Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chemistry comes alive Study guide
front 1 An organic compound is analyzed, and it has twice as many hydrogen atoms as oxygen atoms. This compound is most likely molecule with the formula C5H10O5 is a(n) | back 1 Carbohydrates have CHO with a 1:2:1 ratio CARBOHYDRATE |
front 2 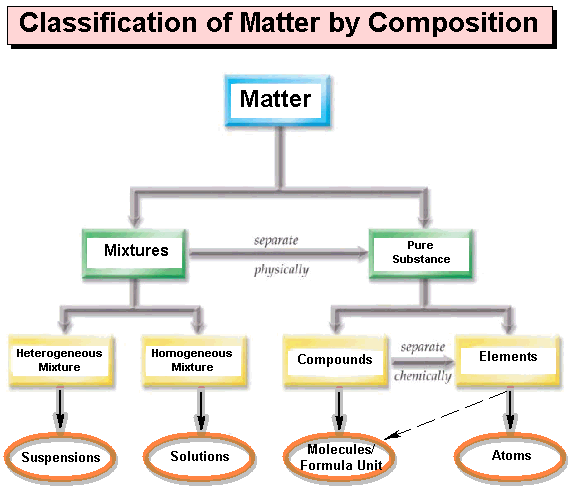
| back 2 
|
front 3 are not involved directly in the linkage between amino acids. | back 3 Removal of a water molecule between each two units |
front 4 Carbohydrates and proteins are built up from their basic building blocks by the | back 4 R groups of amino acids |
front 5  Organic molecules contain particular elements. Based on what you know of organic chemistry, find the mismatched pair. | back 5 a. carbohydrate - CHO b. lipid - CHNOP c. protein - CHNOPS d. nucleic acid - CHNOP |
front 6 that dominate the structure of triglycerides are the basis for the efficient and compact energy storage by fat. | back 6 hydrocarbon groups |
front 7 The single most abundant protein in the body is | back 7 collagen |
front 8 An electron is a(n) | back 8 negatively charged subatomic particle |
front 9 The function of microRNA (miRNA) is to | back 9 T urn some genes on and others off, thus controlling genetic expression |
front 10 Simple sugars are also known as... | back 10 monosaccharides |
front 11 which ranges from 0 to 14, is a logarithmic scale based on the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. | back 11 pH scale |
front 12  Organic chemistry is the chemistry of a. | back 12  carbon compounds |
front 13 The sequence of amino acids in a protein constitutes the __________ structure of the protein. | back 13 Primary |
front 14 Atomic number is determined by the number of ___ in each atom. | back 14 protons only |
front 15 DNA and RNA are nucleic acids | back 15 they are built from nucleotides |
front 16 An atom or a group of atoms possessing a positive or negative electrical charge is called? | back 16 ION |
front 17 Prostaglandins are | back 17 type of eicosanoids, which are diverse lipids found in the cell membrane. |
front 18 are linked by peptide bonds to form polypeptides. | back 18 Amino acids |
front 19 
| back 19 
|
front 20
The space between the pleurae of the lungs that
extends from the sternum to the
vertebral column is | back 20 mediastinum |
front 21 A pentose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base are found in a(n) | back 21 NUCLEOTIDE |
front 22 All isotopes of a particular element possess | back 22  the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons |
front 23  Which of the following is a condensation (dehydration synthesis) reaction? | back 23  the breakdown of a polymer into monomers |
front 24 Which of the following types of energy moves in waves? | back 24 Radiant energy moves in waves |
front 25 Aerobic cellular respiration occurs in the | back 25 RIBOSOMES |
