during a PE, what should you focus on "thorax" wise?
- observation and palpation
- recognize “normal” vs “abnormal”
- Breathing patterns...is everything symmetrical?
- Stethoscope placement
identify:
- Jugular (sternal) notch (JN)
- Sternal angle (SA)
- 2ND rib
- Intercostal spaces (ICS)
- Intercostal spaces 2 - 6
- costal margin (CM)
- subcostal angle (SCA)

look at picture
how do you find and palpate the second rib?
you find the sternal angle ridge on your pt and then feel sideways to feel the ribs and the intercostal spaces...if you move your fingers up and down you can feel the 1st and 2nd rib above and below
what is the bifurcation of the trachea called? what does it divide into?
carina...divides into R and L primary bronchi
the beginning and ending of the aortic arch is found where?
the sternal angle

what do we want symmetry between when we look at the ribs?
the costal margin and the subcostal angle
how to count vertebrae, whats the easiest to do?
find C7 which is the biggest bump and then count down in that direction

look at picture

Identify 2 bony landmarks of the posterior thorax
- What is “CVA tenderness”?

Spinous processes of thoracic vertebrae 1 -12
Costovertebral angle (CVA)
- Clinical: “CVA tenderness”: a medical test in which pain is elicited by percussion of the area of the back overlying the kidney...The test is positive in people with an infection around the kidney
name the 2 anterior vertical lines and describe them?
the 2nd one is a little medial to what?

Anterior median (midsternal) line...vertical line through sternum in mid-sagittal plane
Midclavicular lines (MCL)...vertical through midpoints of the clavicles, parallel to median line...medial to the nipple
name the 3 lateral vertical lines and describe them?
which one is formed by the pec major?
which one goes right through the armpit?
which one is formed by the latissimus dorsi and teres major?

Anterior axillary line...vertical line along anterior axillary fold (formed by pec major)
Mid axillary line...vertical line though apex of axilla (armpit)
Posterior axillary line...vertical line through posterior axillary fold (formed by latissimus dorsi and teres major)
name the 2 posterior vertical lines and describe them?
another 2 names for the 1st one?

Posterior median (midspinal or midvertebral) line ...vertical line through spinous processes of vertebrae in mid-saggital plane
Scapular lines...vertical lines that pass through inferior angles of the scapula, line is parallel to posterior median line
posterior median line goes through the inferior angle of the scapula...look for it in the picture and try to picture the bottom of the scapula along the line
what is the auscultation alley?
- Vertical column between thoracic spinous processes and medial border of scapula...want to put your stethoscope here to listen
- if you put the stethoscope on the other side (to the left of the far line) then the scapula will be in the way for you to hear
point out these spaces:
R/L 2nd ICS
Erb’s point (where is this?)
Left sternal
border (where is this?)
Left 5th ICS (where is this?)

look at picture
- Erb’s point – left 3rd ICS
- Left sternal border – 4th or 5th ICS
- Left 5th ICS - midclavicular
which space listed above can you use to hear the aortic and pulmonary valves?
how about if you wanted to listen to the mitral valve?
tricuspid valve?

right (aortic) and left 2nd ICS (pulmonic)
left 5th ICS
4th or 5th ICS
name the 3 bones of the thoracic wall?
their function?
- Bones of the thoracic wall = ribs, thoracic vertebrae and sternum
- Function – protect thoracic content…heart, lung, blood vessels, esophagus, etc…

Identify the structures of the sternum
- Manubrium
- Sternum (body)
- Sternal angle
- Jugular notch
- Articular sites for clavicle
- Xiphoid

M up top
Body in middle
X point at bottom
jugular notch at top
two facets next to that is articulation sites for the clavicle
identify the sub-divisions of the ribs (true, false and floating) and describe them?

- True (1-7) – attach “directly” to sternum
- False (8-10) – attach “indirectly” to sternum thru cartilage
- Floating (11-12) – do not attach to the sternum AKA dont even make their way around
describe typical vs. atypical ribs?

