative Grid
D
We To deselect all selected tracks in Pro Tools, hold ________ while clicking on the nameplate of one of the selected tracks.
A Option (Mac) or Alt (Windows)
B Command (Mac) or Ctrl (Windows)
C Tab
D Shift
E Control+Shift (Mac) or Start+Shift (Windows)
A
TRUE or FALSE? The New Tracks dialog box allows you to add multiple Audio tracks, MIDI tracks, Aux Input tracks, and other track types simultaneously.
A True
B False
A
How can you change a track name in Pro Tools?
A Double-click on the track name in the Edit window or Mix window
B Select the track and choose Options > Rename
C Choose View > Track Names to display the Track Naming dialog box
D Double-click on any clip on the track
E Select a track, press ESC, and type a new name
A
TRUE or FALSE? The Track Delete command can be reversed by choosing Edit > Undo.
A TRUE
B FALSE
B
Which of the following is a way to create a new track in Pro Tools?
A Choose File > Add Track > Track Type
B Choose Track > New
C Enable "Auto-Generate Tracks" in the Dashboard
D Double-click the Metronome icon in the Transport window
E Press Command+= (Mac) or Ctrl+= (Windows)
B
The Workspace browser can be used to do which of the following:
A Save a session
B Locate and open a session
C Import audio to a session
D Export audio from a session
E Both B and C
E
Pro Tools supports recording at bit depths up to:
A 24 bits
B 48 bits
C 64 bits
D 96 bits
E 32-bit floating point
E
When you delete an Audio track in Pro Tools, any clips that were on the track will:
A Remain in the Clip List
B Be removed from the Clip List and moved to the Unused Files folder
C Be removed from the Clip List and be moved to the Trash
D Be instantly deleted from the session and from the hard drive
E Be placed on an adjacent Audio track
A
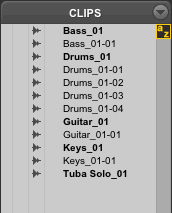
How many whole-file clips are shown in the image below?
A None - all are subset clips
B 1
C 5
D 7
E 12
C
TRUE or FALSE. Removing a clip from a session will also immediately delete the associated audio file from the hard drive.
A TRUE
B FALSE
B
When you record audio on a track, Pro Tools names the resulting file based on the _____________.
A track type
B track name
C Session name
D Input name
E SMPTE time stamp
B
Which control can you use to route a signal from your audio interface into a track for recording?
A The Input Path selector in the I/O section of the Mix window
B The Output Path selector in the I/O section of the Mix window
C The Main Counter control in the Transport window
D The Transport window pop-up menu
E The main Track menu (Track > Select Input)
A
When clearing clips from the Clip List, the Delete and Remove options both ________
A remove the selected clips from the Clip List
B free up additional drive space
C move the selected clips to the Trash/Recycle Bin
D copy the clip metadata to the clipboard
E All of the above
A
A mono 44.1 kHz, 16-bit audio file consumes approximately 5 MB of disk space per minute. How much disk space is consumed by a mono 88.2 kHz, 16-bit audio file?
A 5 MB
B 7.5 MB
C 10 MB
D 15 MB
E 50 MB
C
Which of the following actions is performed by the Track > Create Click Track command?
A Opens the New Tracks dialog box with a Stereo Audio track selected
B Creates a new Aux Input track
C Inserts the Click II plug-in on the new track
D Both A and C
E Both B and C
E
Why is it important to set the input level properly when recording?
A Signals recorded below -6dBFS will have a poor signal-to-noise ratio
B Recording too hot can create excessively large files
C Recording too hot can cause digital clipping
D Quiet input signals have exaggerated high- and low-frequency response
E No files will be created if the input level is set too low
C
What is REQUIRED to complete a record pass in Pro Tools?
A Enable the Tempo ruler
B Record-enable the target track(s)
C Click the Record button in the Transport controls
D All of the above
E B and C Only
E
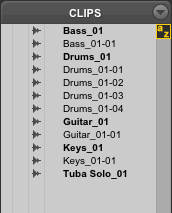
How many subset clips are shown in the image below?
A None - all are whole-file clips
B 1
C 5
D 7
E 12
D
Which of the following are ways to rename an existing audio clip in your session?
A Double-click the clip with the Grabber tool.
B Right-click the clip and select Rename from the pop-up menu.
C Rename the track where the clip currently resides.
D All of the above.