front 26  Which protein types are vitally important to cell function in all types of stressful circumstances? | back 26 molecular chaperones |
front 27
| back 27
|
front 28 Detoxification of certain potentially poisonous molecules occurs in the | back 28 peroxisomes |
front 29  This organelle is the command and control center of the cell | back 29 nucleus |
front 30
| back 30
|
front 31 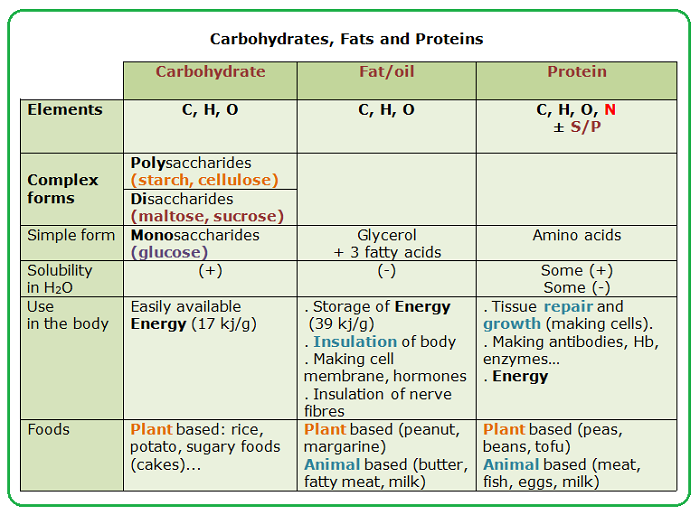
| back 31 
|
front 32 The difference between a colloid and a suspension is | back 32 colloid can undergo sol-gel transformation, whereas a suspension cannot. |
front 33
| back 33
|
front 34 Identify the mismatched pair | back 34 a. ribosome synthesis – nucleolus b. rough endoplasmic reticulum – attached ribosomes c. Golgi apparatus – lytic enzymes d. cytoskeleton – microtubules |
front 35  Proteins that are secreted outside the cell in the process of exocytosis are released by | back 35  secretory vesicles |
front 36 Cilia and flagella are specialized structures used | back 36 for locomotion |
front 37
| back 37
|
front 38 Why are ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)? | back 38 Newly synthesized polypeptides can move directly through the ER membrane. |
front 39 Which of the following is an example of a suspension? | back 39 BLOOD |
front 40 Enzymes are important as | back 40 catalysts for chemical reactions |
front 41 What is activation energy? | back 41 the energy required to start a chemical reaction |
front 42 Enzymes? | back 42 lower activation energy requirement |
front 43 The reactants in an enzyme catalyzed reaction are called? | back 43 substrates |
front 44  The information about the synthesis of enzymes comes from | back 44 DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) |
front 45 Lungs, heart, or brain are examples of | back 45 organs |
front 46 Circulatory, respiratory, or digestive are examples of | back 46 systems |
front 47  Diffusion is the process by which a substances moves from an area of | back 47 higher concentration to an area of lower concentration |
front 48 A diffusion equilibrium is reached when | back 48 there is no net movement between two areas |
front 49 Osmosis is a special case of | back 49 diffusion that involves the movement of water across a membrane |
front 50 The net movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane is always | back 50 from the hypotonic solution to the hypertonic one |
front 51  The direction of osmosis is determined by the | back 51 concentration of dissolved solutes on both sides of the membrane. |
front 52 is the process by which the undigested contents of food vacuoles are removed from the cell. | back 52 Exocytosis |
front 53 A cell placed in a beaker of sea water will | back 53 shrink due to the loss of water by osmosis |
front 54 When a neuron is stimulated and Na+ ions move through an open Na+ channel, the process is | back 54 facilitated diffusion |