- Typical ribs = 3-9...have all the "usual" landmarks of the rib
- Atypical ribs = 1,2 10-12...dont have the typical landmarks that a rib would have
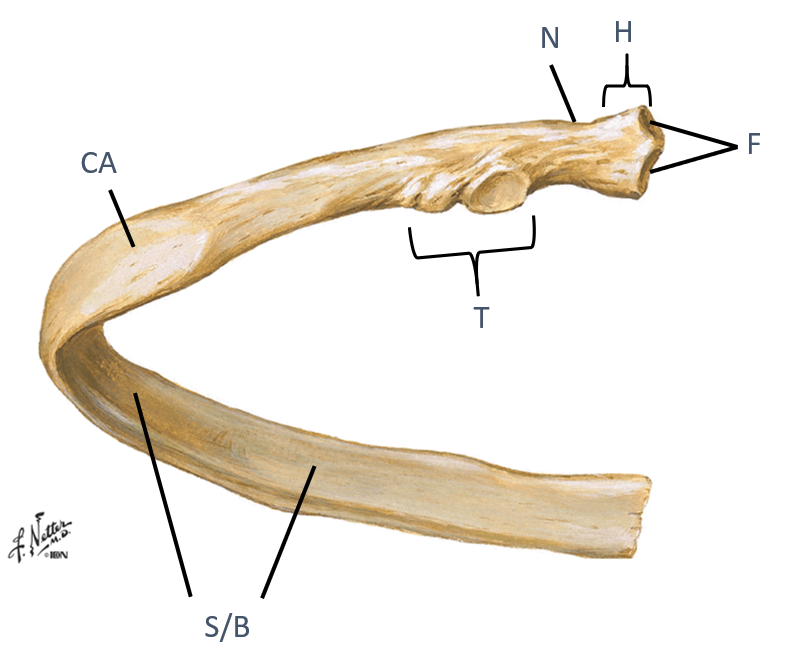
Identify the landmarks of a typical rib?
Head (H)
Neck
(N)
Tubercle (T)
Shaft/body (S/B)
Costal angle (CA)
look at picture
the head of a typical rib has what that do what?
what does the tubercle articulate with?
how would you describe the shaft/body region?
what is the costal angle a common site for?why is that?
Have facets (F) that articulate with two different vertebrae
Tubercle (T)...articulates with transverse process
Shaft/body (S/B)...thin, flat portion
Costal angle (CA)...common site of rib fracture, weakest point of the rib
Identify the landmarks thoracic vertebrae 1-12
Spinous process
(SP)?
Transverse process (TP)?
Costal facets along vertebral
bodies (CF)?
Transverse costal facets (TCF)?


study picture
look at picture
what do the costal facets have along the vertebral bodies, except for where?
what is the transverse costal facets along? except for where?

Costal facets along vertebral bodies (CF)...Pairs of inferior (ICF) and superior (SCF) on vertebrae except lower 4 thoracic vertebrae
Transverse costal facets (TCF)..along transverse processes except lower 2 thoracic vertebrae...notice how T12 in pic does have a transverse costal facet
in theory, typical ribs should articulate with what?
2 vertebrae

show what the superior thoracic aperture and inferior thoracic aperture are?

notice how in the first picture the esophagus and trachea, nerves and BV's are popping through
what does the superior thoracic aperture contain?
what does the inferior thoracic aperture allow?
- Superior...contains esophagus, trachea, nerves & blood vessels that supply the head, neck and UE
- Inferior...allows the esophagus, IVC (inferior vena cava) and aorta to pass inferior to abdominal cavity
describe what these joints articulate with?
- Costovertebral joints (CVJ)
- Costotranservse joints (CTJ)
- Intervertebral joints (IVJ) of the thoracic spine

- Costovertebral joints (CVJ)...rib articulation with vertebrae body
- Costotranservse joints (CTJ)...rib articulation with transverse process of vertebrae
- Intervertebral joints (IVJ) of the thoracic spine...Disc and facets
Identify/describe the joints of the anterior thorax...what are they articulations with?
- Costochondral joints?
- Sternocostal joints?
- Sternoclavicular joint (“SC” joint)?

Costochondral joints...Rib articulation with costal cartilage
Sternocostal joints ...articulation between costal cartilage and
sternum
Sternoclavicular joint (“SC” joint) ...Articulation
between sternum and clavicle
Identify/describe the joints of the anterior thorax and what they articulate with?
- Interchondral joints (ICJ)
- “articulation” between costal cartilages of lower ribs
- Manubriosternal joint (sternal angle – SA)
- Xiphisternal joint (XS)
- junction of xiphoid and sternum

Interchondral joints (ICJ)...“articulation” between costal cartilages of lower ribs
Manubriosternal joint (sternal angle – SA...manubrium and sternal body meet)
Xiphisternal joint (XS)...junction of xiphoid and sternum
essentially, the interchondral joints is where what articulates with what?
where the false ribs articulate with the cartilage above it

what 3 things to assess during a PE with patterns of ventilation?
what 2 things should we look for in inspiration?

