Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Ch. 9 & 11 Art Questions (A&P)
front 1 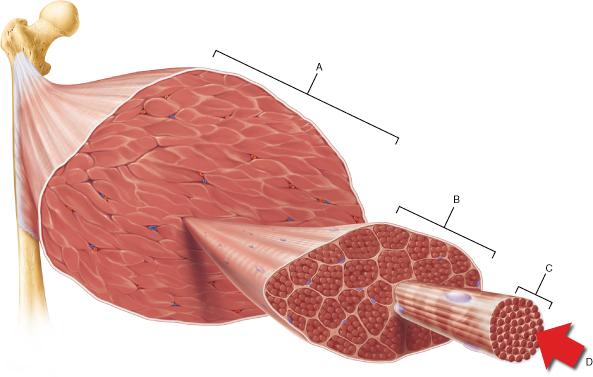 In the figure above, which structure corresponds to a single skeletal muscle cell?
| back 1 C |
front 2  The connective tissue that covers structure A is continuous with which of the following?
| back 2 Tendon |
front 3  Which structure corresponds to a single fascicle?
| back 3 B |
front 4  Which of the following is the smallest structural unit in which the distinctive striated bands characteristic of skeletal muscle are observed?
| back 4 D |
front 5  The smallest contractile unit within skeletal muscle would correspond to the distance between which two points in the figure?
| back 5 1 and 7 |
front 6  Between which two points would there be substantial amounts of both the proteins actin and myosin?
| back 6 2 and 3 |
front 7  The region between which two points corresponds to the entire A band?
| back 7 2 and 6 |
front 8 The region between which two points corresponds to the I band?
| back 8 None of the listed responses is correct. |
front 9  What cellular event is indicated by A?
| back 9 exocytosis |
front 10  What event directly triggers the release of neurotransmitter shown in A?
| back 10 diffusion of Ca2+ into the axonal terminus |
front 11  What specific neurotransmitter is released from the axonal terminus as shown in A?
| back 11 acetylcholine |
front 12  Which statement accurately describes the event indicated by B?
| back 12 Binding of acetylcholine to a receptor triggers the opening of an ion channel. |
front 13  Which event is most significant in initiating the "wave of depolarization" shown in event C?
| back 13 diffusion of Na+ into the muscle fiber |
front 14  The protein actin is indicated by which letter?
| back 14 A |
front 15  Which protein is indicated by E?
| back 15 myosin |
front 16  The molecular interaction described as a "cross bridge" involves the binding of which two of the letters below?
| back 16 A and C |
front 17  Which lettered protein functions as a motor protein?
| back 17 C |
front 18  The protein troponin is shown in this figure to be bound to which substance?
| back 18 calcium ion |
front 19  How many motor units are illustrated in the figure?
| back 19 2 |
front 20  Which of the following describes the neurons shown in this figure?
| back 20 somatic motor neurons |
front 21  If both of the neurons in the figure were activated, more muscle fibers would contract than if either neuron alone were active. This mechanism for control of the force of muscle contraction is known as ______.
| back 21 recruitment |
front 22  In which phase of the muscle twitch shown in the above figure would the maximum amount of ATP be consumed by myosin head groups?
| back 22 B |
front 23  In which phase in the figure would the net movement of Ca2+ into the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) be greatest?
| back 23 C |
front 24  What result would be expected if an additional stimulus, equal in intensity to the first, were to be applied to the muscle at the 60 millisecond (ms) time point?
| back 24 The muscle would increase in tension to a level greater than that measured at the beginning of phase C. |
front 25  Which mechanism requires energy input by the cell in the form of ATP hydrolysis?
| back 25 none of the mechanisms require energy input |
front 26  Which of the following events might the solid arrow at the bottom of B represent?
| back 26 the activation of specific cytoplasmic enzymes |
front 27  Which of the following is true regarding a response to an excitatory event which might occur soon after the initial stimulus indicated in the graph?
| back 27 An excitatory event may result in an action potential, but this will be less likely if the excitatory stimulus occurs during the response to the stimulus observed in the graph. |
front 28  What event is depicted in the structure labeled A?
| back 28 movement of Ca2+ into the interior of the axonal terminus through voltage-gated channels |
front 29  Which of the following most accurately describes the involvement of the structure labeled B in synaptic signaling?
| back 29 release of neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis |
front 30  Which of the following statements most accurately describes the effects caused by binding of the ligand shown to the structure labeled C?
| back 30 The membrane potential of the postsynaptic membrane changes. |
front 31  The box labeled D illustrates three mechanisms by which the effects of a neurotransmitter may be terminated. Which of the following mechanisms is NOT included in the figure?
| back 31 reuptake of the neurotransmitter by transport into the postsynaptic cell |
front 32  Signals generated at a chemical synapse are said to move only in the direction of the presynaptic cell to the postsynaptic cell. Which of the following statements regarding the mechanisms determining this one way transmission is INCORRECT?
| back 32 Ions diffusing out of the presynaptic cell can enter the postsynaptic cell, but cannot reenter the presynaptic cell. |
front 33  In which area of the neuron is an action potential initially generated?
| back 33 C |
front 34  Which of the following membrane regions would have significant numbers of voltage-gated Na+ and K+ ion channels?
| back 34 C and D |
front 35  Which of the following statements is true of both membrane potential responses shown in the graphs?
| back 35 Both responses are examples of graded potentials. |
front 36  Which result of the stimulus applied is the likely cause of the response observed in the left graph?
| back 36 opening of gated Na+ channels |
front 37  Which of the following is expected to occur first if the membrane potential increase shown in the graph were to reach the threshold value indicated at -55 mV?
| back 37 opening of voltage gated Na+ channels |
front 38  What change in a neuron is being measured in the graph?
| back 38 the voltage measured across the axon membrane at a specific point as an action potential travels past |
front 39  At which point of the illustrated action potential are the most gated Na+ channels open?
| back 39 B |
front 40  What major ion currents occur at the point along the action potential phase labeled D?
| back 40 diffusion of K+ out of the axon through gated ion channels |
front 41  Which of the following mechanisms is most significant in returning the membrane potential to the resting state (from point D to point E)?
| back 41 closure of the voltage-gated K+ channels |
front 42  At which of the points along the illustrated action potential can a second action potential be produced, but only with a stimulus significantly greater than that which produced the first?
| back 42 D |