Anatomy Block III- Gluteal Region, Thigh, Lumbosacral Plexus
os coxae
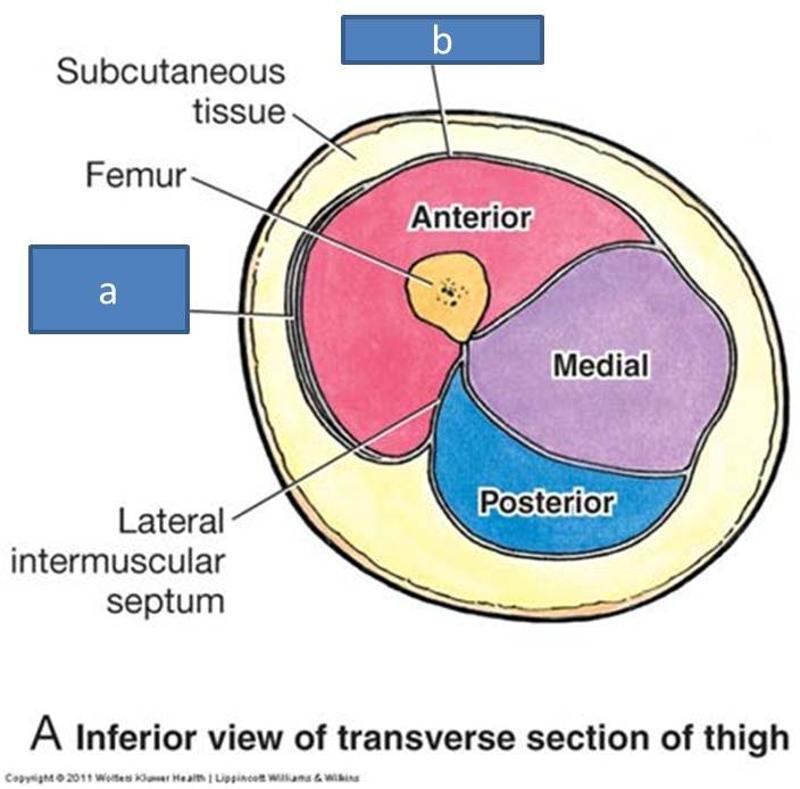
femur
patella
tibia
fibula
what makes up the bony structure of the lower limb
a. os coxae
b. femur
c. patella
d. fibula
e. tibia

a. iliac crestes
b. anterior superior iliac spine
c. greater trochanter
d. ischial tuberosity
e. pubic crest and symphysis
f. posterior superior iliac spine

a. iliac crest
b. iliotibial tract
c. tensor fasciae latae
d. gluteus maximus
e. ischial tuberosity
f. iliotibial tract

a. gluteus medius
b. gluteus maximus
c. iliotibial tract

a. gluteus medius
b. piriformis
c. superior gemellus
d. tendon of obturator internus
e. inferior gemellus
f. quadratus femoris

a. gluteus minimus
b. piriformis
c. superior gemellus
d. inferior gemellus
e. obturator internus

a. piriformis muscle
b. sciatic nerve
c. inferior gemellus muscle
d. quadratus femoris muscle
e. gluteus medius

tensor fascia lata

a. tensor fascia latae
b. gluteus minimus
c. gluteus medius
d. quadratus femoris
e. gluteus maximus
f. piriformis
g. superior and inferior gemelli
h. obturator internus
i. obturator externus

quadratus femoris
gluteus maximus
piriformis
superior and inferior gemelli
obturator internus
obturator externus
(sartorius)
what contributes to lateral rotation of the thigh
gluteus medius
gluteus minimus
tensor fasciae latae
(pectineus)
what contributes to medial rotation of the thigh
a. inferior gluteal nerve and vessels
b. supeiror gluteal nerve and vessels
c. sciatic nerve