Physical exam ...assess rate, symmetry, quality of movement, etc…
Inspiration ...increase in AP and lateral diameter due to “bucket
handle” motion of ribs
increase superior to inferior length
look at pictures to help visualize

describe what the external intercostal muscles do during inhalation? what do the ribs do? what does the sternum do?
what does the diaphragm do?
the external muscles contract causing the expansion of the chest cavity and an influx of air into the lungs
ribs elevate
sternum flares
diaphragm moves inferiorly during contraction
inspiration while at rest and not exercising involves what 2 muscles?
with exercise what 3 muscles can help out with inspiration?
diaphragm and external intercostals
accessory muscles like the SCM and scalenes can help...pecs can also help
expiration while at rest and not exercising involves what?
with exercise what muscles get recruited to help with expiration?
- rest...elastic recoil of the lungs
- exercise...recruit the internal intercostals + abdominal muscles like (rectus abdominis, int/ext oblique)
what is one abnormal movement pattern of ventilation? who typically displays this?
name another abnormal ventilation quality? when do you typically see this with?

“Shrug” shoulders...Patients with COPD and other pulmonary disease may display this type of breathing pattern
Asymmetry... see this with trauma/pathology to one lung
- Ex: pneumothorax, etc…
identify the actions of these muscles and their relationship to each other in space?
- External intercostals (E)
- Internal intercostals (I)
- Innermost intercostals (IM)

External intercostals (E)...inspiration...most superficial
Internal intercostals (I)...expiration
Innermost intercostals (IM)...elevate?…not completely understood...most deep
what is between the internal intercostals and the innermost intercostals? which muscle is on top?
when looking at a picture how do you identify these muscles, what should you look for?

BV's and nerves in between them
internal intercostal on top
basically, look for the innermost muscle and if its muscle colored it is the innermost intercostals...if it looks like a layer was peeled and you see nerves traveling horizontal, it indicates that you are looking at the internal intercostals

notice the external intercostal muscles
look at picture

what muscle do you see here and how do you know?
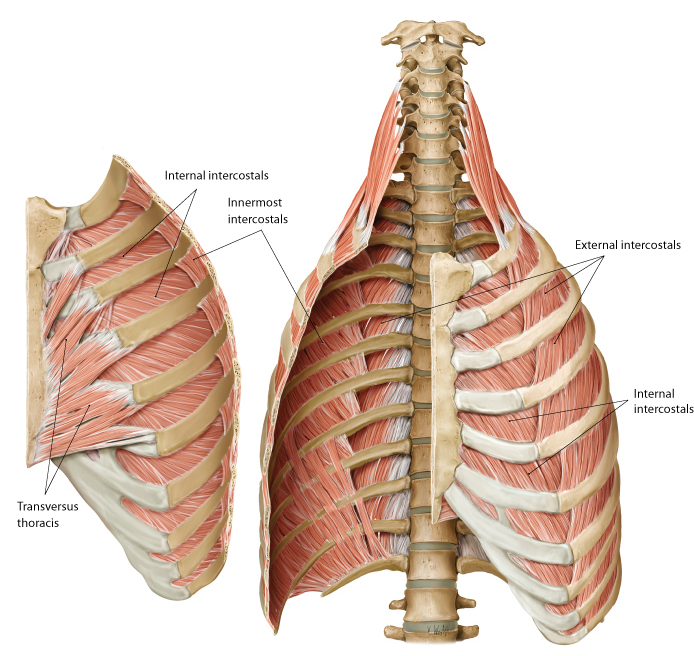
innermost intercostals because you can see the nerve and vessels driving into the muscle indicating that you can see the innermost intercostals (you are looking inside the chest so the IM are the deepest muscles inside)

action and location of the:
transversus thoracis?
subcostal muscles?