E A and B only.
E
Which video formats can be imported into Pro Tools?
A Quicktime
B MXF
C FLV
D Both A and B
E Both B and C
D
TRUE OR FALSE? A stereo interleaved file is audibly inferior to two mono files (representing separate left and right channels).
A True
B False
B
Selecting "New Track" in the Audio Import Options dialog box will do which of the following?
A Place the imported audio on the last created Audio track
B Place the imported audio on a new Audio track
C Place the imported audio on a new Instrument track
D Place the imported audio on a new Master Fader track
E Open the New Tracks dialog box to create a destination track for the audio
B
If an audio file with a 44.1 kHz sample rate is dragged into a 48 kHz session, what will happen?
A The file will be added to the session, but will play too slow and with a lower pitch.
B The file will be added to the session, but will play too fast and with a higher pitch.
C The file will be converted on import (to a new file in the Audio Files folder), and will play at the correct speed and pitch
D The session's sample rate will automatically change to match the imported audio.
E A message box will appear, indicating that files of different sample rates cannot be imported into the session.
C
Audio files in one of Pro Tools' native formats can be imported without requiring format conversion. The native audio file formats in Pro Tools include:
A WAV
B MP3
C AIFF
D A and B
E A and C
E
A split stereo or multi-mono recording is...
A a recording with separate mono files for the left and right channels
B a recording with the stereo information combined into a single file containing both left and right channel information
C A stereo source that has been recorded in mono with the left and right signals combined in a single channel
D a stereo clip that has been split into 2 or more subset clips
E A mono or stereo file that has been recorded to local storage as well as your Avid Cloud storage
A
The difference between ADDING an audio file or clip and COPYING an audio file or clip when using the Import Audio dialog box is:
A Adding imports to an existing track; copying imports to the Clip List.
B Adding references the audio file in its original location; copying makes a copy in the session's Audio Files folder.
C Adding appends the file to the currently selected clip; copying places the file in the computer's RAM.
D Adding will convert the sample rate to match the session; copying will not.
E Adding will convert the bit depth to match the session; copying will not.
B
Audio can be imported from __________.
A the Import Audio dialog box
B the Workspace browser
C an open Finder (Mac) or File Explorer (Windows) window
D All of the above
E A and B only
D
An interleaved stereo file is...
A a recording that includes separate mono files for the left and right channels
B a file that includes both the left and right channel information combined into a single stereo file
C a stereo file that has been recorded to local storage as well as your Avid Cloud storage
D two or more stereo recordings that have been grouped together
E a recording on a stereo Instrument track
B
Selecting "Clip List" in the Audio Import Options dialog box will do which of the following?
A Place the imported audio in the Clip List onl
B Place the imported audio on the selected track and in the Clip List
C Place the imported audio on a new Audio track and in the Clip List
D Create a looping pattern from the imported audio
E List all locations where the selected audio file has been used
A
Which of the following is true regarding importing video in current versions of Pro Tools?
A Pro Tools can import QuickTime video files
B Pro Tools can import Avid MXF video files
C Importing video files will always import any audio associated with the video
D A and B only
E A and C only
D
How many separate channels of MIDI information can be sent over a single MIDI cable?
A 4
B 8
C 16
D 24
E 32
C
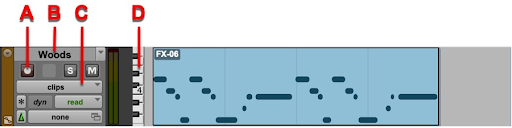
Refer to the image. Where can you click to change the track display to Notes view?
A The Record-enable button
B The track nameplate
C The Track View selector
D The mini-keyboard display
E None of the above
C
The default meter for a Pro Tools session is:
A 3/4
B 4/4
C 6/8
D 5/4
E Varies based on the sample rate
B
You can display or hide the Instruments view in either the Mix or Edit window from the ________ menu in Pro Tools.
A File
B Edit
C View
D Setup
E Options
C
Pro Tools subdivides the bars and beats of a session into ticks. How many ticks comprise a quarter note?
A 4
B 16
C 192
D 960
E 44,100
D
MIDI and Instrument tracks are tick-based by default. When recording onto a tick-based track, recorded data is tied to specific _______ locations on the timeline.
A Bar|Beat
B Sample
C Min:Secs
D Timecode
E Tap Tempo
A
Which of the following are ways to view MIDI data in Pro Tools?