front 55 A hypothetical “microbullet” shot through a phospholipid bilayer would pass the components in which order? | back 55 a. polar >>> nonpolar>>>polar>>>nonpolar b. polar>>>polar>>>nonpolar>>>nonpolar c. nonpolar>>>polar>>>polar>>>nonpolar d. polar>>>nonpolar>>>nonpolar>>>polar |
front 56 Identify the mismatched pair: | back 56 a. hydrophilic – polar molecules b. hydrogen ion – proton c. acid solution – pH more than 7 d. water – universal solvent |
front 57 Which of the following statements is true about a solution with a pH of 9, one with a pH of 2 and one with a pH of 7? | back 57 The pH 2 solution has a higher hydrogen (H+) ion concentration than the pH 7 solution. |
front 58  The relationship between mass and volume could best be described as | back 58  Increasing volume results in an increase of mass |
front 59 An atom whose atomic number is 10 has how many electrons in its outermost energy level? | back 59 8 |
front 60 Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in their | back 60 Number of Neutrons |
front 61  Which of the following are found in the nucleus of an atom? | back 61  Protons & Neutrons |
front 62  An element with 22 protons, 22 neutrons, and 22 electrons would have an atomic number of | back 62  22 |
front 63  Which of the following results from the making of a bond? | back 63 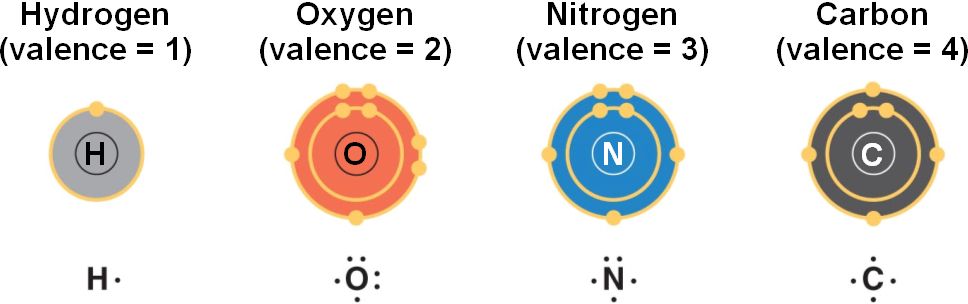 Atoms become more stable |
front 64 For an atom to be considered an ion | back 64 Protons can outnumber electrons |
front 65  An atom becomes an ion when | back 65  It gains or loses electrons |
front 66 Hydrogen bonds are very important in the functional shape of | back 66 Proteins & Nucleic acids |
front 67  The symbol 3CO2 represents | back 67  3 molecules of carbon dioxide |
front 68  In a bottle of water, hydrogen bonding occurs between the hydrogen of 1 atom and | back 68 An oxygen atom in a different molecule |
front 69 Which of the following is not a compound? | back 69 Sodium |
front 70 Atoms form bonds to | back 70 Fill their outer shells with electrons |
front 71 Water is a polar molecule because | back 71 Oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen |
front 72 Potassium has one electron in its fourth shell, and chloride has seven electrons in its third shell. Which of the following is most likely to be true? | back 72 Potassium will give an electron to chloride to form an ionic bond |
front 73 You mix sugar in water and stir until it’s completely dissolved. In this system, the water is the ______, the sugar is the______ and the end result is a _______. | back 73 Solvent; solute; solution |
front 74  Each element has a unique_________, which refers to the number of protons present in its atoms. | back 74  Atomic number |
front 75 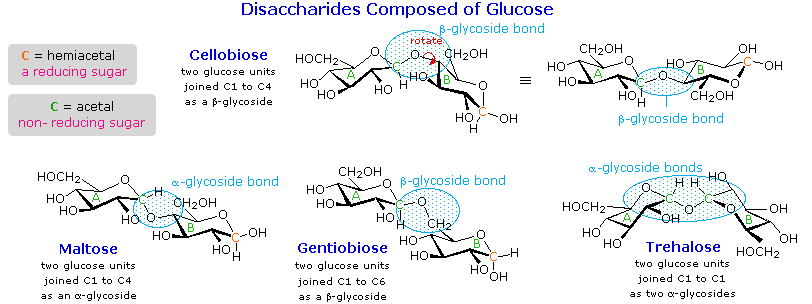 A molecule is ________. | back 75  A bonding together of two or more atoms |
front 76 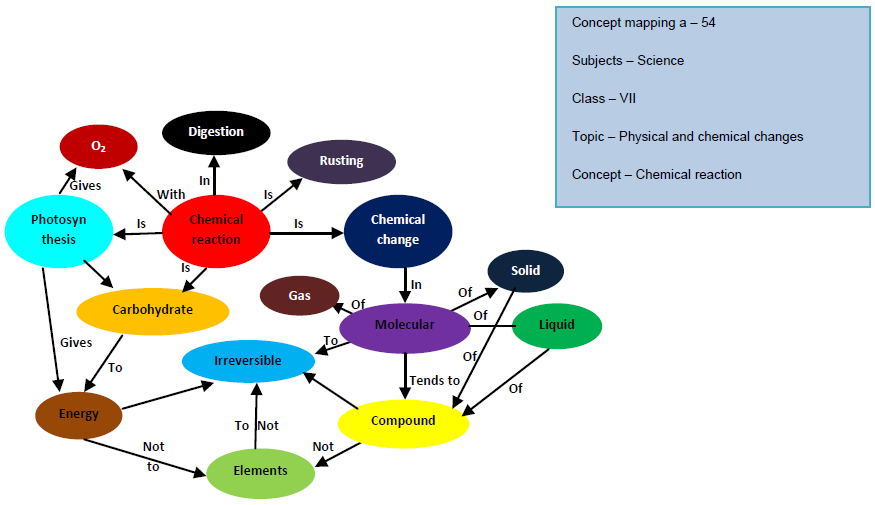 If lithium has an atomic number of 3, and an atomic mass of 7, it has________ neutron(s) in its nucleus. | back 76  4 |