Transversus thoracis (TT) (in front)...expiration (depress
ribs)...located on internal anterior thoracic cage...in 1st
picure
Subcostal (SC) muscles (in back and on
inside)...inspiration (elevate ribs)...located on internal posterior
thoracic cage (in second picture they are the strips going up)

Identify/describe actions of the following muscles
- Levator costarum (lc)
- where is this one located?
- Serratus posterior superior (SPS)
- Serratus posterior inferior (SPI)
basically, what do the SPS and SPI do?

Levator costarum (lc)...inspiration (elevate the ribs)...the very
small slanted muscles down the posterior spine in the 1st
pic...opposite of "/")
Located external posterior
attach to ribs and Transverse process
Serratus posterior superior (SPS)...inspiration (elevates the
ribs)...on top in second picture
Serratus posterior inferior (SPI)...expiration (depresses the
ribs)...on bottom in second picture
they anchor onto the ribs and spine and either bring it up or down
what nerve supplies the diaphragm? what 2 components does it provide? this nerve comes out of which vertebrae?
phrenic nerve (C3-C5)
motor and sensory components

the diaphragm is the major muscle of ____________? contraction will "________" the diaphragm causing _________ changes that increase what into the lungs?
what is the diaphragm shaped like?
name 3 regions of the diaphragm?
inspiration
flatten
pressure
increase air into the lungs
parachute
sternal, costal and lumbar regions

the phrenic nerve passes over what as it goes down to the diaphragm?
notice the R and L phrenic nerve going down to attach to the diaphragm
the anterior scalene

looking inside the diaphragm what can you see in the middle? what color is it? what does it serve as?
name the 3 openings of inside the diaphragm? point them out in picture
which hole opens through the central tendon?
central tendon
white
muscles all converge here on this central circle
central tendon is the upside down C
caval foramen is the big hole...opens up through the central tendon
esophageal hiatus is the oval oblong hole in center and inferior
aortic hiatus is the hole where you can even see part of the aorta coming through...most posterior of the 3 openings
what passes through these openings in the diaphragm?
Openings:
- Caval foramen...Inferior vena cava
- Esophageal hiatus...esophagus
- Aortic hiatus...Aorta
the sternal region of the diaphragm has attachments where?
the costal part has attachments where?
the lumbar part has attachments where?

Regions:
- Sternal part...attachments “along sternum”
- Costal part...attachments “along ribs”
- Lumbar part...attachments “along quadratus lumborum and psoas”
in picture: all regions form around the central tendon...small spot above is the sternal part...two huge kidney shapes on sides of central tendon are the costal regions...and the lumbar region is the space underneath the central tendon

what is the:
costodiaphragmatic recess (CDR)...what is it a potential site for?
costomediastinal recess (CMR)
Potential pleural space located “between” the junction of diaphragm
and ribs
Potential site for pleural fluid accumulation
Potential pleural space located anteriorly “between” the junction of diaphragm and mediastimum
in picture you are looking from the top down...the CDR is wrapped around the 2 mickey mouse ears on the side where the ribs and diaphragm meet...the CMR is the small corners below the front circle on either side (slightly more yellow in color)

notice how the lung doesnt go all the way down and how there is a small corner where there can be an accumulation of fluid in the CDR
notice the cardiac notch in the CMR and how that can leave more space for the heart

the CDR is on the bottom of the lung in the kiddie-corner
the CMR is seen when you look down on the diaphragm from the top and see a small space in front
_______ thoracic spinal nerves exit the spinal IVF?
what supplies the intercostal spaces? what is the spacial relationship of these things that enter the intercostal space?
12
Anterior rami supplies the intercostal spaces
“VAN” – vein, artery, nerve bundle entering the intercostal space (from top to bottom)

what are these nerves that are going horizontal?
follow how it curves around and notice how it splits and then goes to the front and back
intercostal nerves

what is herpes zoster? another name for it?
what do you get/features?
where is it very common?
where else can you see it?
its a dormant virus in a single segmental nerve that will become active later on in life
painful, red, vesicular lesion in dermatome pattern
Shingles very common in thoracic region but is not limited to
thoracic region
will see in head/face and Lower extrems