A Notes view in the Edit window
B Clips view in the Edit window
C Notation view in a MIDI Editor or Score Editor window
D All of the above
E A and C only
D
Pro Tools allows users to record MIDI information on which of the following track types:
A Audio Tracks
B MIDI Tracks
C Instrument Tracks
D A, B, and C
E B and C only
E
to begin recording MIDI with Wait for Note active, you would Record-arm the transport to enter Record Ready mode, and then…
A Click the Wait for Note button to begin a record pass
B Begin playing your MIDI controller to start a record pass
C Press Command+= (Mac) or Ctrl+= (Windows) to start a record pass
D Press [7] on the numeric keypad to start a record pass
E Any one of the above
B
RUE OR FALSE? MIDI is a form of digital audio.
A True
B False
B
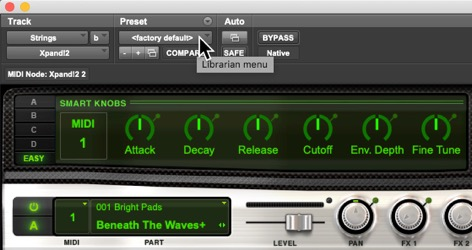
Refer to the image. What is the Librarian menu used for in Xpand!2?
A Selecting an insert position
B Muting and unmuting
C Selecting patches and presets
D Enabling automation
E Selecting the target track
C
What is the function of the Tab key when Tab to Transients is disabled?
A Advances the Edit cursor through clip boundaries
B Toggles between the Mix and Edit windows
C Opens the Spot dialog box
D Separates a clip at the cursor location
E Moves the selected clip forward by the Grid increment
A
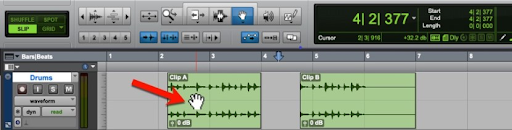
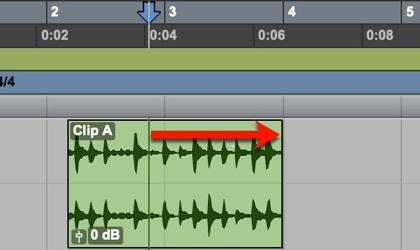
Refer to the image. What will be the result when the mouse is clicked at the current location (marked by the red arrow)?
A Clip A will become selected.
B Both Clip A and Clip B will become selected.
C The Edit cursor will be positioned at the clicked location.
D The Edit cursor will be positioned at Bar 3.
E There will be no change in the Timeline or Edit selection.
A
How can you set all tracks in your session to the same height?
A Hold Command (Mac) or Ctrl (Windows) while changing the height of any track
B Hold Option (Mac) or Alt (Windows) while changing the height of any track
C Hold Control (Mac) or Start (Windows) while changing the height of any track
D Select all tracks, and then select a track height from a Track Height selector
E Choose Window > Resize Tracks
B
The Universe view appears above the Rulers in the Edit window. This view displays...
A an overview of your audio connections to Pro Tools
B a miniature representation of all clips on your displayed tracks
C a summary of all virtual instruments used in your session or project
D a list of all session files and folders on your system
E clickable icons for instantiating plug-ins on a track
B
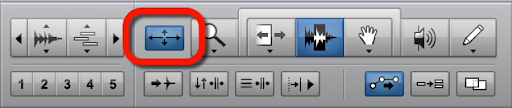
Refer to the image. What function is represented by the icon with arrows pointing in all directions (outlined in red)?
A The Smart Tool
B Insertion follows Playback
C The Scrubber Tool
D Zoom Toggle
E The Selector Tool
D
Which of the following is a way to recall a Memory Location
A Click the entry in the Memory Locations Window
B Click the marker in the Ruler
C Type . - number - . [decimal - keypad number - decimal]
D A & B only
E A, B, and C
E
Which of the following is a way to make a selection on a track when Tab to Transients is enabled?
A Hold Command (Mac) or Ctrl (Windows) and press the Tab key
B Hold Option (Mac) or Alt (Windows) and press the Tab key
C Hold Control (Mac) or Start (Windows) and press the Tab key
D Hold Shift (Mac or Windows) and press the Tab key
E Press the Tab key without holding a modifier
D
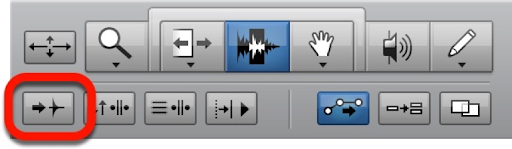
In the screenshot below, what is outlined by the red rectangle?