front 77 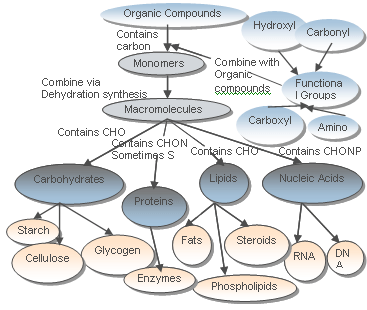 Substances that are nonpolar and repelled by water are ________. | back 77  Hydrophobic |
front 78 A hydrogen bond is _________. | back 78 Formed when an electronegative atom of a molecule weakly interacts with a hydrogen atom that is already participating in a polar covalent bond |
front 79  An ionic bond is one in which ________. | back 79  Two charged atoms have a mutual attraction due to electron transfer or donation |
front 80 A covalent is one in which? | back 80 Two charged atoms have a mutual attraction due to electron transfer |
front 81 Lipids ______. | back 81 Include triglycerides that serve as energy sources |
front 82 is energy directly involved in moving matter. | back 82 Mechanical energy |
front 83 DNA _______. | back 83 Contains protein-building instructions |
front 84 The building blocks of RNA and DNA are | back 84 nucleotides |
front 85  A nonpolar covalent bond implies that ________. | back 85  There is no difference in charge at the ends (the two poles) of the bond |
front 86 A solution with a pH of 11 is ______ times as basic as one with. | back 86 1,000 |
front 87 Carbon is part of so many different substances because _______ | back 87 A carbon atom generally forms four covalent bonds with a variety of atoms |
front 88 A solution with a pH of 4 has_________. | back 88 More H+ ions than OH- ions |
front 89 Hydrolysis could be correctly described as the ________ | back 89 Breaking of a long-chain compound into its subunits by adding water molecules to its structure between the subunits Process of condensation in reverse. |
front 90  Genetic instructions are encoded in the base sequence of________; molecules of _________ function in processes using genetic instructions to construct proteins | back 90  DNA;RNA |
front 91 Membranes consist of ___________. | back 91 a. A phospholipid bilayer b. proteins c. glycolipids and glycoproteins d. cholesterol e. all of the above are correct |
front 92 The nucleolus is the site where | back 92 The protein and RNA subunits of ribosomes are assembled |
front 93 Which of the following forms of energy travels in varying wavelengths, such as visible light, infrared waves, radio waves, ultraviolet waves, and X-rays? | back 93 electromagnetic energy |
front 94
| back 94
|
front 95 The _________ is free of ribosomes and curves through the cytoplasm like connecting pipes; the main site of lipid synthesis. | back 95 Smooth ER |
front 96 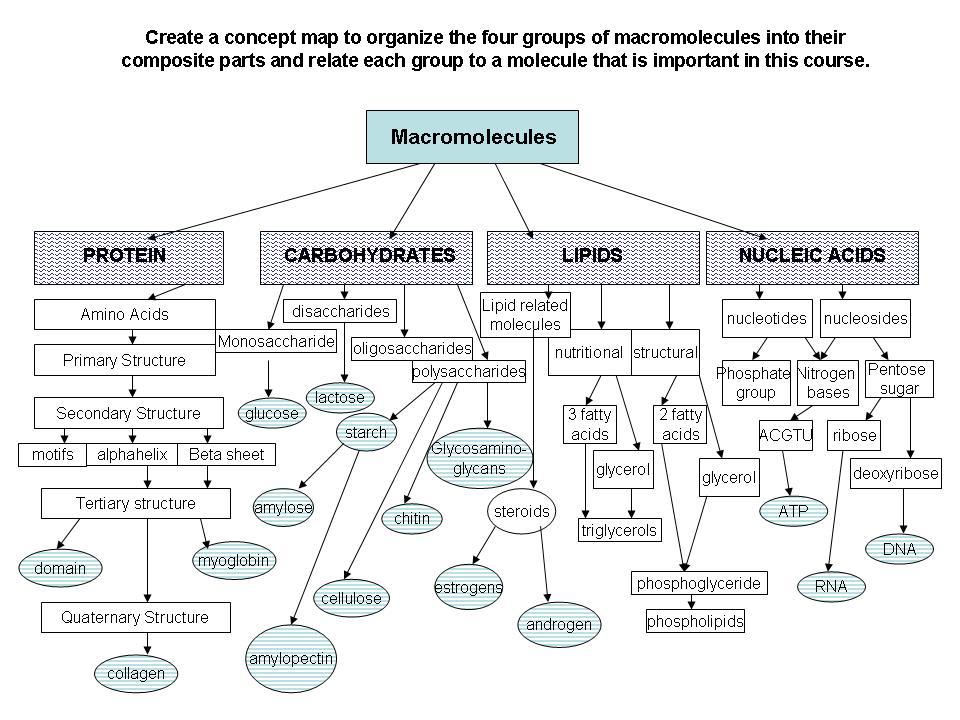 Mitochondria convert energy stored in ______ to forms that the cell can use, principally ATP. | back 96 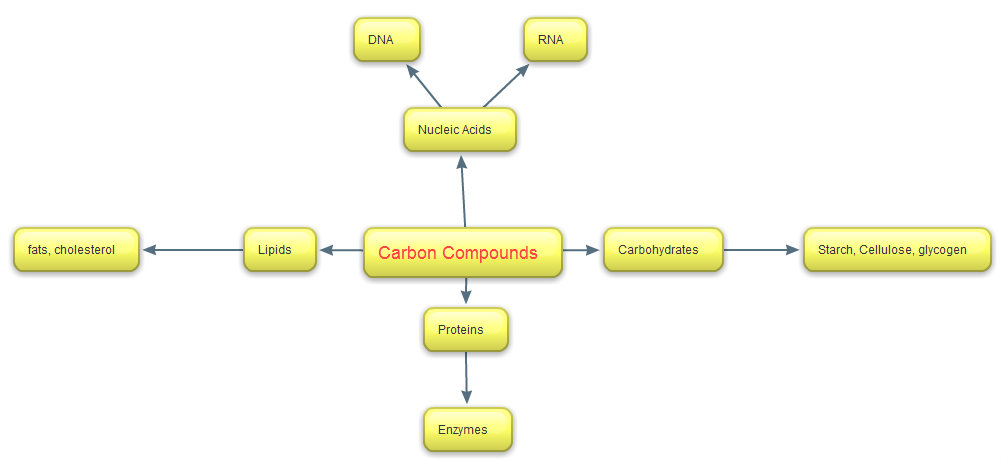 Carbon compounds |
front 97 ______are sacs of enzymes. They digest or break down worn out organelles so that the material can be recycled and reused by the cell. | back 97 Lysosomes |
front 98 Two classes of cytoskeletal elements underlie nearly all movements of eukaryotic cells; they are __________ | back 98 Microtubules and microfilaments |