- Blood supply to the rib cage originates from what 2 places?
- what 2 arteries supply the intercostal spaces of the rib cage
- what branch off of the subclavian artery goes down specifically to the diaphragm?
aorta and subclavian artery
Anterior and posterior intercostal arteries
notice how branches from the aorta go around and supply the rib cage
the internal thoracic artery

look at picture
study picture
Identify/describe the intercostal artery pathway?
- Intercostal arteries/veins run in the ___________ aspect of
the intercostal space?
- They are ________ to the “superior rib” of the intercostal space?
- Collateral branches of intercostal arteries/veins run in the _________ aspect of the intercostal space
superior aspect
inferior
inferior

go back and rememeber the subclavian artery and how it had the VA, the thyrocervical trun and the costocervical trunk.....one branch from the costcervical trunk that went up to the skull was the deep cervical artery....what is the branch of this trunk that goes down?
what then branches from the artery?

the supreme intercostal artery
the 1st and 2nd posterior intercostal arteries
notice the subclavian, the costcervical trunk and the deep cervical artery and the supreme intercostal artery...then notice how it splits off into 2 branches under the clavicle
the 3rd through the 11th intercostal arteries branch off from what?
notice it in the picture?

from the aorta
Posterior intercostal arteries:
- There are only 11 “posterior intercostal arteries” that supply what?
- The ________ which arises from aorta helps supply what as it runs inferior to the rib?

the 11 intercostal spaces
subcostal artery
the 12th rib
notice how in the picture you can see the subcostal artery down below the ribs as it branches from the aorta
Anterior intercostal arteries:
- These arteries branch from where?
- then this originates from where?
internal thoracic artery
- Internal thoracic artery originates from subclavian artery

the internal thoracic artery comes from the ____________ vein and then runs behind the anterior ________?
subclavian vein
anterior sternum
notice the internal thoracic artery coming down right near the sternum