A Metronome
B Real-Time Audition
C Wait for Note
D Tab to Transients
E Strip Silence
D
How can you change the display order of tracks in your session?
A Click a track's nameplate in the Edit window and drag the track above or below other tracks
B Click a track's nameplate in the Mix window and drag the track to the right or left of other tracks
C Click a track's name in the Track List and drag it to a higher or lower position in the list
D All of the Above
E None of the Above
D
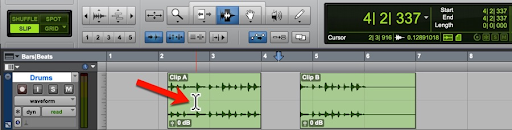
Refer to the image. What will be the result when the mouse is clicked at the current location (marked by the red arrow)?
A Clip A will become selected.
B Both Clip A and Clip B will become selected.
C The Edit cursor will be positioned at the clicked location.
D The Edit cursor will be positioned at Bar 3.
E An Edit selection will be made from the start of the session to the clicked location.
C
The difference between Duplicating and Repeating is _______________.
A Duplicate creates one copy of a selection at a time; Repeat lets you create multiple copies at once.
B Duplicate makes a copy of a track; Repeat makes a copy of a selection.
C Duplicate applies to Audio clips; Repeat applies to MIDI clips.
D Duplicate applies to whole clips only; Repeat applies to selections within a clip.
E Duplicate reapplies a previous edit action, whereas Repeat makes a copy of a selection.
A
What is required to create a fade-in effect using the Edit > Fades > Create command?
A You must make a selection at the start of a clip that touches or crosses the clip boundary
B You must make a selection at the end of a clip that touches or crosses the clip boundary
C You must enable Zoom Toggle
D Both A and C
E Both B and C
A
Which of the following can be undone with the Undo command?
A Deleting Tracks
B Trimming a Clip
C Closing a session
D Clearing audio from the Clip List
E All of the above
B
Which of the following scrolling modes are available in standard Pro Tools (non-Ultimate)?
A No Scrolling
B After Playback
C Page Scrolling
D All of the above
E A and B only
D
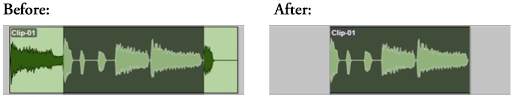
Refer to the image. How can audio be removed on either side of a selection?
A EDIT>CUT
B EDIT>COPY
C EDIT>SEPARATE>AT SELECTION
D EDIT>TRIM CLIP>TO SELECTION
E EDIT>HEAL SEPARATION
D
What will be the result of selecting a clip and pressing the Plus [+] key on the numeric keypad?
A The clip start will snap to the next grid line
B The clip end will snap to the next grid line
C The clip will move earlier by one Nudge increment
D The clip will move later by one Nudge increment
E A copy of the clip will be created adjacent to the clip
D
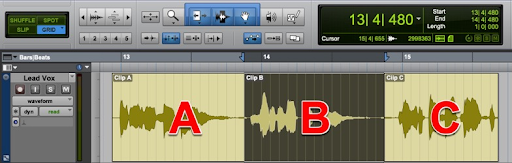
Refer to the image. What will be the result if the delete/backspace key is pressed?
A There will be space between Clip A and Clip C.
B Clip B will be removed from the Clip List.
C Clip B will be removed from the session.
D Clip C will snap to the end of Clip A.
E Clip A will snap to the start of Clip C.
A
What will be the result of selecting a clip and pressing the Plus [+] key on the numeric keypad?
A The clip start will snap to the next grid line
B The clip end will snap to the next grid line
C The clip will move earlier by one Nudge increment
D The clip will move later by one Nudge increment
E A copy of the clip will be created adjacent to the clip
D
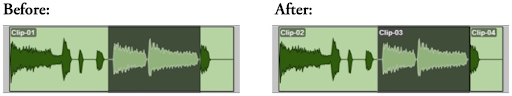
Refer to the image. How can a single new clip be created from a selection as shown below?
A EDIT>CUT
B EDIT>COPY
C EDIT>CLEAR
D EDIT>SEPARATE CLIP>AT SELECTION
E EDIT>HEAL SEPARATION
D
The Nudge function works in which of the following edit modes?