front 99  White blood cells use________ to devour disease agents invading your body. | back 99  Phagocytosis |
front 100  In a lipid bilayer, tails point inward and form a(n) _______ region that excludes water. | back 100 Hydrophobic |
front 101 Which of the following is not a form of active transport? | back 101 Bulk flow |
front 102 Which of the following is not a form of passive transport? | back 102 Exocytosis |
front 103 O2, CO2, H2O, and other small, electrically neutral molecules move across the cell membrane by________. | back 103 Passive transport |
front 104 Ions such as H+, Na+, K+, and Ca++ move across cell membranes against its concentration gradient by_________. | back 104 Active transport |
front 105 An enzyme is best described as _________. | back 105 Protein & Fat |
front 106 Which is not true of enzyme behavior? | back 106 An individual enzyme can catalyze a wide variety of different reactions |
front 107
| back 107
|
front 108 As to major function, NAD+, FAD, and NADP+ are classified as _________. | back 108 cofactors that function as coenzymes |
front 109 When a phosphate bond is linked to ADP it then makes ATP, this bond __________. | back 109 releases a large amount of usable energy when the phosphate group is split off during hydrolysis |
front 110 Glycolysis would quickly halt if the process ran out of _________, which serves as the hydrogen and electron acceptor. | back 110 NAD+ Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
front 111 The ultimate electron acceptor in aerobic respiration is _________. | back 111 Oxygen (O2) |
front 112 When glucose is used as an energy source, the largest amount of ATP is generated by the ________ portion of the entire respiratory process. | back 112 electron transport chain |
front 113  What is the name of the process by which reduced NADH transfers electrons along a chain of acceptors to oxygen so as to form water and in which the energy released along the way is used to generate ATP? | back 113  the electron transport chain |
front 114  Pyruvic acid can be regarded as the end product of _________. | back 114  glycolysis |
front 115 ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) production by chemiosmosis involves __________. | back 115 a. H+ concentration and electric gradients across a membrane b. ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) synthesis c. formation of ATP in the inner mitochondrial compartment d. all of the above |
front 116 During the fermentation pathways, a net yield of two ATP is produced from __________; the NAD+ necessary for _________ is regenerated during the fermentation reactions. | back 116 glycolysis; glycolysis |
front 117 The replication of DNA occurs | back 117 between the growth phase of interphase |
front 118  is o carry out the genetic instruction (provided by DNA) for protein synthesis | back 118 major function of RNA |