The Anterior intercostal arteries supply which intercostal spaces?
- The lower intercostal spaces supplied by what?
1-9
posterior intercostal arteries
notice how the intercostal arteries run superior and inferior in the intercostal spaces
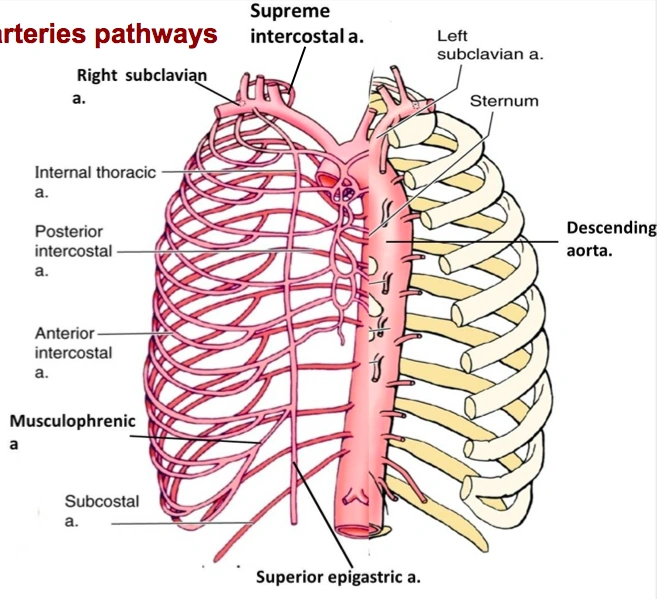
look at all the arteries and their relationship
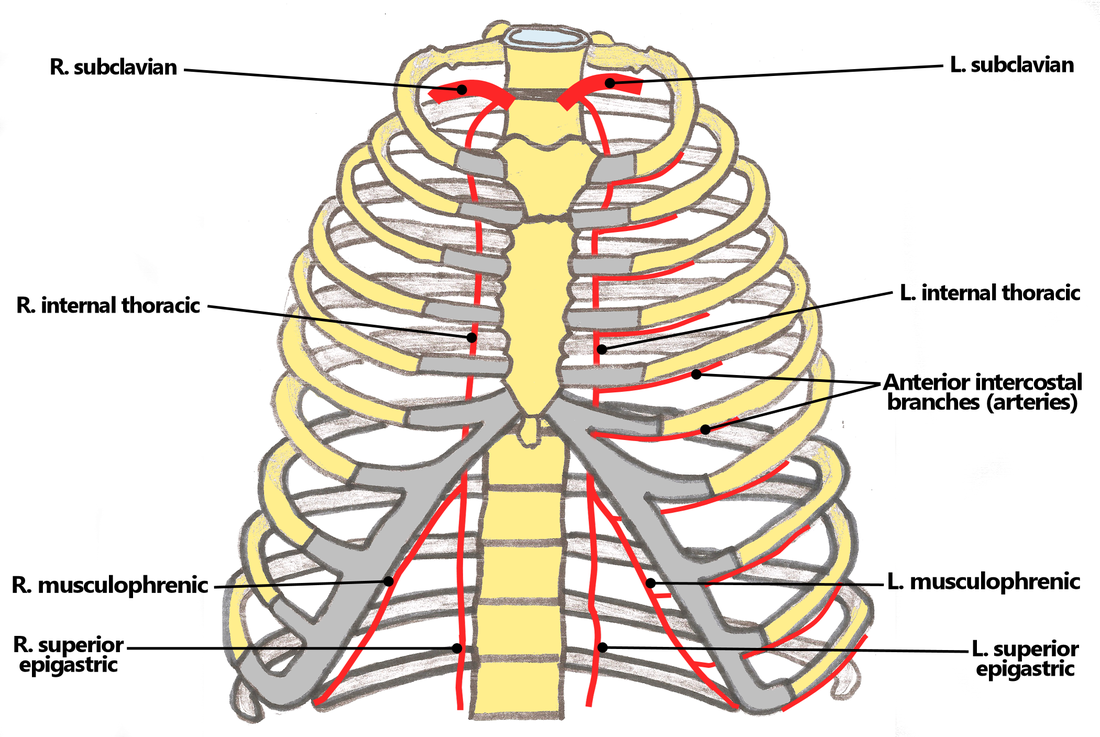
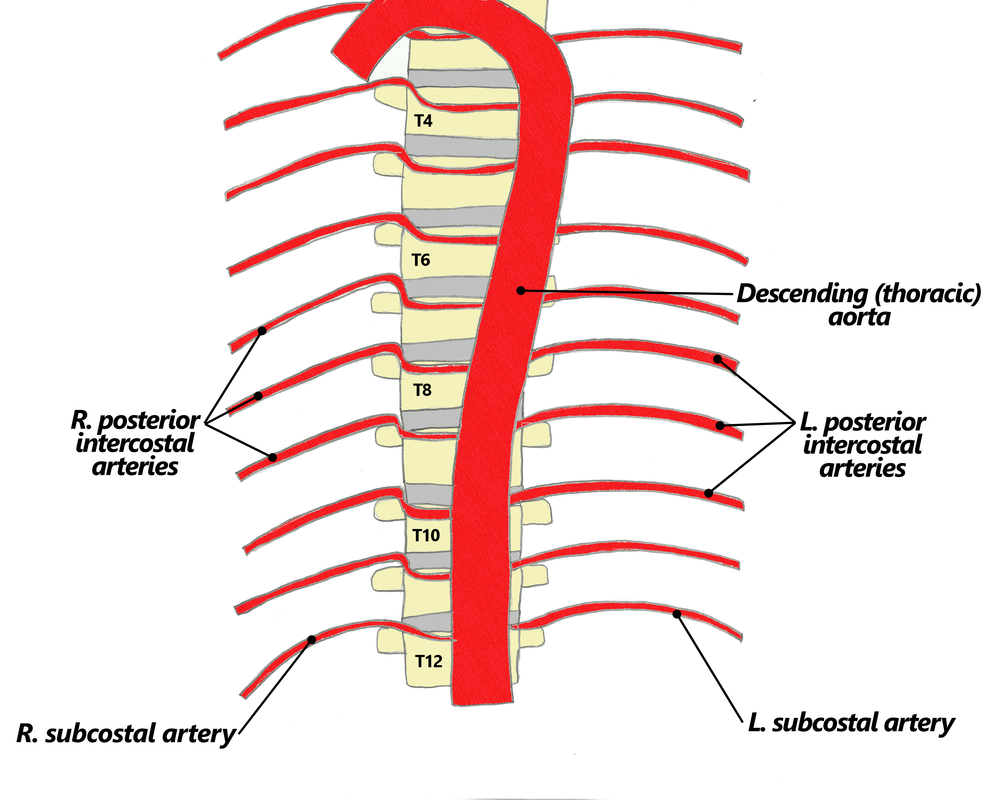
look at how the posterior intercostal arteries come from the back and wrap around the intercostal spaces from the back
look at picture
what artery may be used as a bypass graft?
the left internal thoracic artery
the intercostal spaces are drained via what?
via the intercostal veins
Intercostal veins drain __________ into azygos system and ________ into internal thoracic veins?
so overall the intercostal veins are coming back towards the center (arteries go out latterally) and go inside what?
posteriorly
anteriorly
the azygos vein