A Shuffle
B Slip
C Spot
D Grid
E All of the Above
E
Which of the following statements relating to Nudging is/are TRUE?
A The Nudge value is always equivalent to the Grid size
B Nudging works only in Slip and Grid modes
C Clips and selections can be nudged earlier or later in the session using the minus and plus keys on the numeric keypad
D All of the Above
C
The Save Copy In command can be used for all of the following EXCEPT:
A Creating a session copy with a different sample rate, bit depth, or file format
B Creating a session copy that is compatible with older Pro Tools systems
C Converting a session file to a template file
D Converting a local session file to a cloud-enabled project document
E Converting a cloud-enabled project to a local session
C
What keyboard shortcut will toggle between the Mix and Edit windows in Pro Tools?
A COMMAND+= (Mac)/CTRL+= (Windows)
B SHIFT+TAB (Mac or Windows)
C COMMAND+SPACEBAR (Mac)/CTRL+SPACEBAR (Windows)
D All of the above
E None of the above
A

Refer to the image. Where can you click to display volume automation for a track?
A - The Show/Hide Automation Lanes button
B - The track nameplate
C - The Track View selector
D - The Automation Mode selector
E Either A or C
E
How many Sends are available on a single Audio track in Pro Tools?
A 5
B 10
C 100
D 999
E Unlimited
B
Which plug-in can be used to boost or cut specific frequencies on a track?
A Avid Channel Strip
B Avid Dynamics III – Compressor/Limiter
C Avid Dynamics III – Expander/Gate
D All of these
E None of these
A
Immediately after backing up your session using FILE>SAVE COPY IN, which session will you be working in?
A The original session (not the copy)
B The session copy
C Neither - the Dashboard will appear, allowing you to choose which recent session to open.
D Neither - Pro Tools will automatically quit.
E Both sessions will be open under separate tabs
A
TRUE or FALSE. When creating a bounce to disk, Pro Tools always bounces the entire session, regardless of any timeline or edit selections you may have.
A True
B False
B
Creating a mixdown with Bounce to Disk allows for_____________.
A Faster than real-time offline bounces
B Simultaneous Bouncing to WAV and MP3 formats
C Creating a mixdown with a different sample rate than the session.
D All of the above
E A and B only
D
Which audio file formats are available when creating a stereo bounce to disk from Pro Tools?
A WAV
B AIFF
C MP3
D All of the above
E A and B only
D
____________ can be used to route a copy of a track's audio signal to a destination track or output BEFORE volume settings are applied to the signal.
A An input
B An output
C An insert
D A pre-fader send
E A post-fader send
D
How many Inserts are available on a single Audio track in Pro Tools?
A 5
B 10
C 100
D 999
E Unlimited
B
Pro Tools supports recording at sample rates up to ______ with a compatible audio interface.
A 24 kHz
B 44.1 kHz
C 48 kHz
D 96 kHz
E 192 kHz
E
A subset clip is...
A An original, unedited clip representing the entire audio file stored on disk
B An edited clip that represents a portion of the audio file stored on disk
C An audio file that has been recorded or imported to a cloud-based project
D A collection of audio assets in the Clip List
E A highlighted selection on a track playlist
B
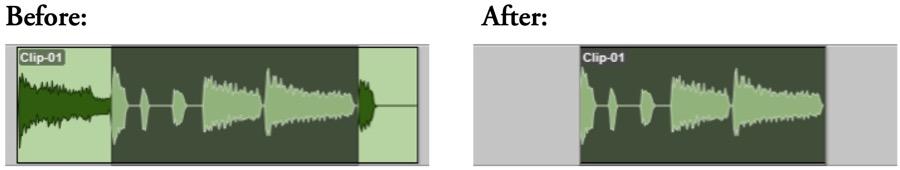
Refer to the image. How can audio be removed on either side of a selection?
A EDIT>CUT
B EDIT>COPY
C EDIT>SEPARATE>AT SELECTION
D
EDIT>TRIM CLIP>TO SELECTION
E EDIT>HEAL SEPARATION
D
The point at which a plug-in effect can be placed directly into the signal path of an audio track is called __________.
A an input
B an output
C an insert
D a pre-fader send
E a post-fader send
C
Pro Tools' real-time plug-in format is called _______.