Trendelenberg Test

paralysis of the gluteus minimus and medius
what does the Trendelenberg Test try to show
hip falls to the opposite side of paralysis
what will the trendelenberg test show
extends the thigh and does lateral/external thigh rotation
what is the action of the gluteus maximus
inferior gluteal nerve L5-S2
what innervates the gluteus maximus
off posterior superior iliac spine and down near sacrum, runs over and blends with iliotibial tract
where does the gluteus maximus run
abducts and medially rotates thigh (when hip flexed)
what is the action of the gluteus medius and minimus
superior gluteal nerve L4-S1
what innervates the gluteus medius and minimus
directly underneath gluteus maximus but pokes out top, under gluteus minimus
where is the gluteus medius? minimus?
from posterior os coxae to femur
where does the gluteus medius run
triangular shaped
what is the shape of the piriformis
lateral thigh rotation
what action does the piriformis do
anterior rami S1-S2
what innervates the piriformis
lateral rotators of thigh
what are the roles of the superior gemellus and obturator internus
nerve to obturator internus L5-S1
what innervates the superior gemellus and obturator internus
lateral rotators of thigh
what are the roles of the inferior gemellus and quadratus femoris
nerve to quadratus femoris L5-S1
what innervates the inferior gemellus and quadratus femoris
anterior muscle on front of hip joint, tenses in IT band/tract
where is the tensor fascia latae and what does it tense on
deep CT around most of thigh muscles
what is the fascia latae
can be at hip or condyle of femur as it crosses knee
how to tight IT band symptoms manifest themselves
superior and inferior gluteal arteries
what supplies the blood to the gluteal region
upper lateral quadrant of buttock to avoid sup/inf gluteal nerves and sciatic nerves
where should you do a gluteal intramuscular injection
a. iliotibial tract
b. fascia lata
fascia latae and iliotibial tract/band
what deep fascia surrounds the thigh
anterior, medial, posterior
what compartments are formed by intermuscular septa
muscle action
innervation
blood supply
what do muscles in the same compartment normally share
flex thigh at hip, extend leg at knee
what is the shared action of the muscles in the anterior compartment of the thigh
femoral nerve L2-L4
what is the innervation of the anterior thigh compartment
iliopsoas
what is the major hip flexor muscle
femoral nerve L2-L3
what innervates the iliacus
L1-L3 lumbar nerves
what innervates the psoas major
rectus femoris
which of the quadriceps femoris muscles crosses the hip and can cause hip flexion
femoral nerve
what innervates the quadriceps femoris
iliopsoas
quadriceps femoris
sartorius
(pectineus)
what are the muscles in the anterior compartment of the thigh
iliacus
psoas major
what muscles make up the iliopsoas
rectus femoris
vastus medialis
vastus lateralis
vastus intermedius
what muscles make up the quadriceps femoris
onto quadriceps tendon, which inserts on patella and then patella inserts onto tibia via patellar ligament
where do the four muscles of the quadriceps femoris insert
a. psoas major
b. iliacus
c. sartorius
d. rectus femoris
e. vastus lateralis
f. vastus medialis
g. pectineus

originates at anterior superior iliac spine, crosses anterior portion of the thigh and knee, inserts at media side of tibia
what is the path of the sartorius
flexes thigh and knee and laterally rotates leg (due to crossing orientation)
what is the role of the sartorius
because it is innervated by the femoral nerve
why is the pectineus included in the anterior compartment muscles even though it is an ADDUCTOR and should be in the medial compartment functionally?
adduction of the leg
weak thigh flexor
medial rotator
what is the action of the pectineus
femoral artery
what is the blood supply of the anterior compartment of the thigh
a. vastus intermedius
b. femoral nerve and vessels
c. sartorius
d. vastus medialis
e. rectus femoris
f. vastus lateralis

a. adductor longus
b. gracilis

adduction of the thigh
what is the function of the medial compartment of the thigh
gracilis
adductor longus
adductor brevis
adductor magnus
obturator externus
what muscles make up the medial compartment of the thigh
from pubic region of os coxae and inserts to tibia to the same region as sartorius
what is the path of gracilis
adduction of leg
flexes thigh and knee
what is the action of the gracilis
obturator nerve L2-L4
what innervates the gracilis
obturator nerve
what innervates the adductor longus
obturator nerve
what innervates the adductor brevis
lateral rotation of the thigh, not much adduction
what does the obturator externus do
obturator nerve L2-L3
what innervates the obturator externus
adduct the thigh
what do the adductor brevis and longus do
adductor portion and hamstring portion
what are the two portions of the adductor magnus
adduction and flex thigh
what are the funcitons of the adductor portion of the adductor magnus
obturator nerve L2-L4
what innervates the adductor portion of the adductor magnus
tibial nerve or sciatic before tibial branches off, from L4
what innervates the hamstring portion of the adductor magnus
obturator artery
what gives blood supply to the medial leg
deep femoral artery
what artery gives off branches to the posterior compartment but runs in the medial compartment
pectineus (femoral)
hamstring portion of adductor magnus (tibial)
which adductors doesnt the obturator innervate
extend hip
what is the function of the hamstring portion of the adductor magnus
a. adductor longus
b. adductor magnus

a. obturator externus
b. adductor brevis
c. adductor longus
d. adductor magnus

to the adductor tubercle
where does the hamstring portion of the adductor magnus attach?
a. adductor tubercle, where hamstring attaches

a. deep femoral vessels
b. adductor magnus
c. adductor brevis
d. gracilis
e. adductor longus