front 119 Diploid refers to ______. | back 119 having two chromosomes of each type in somatic cells |
front 120 Somatic cells are __________ cells; germ cells are _________ cells. | back 120 BODY; MEIOTIC |
front 121 If a parent cell has sixteen chromosomes and undergoes mitosis, the resulting cells will have__________ chromosomes. | back 121 c. sixteen |
front 122 The correct order of the stages of mitosis is. | back 122 prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase |
front 123 The nuclear envelope breaks completely into numerous tine, flattened vesicles. Now the chromosomes are free to interact with microtubules that are extending toward them, from the poles of the forming spindle.” These sentences describe the __________ of mitosis. | back 123 prophase |
front 124 During ______, sisters chromatids of each chromosome are separated from each other, and those former partners, now chromosomes move to opposite poles. | back 124 anaphase |
front 125 In the process of cytokinesis, cleavage furrows are associated with _______ cell division, and cell plate formation is associated with ______ cell division. | back 125 animal; plant |
front 126 Each DNA strand has a backbone that consists of alternating ________. | back 126 sugar and phosphate molecules |
front 127 In DNA, complementary base-pairing occurs between. | back 127 adenine and thymine |
front 128  The chemical symbol O:O means. | back 128 the atoms are double bonded |
front 129 Adenine and guanine are _________. | back 129 double-ringed pyrimidines |
front 130
| back 130
|
front 131  Transcription _________. | back 131  occurs during the synthesis of any type of RNA by use of a DNA template |
front 132 ________ carry(ies) amino acids to ribosomes, where amino acids are linked into the primary structure of a polypeptide. | back 132 tRNA Transfer ribonucleic acid |
front 133 
| back 133
|
front 134 Transfer RNA differs from other types of RNA because it ___. | back 134 carries an amino acid at one end |
front 135
| back 135 
|
front 136  ______ and ______ are found in RNA but not in DNA. | back 136 Uracil; ribose |
front 137  You notice that you cannot read your book through a test tube of patient fluid held against the print, making it so blurred as to be unreadable. There is no precipitant in the bottom of the beaker, though it has been sitting for several days in a rack. What type of liquid is this? | back 137  colloid |
front 138 are built from nucleotide building blocks. | back 138 Nucleic acids |
front 139 are two of the three major types of lipids. | back 139 Triglycerides and phospholipids |
front 140 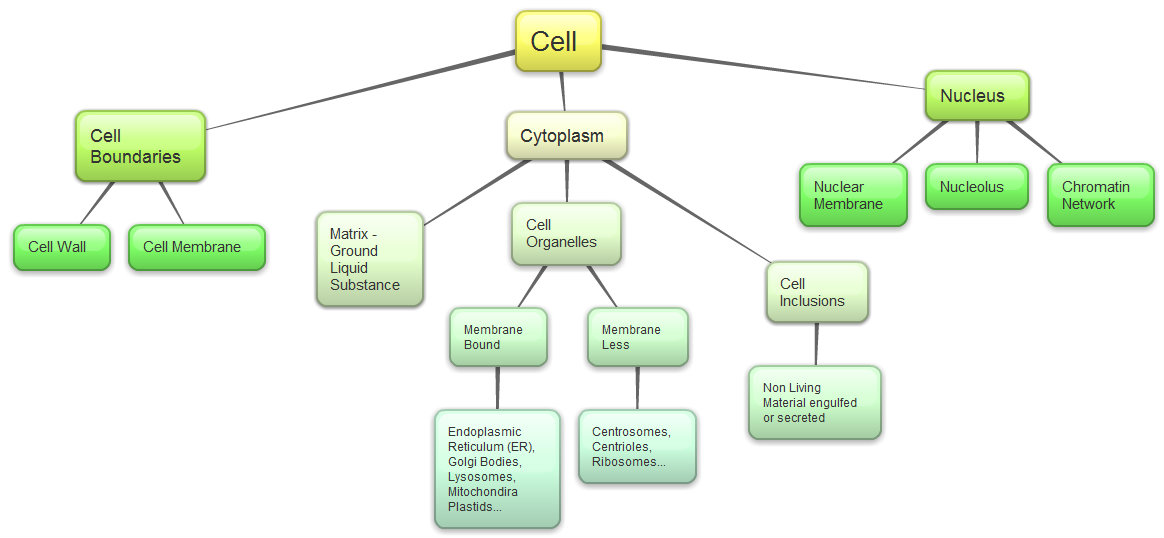
| back 140 
|
front 141 
| back 141 
|
front 142  Which of the following is not true of proteins? | back 142  Their function depends on their three-dimensional shape. They appear to be the molecular carriers of coded hereditary information. They have both functional and structural roles in the body.. They may be denatured or coagulated by heat or acidity. |