A AudioSuite
B AudioFex
C AAX
D DSD
E DX7
C
Which of the following is used to authorize Pro Tools software, and is required in order for Pro Tools to run?
A A USB audio interface
B An iLok authorization (via USB key or iLok Cloud)
C An Avid control surface
D Pro Tools | HDX hardware
E None of these
B
The Save Copy In command can be used for all of the following EXCEPT:
A Creating a session copy with a different sample rate, bit depth, or file format
B Creating a session copy that is compatible with older Pro Tools systems
C Converting a session file to a template file
D Converting a local session file to a cloud-enabled project document
E Converting a cloud-enabled project to a local session
C
When turning on the devices in your system, which device should be turned on last?
A MIDI Interfaces and MIDI Devices
B External Hard Drives
C Audio Interfaces
D Host Computer
E Monitor Speakers
E
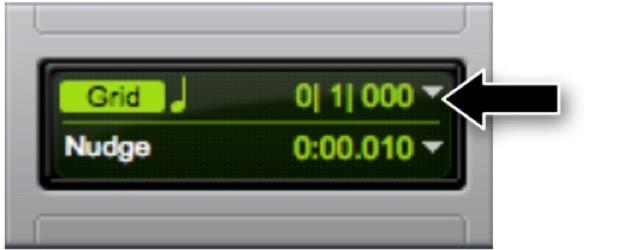
Refer to the image. What is the indicated selector used for?
A Setting the track view
B Setting the grid value
C Setting the tempo
D Setting the nudge value
E Setting the playback cursor location
B
To deselect all selected tracks in Pro Tools, hold ________ while clicking on the nameplate of one of the selected tracks.
A Option (Mac) or Alt (Windows)
B Command (Mac) or Ctrl (Windows)
C Tab
D ShiftE Control+Shift (Mac) or Start+Shift (Windows)
A
In the image below, which key press will move the insertion cursor to the next clip boundary (as indicated by the red arrow)?
A The Tab Key
B The Space Bar
C The Shift key
D The Right Arrow key
E The Left Arrow key
A
What is the purpose of FILE>REVERT TO SAVED?
A to open the last autosaved session file backup
B to restore the session to the last saved version
C to restore your most recent edit selection
D to restore your most recent timeline selection
E Both C and D
B
Which of the following is a function of the Save As command?
A To save a local session document under a different name
B To save a cloud-based project document under a different name
C To transfer a session or project document onto a portable drive with all associated audio files
D To convert a session document into a project document
E To convert a project document into a session document
A
Pro Tools (NOT Pro Tools | Ultimate) supports up to ____ simultaneous imported video files.
A 1
B 2
C 64
D 99
E Unlimited
A
The frequency range of human hearing is generally accepted to be between _____________________.
A 2 Hz and 20 Hz
B 20 Hz and 200 Hz
C 20 Hz and 2,000 Hz
D 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz
E 200 Hz and 20,000 Hz
D
Which is an advantage of a Pro Tools Project compared to a Pro Tools Session?
A Projects can use cloud backup to protect your work against loss in the event of drive failure
B Projects run faster and use less CPU than Sessions
C Projects can be shared with other Pro Tools users for cloud-based collaboration
D Both A and B
E Both A and C
E
TRUE or FALSE? The Pro Tools tempo map can be toggled on/off using the Metronome button in the MIDI Controls section of the Transport window.
A True
B False
B
TRUE or FALSE? When viewing MIDI data in Clips view, you can select, edit, and delete individual MIDI notes within a MIDI clip.
A True
B False
B
The Grabber Tool can be used to edit an automation graph in which of the following ways?
A Add Breakpoints
B Move Breakpoints
C Delete Breakpoints
D All of the Above
E None of the Above
D
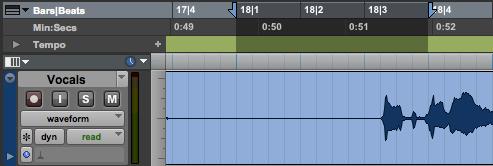
Refer to the image. The Rulers area highlighted with a dark overlay is called:
A A time-blocked range
B A timeline selection
C An edit-blocked range
D An edit selection
E An auto-insert zone
B
Which of the following methods can be used to select a clip on a track?
A Click on the clip with the Grabber tool
B Click on the clip with the Selector tool
C Double-click on the clip with the Selector tool
D Both A and B
E Both A and C
E