obturator nerve

a. semitendinosus
b. biceps femoris
c. semimembranosus

extend thigh and flex leg
what is the functino of the posterior compartment of the thigh
semitendinosus
semimembranousus
biceps femoris
what are the components of the hamstrings muscles
medial side on top of semimembranosus but thickens near popliteal fossa
where is the semitendinosus muscle
medial side under semitendinosus, flatter and more membranous
where is the semimembranosus muscle
thigh extension and knee flexion
what are the actions of the semitendinosus
thigh extension and knee flexion
what are the actions of the semimembranosus
thigh extension and knee flexion
what are the actions of the biceps femoris
tibial nerve
what innervates semitendinosus
tibial nerve
what innervates semimembranosus
long head: tibial division of sciatic nerve L5-S2
short head: common fibular division of sciatic nerve
what innervates the biceps femoris
sciatic nerve
what nerve is present in the posterior compartment of the thigh
perforating branches of the deep femoral artery
what gives blood to the posterior compartment
tibial division
common fibular division
what are the parts of the sciatic nerve
a. piriformis
b. common fibular nerve
c. common fibular nerve
d. tibial nerve

a. iliotibial band/tract
b. biceps femoris: short head
c. biceps femoris: long head
d. semitendinosus
e. semimebranosus
f. sciatic nerve

a. inguinal ligament
b. adductor longus
c. apex of femoral triangle
d. sartorius

great saphenous vein
what passes through the saphenous opening
small intestine
what often protrudes through the femoral canal in a femoral hernia
can interfere with venous drainage, usually doesnt fix itself
how can the femoral hernia affect the body
triangular space containing femoral vessels and nerve
what is the femoral triangle and canal
inguinal ligament
what is the base of the femoral triangle
sartorius
what is the lateral border of the femoral triangle
adductor longus
what is the medial border of the femoral triangle
adductor longus and sartorius
what forms the apex of the femoral triangle
all but the femoral nerve
what does the femoral sheath cover
herniation through the femoral canal
what is a femoral hernia
women
is femoral herniation more common in women or men
what is the difference between hiatal and inguinal hernias
iliohypogastric nerve
ilioinguinal nerve
lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
femoral nerve
obturator nerve
lumbosacral trunk
what nerves make up the lumbar plexus
superior gluteal nerve
inferior gluteal nerve
nerve to piriformis
sciatic nerve (common fibular division and tibial division)
posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
pudendal nerve
what nerves make up the sacral plexus
posterior division of anterior ramus
what kind of innervation supplies the leg extensors?
posterior division of anterior ramus
what kind of innervation supplies the thigh abductors
anterior division of anterior ramus
what kind of innervation supplies the leg flexors
anterior division of anterior ramus
what kind of innervation supplies the thigh adductors
a. femoral nerve
b. lateral femoral sheath
c. intermediate femoral sheath
d. medial/canal femoral sheath

femoral hernia

a. femoral nerve
b. obturator nerve
c. lumbosacral trunk

a. superior gluteal nerve
b. inferior gluteal nerve
c. sciatic nerve, top part common fibular division and bottom part tibial division

a. dorsal ramus
b. posterior division of anterior ramus
- supplies dorsal mass muscles (leg extensors, thigh abductors)
d. anterior division of anterior ramus
- supplies ventral mass muscles (leg flexors, thigh adductors)
e. ventral ramus
f. ventral root
g. spinal nerve
h. dorsal root

lumbosacral plexus
what provides autonomics to the lower extremities
sympathetics only= vasomotor to blood vessels and stimulation of arrector pili and sweat glands in the skin
what type of general nervous function does the lumbosacral plexus provide
posterior divisions L2-L4
what levels does the femoral nerve originate from
anterior thigh
what region does the femoral nerve innervate
anterior divisions L2-L4
what levels does the obturator nerve originate from
medial thigh
what region does the obturator nerve innervate
superior and inferior gluteal nerves
which sacral plexus nerves form the posterior divisions of the anterior rami
L4-S3
what levels does the sciatic nerve originate from
posterior thigh, anterior division
what does the tibial division of the sciatic nerve innervate? which division of the anterior ramus is it from
mostly to lower leg and foot, posterior division
what does the common fibular division of the sciatic nerve innervate? which division of the anterior ramus is it from
a. ventral rami
b. ventral rami
c. ventral rami
d. dorsal rami

posterior rami for upper inner quadrant, ventral rami for the rest
what contributes to the cutaneous innervations of the gluteal region
a. lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
b. cutaneous branches of femoral nerve
c. cutaneous branches of obturator nerve
d. genitofemoral nerve

genitofemoral nerve
cutaneous branches of obturator nerve
cutaneous branches of femoral nerve
lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
what nerves innervate the anterior thigh cutaneously
cutaneous region of the upper anterior part of the thigh
what does the genitofemoral nerve innervate cutaneously
upper medial part of the anteiror cutaneous region of the thigh
what do the cutaneous branches of the obturator nerve innervate cutaneously
anterior and lower medial cutaneous region of the thigh
what do the cutaneous branches of the femoral nerve innervate cutaneously
upper lateral region cutaneous region of the thigh
what does the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve innervate cutaneously
posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
cutaneous branches of obturator nerve
lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
what nerves innervate the posterior thigh cutaneously
a. cutaneous branches of obturator nerve
b. posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
c. lateral femoral cutaneous nerve

posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
what is the main innervation of the posterior thigh?