front 143 
| back 143 
|
front 144 contains a carboxyl group (-COOH), which may ionize to form an acidic solution. | back 144 R group of amino acid |
front 145
| back 145
|
front 146
| back 146
|
front 147
| back 147
|
front 148 Which of the following is the primary energy-transferring molecule in cells? | back 148 ATP |
front 149 are necessary for salivary amylase to hydrolyze starch to glucose in your mouth. Thus, water acts as an important reactant. | back 149 water molecules |
front 150
| back 150
|
front 151 Carbohydrates and proteins are built up from their basic building blocks by the | back 151 removal of a water molecule between each two units |
front 152 What level of protein synthesis is represented by the coiling of the protein chain backbone into an alpha helix | back 152 secondary structure |
front 153 In plasma, a typical body fluid, protein floating around would be considered to be which of the following? | back 153 a solute, specifically both a colloid and an electrolyte.Colloids are large particles dispersed in body fluids. Since most proteins have a negative charge, they are also considered to be electrolytes. |
front 154 Cortisol is a type of lipid hormone. Which type of lipid would cortisol be classified as? | back 154 cortisol is a steroid hormone synthesized from cholesterol. |
front 155 Electrolytes are charged particles called ions that are dissolved in body fluids. Which of the following ions would be considered a major anion in the body? | back 155 chloride is a major extracellular anion (negative ion). |
front 156 Cell junctions that promote the coordinated activity of cells by physically binding them together into a cell community include all of the following except? | back 156 peroxisomes |
front 157 Which statement about enzymes is false? | back 157 Enzymes raise the activation energy needed to start a reaction. |
front 158 which are capable of conducting an electrical current? | back 158 ions, which are capable of conducting an electrical current. |
front 159 is a reactant in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. | back 159 substrate |
front 160 Which of the following does NOT represent an accurate hierarchy in the natural combination of matter? | back 160 When two or more similar kinds of atoms bind, they form an isotope. |
front 161 In order for the DNA molecule to get "short and fat" to become a chromosome, it must first wrap around small molecules called | back 161 histones |
front 162
. | back 162
|
front 163
| back 163
|
front 164 Which of the following is true regarding the generation of a membrane potential? | back 164 Both potassium and sodium ions can "leak" through the cell membrane due to diffusion |
front 165 Transcytosis is? | back 165 transporting an endosome from one side of a cell to the other and releasing the contents by exocytosis |
front 166
| back 166
|
front 167
| back 167
|
front 168
| back 168 
|