point out the azygos vein, the accesorry hemi-azygos vein and the hemi-azygos vein?
the azygos vein is on the right side under the big "faucet" going up
you can see a divit on the left side where the accessory hemi and hemi azygos travel behind and into the right side
the accessory hemi-azygos vein is the vein on the left side connecting the intercostal spaces from above the divit (on top)
the hemi-azygos vein is below the divit (on bottom)

overall, the "azygos system":
- drains what 2 things?
- consists of what 3 veins?
- “azygos system” also receives blood from where?
- this system acts as “collateral pathway” to “bypass” what?
the back & thoracoabdominal walls
azygos, hemi-azygos and accessory hemi-azygos veins
trunk and lower extremities
the IVC (inferior vena cava)

accessory hemi-azygos vein:
- receives blood from ______________ intercostal spaces
- Accessory hemi-azygos vein crosses midline and drains into where?
- NOTE: left side 1st – 4th intercostal spaces drain directly into where?
left side 5th - 8th
the azgos vein
left brachiocephalic vein
look at picture

hemi-azygos vein:
- receives blood from where?
- also receives blood from what other 2 left places?
- Hemi-azygos vein crosses midline and drains into __________?
left side 9th - 11th intercostal spaces
abdominal/pelvic trunk and lower extremity
azgos vein
look at picture

how is the lumbar veins a plan B?
they are a plan B in case there is some sort of obstruction in the inferior vena cava
(look at ascending lumbar vein in picture)
what do the right and left common illiac veins take care of?
the legs

azygos vein:
Receives blood from what 3 places?
Azygos veins continues on to drain into the ___________?
right side intercostals
hemiazygos & accessory hemiazygos veins
also receives blood from right abdominal/pelvic trunk and lower extremity
SVC (superior vena cava)
notice how it gets blood from the hemi azygos and accessory azygos and how it travels up into the SVC

describe whats in the intercostal spaces from superior to inferior?
These travel in intercostal space together just ________ to rib
- There is a second set of smaller collaterals located ________ to each rib
- Vein
- Artery
- Nerve
inferior
superior
notice in picture how the vein artery and nerve (VAN) is just below the rib and then more down in the intercostal space just above the rib are the collateral vessels

vein, artery and nerves are located just ______ each rib?
what is a thoracentesis? what do you want to avoid when you insert the needle? overall, where do you wanna put the needle?
below
- Procedure to remove fluid from pleural cavity
- Avoid damage to intercostal structures (and lung) when inserting needle
put the needle on the superior margin of the rib...avoids hitting the VAN's

the bronchial arteries come from where? what will you commonly see with these?
from the aorta
you will see them coming from variable pathways from the aorta

in this person, what bronchial arteries can you point out?
you can point out the right bronchial artery and then on the other side, the left superior bronchial artery and the left inferior bronchial artery both going to the same bronchi tube on bottom

Bronchial veins:
- Right bronchial vein drains into the _____________?
- Left bronchial vein drains into the _______________?
azygos vein
accessory azygos vein
in picture, you can see the azygos vein on the left and the small vessel (right bronchial vein) draining into the azygos
on the other side you see the small left bronchial vein draining into the accessory hemi-azygos

pulmonary circulation: how many pulmonary veins are there?
show the pulmonary trunk, 2 pulmonary arteries and 4 pulmonary veins in the picture?
4....2 on the right and 2 on the left
big blue tube in middle is the pulmonary trunk...two blue pathways going in either direction from this are your right and left pulmonary arteries...then you can see the 4 little red vessels coming in from the sides going back to the heart (pulmonary veins)
briefly summarize the pulmonary circulation
- Deoxygenated blood from your body enters the right atrium of your heart through the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava.
- From the right atrium, the deoxygenated blood drains into the right ventricle
- The right ventricle then contracts, forcing the deoxygenated blood through the pulmonary semilunar valve up top and into the pulmonary artery
- The pulmonary artery carries the blood that’s very low in oxygen to the lungs, where it becomes oxygenated.
- Freshly oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart via the pulmonary veins...then goes into left ventricle to them get pumped to the peripheries

notice the hilum of the lungs and the pulmonary trunk and the superior and inferior vena cava and the aortic arch
look at picture