Metric System
- the standard system of measurement in chemistry
International System of Units
- the official system of measurement throughout the world except for the United States
Length
-
Metric System
- meter (m)
-
SI
- meter (m)
Volume
-
Metric System
- liter (L)
-
SI
- cubic meter (m^3)
Mass
-
Metric System
- gram (g)
-
SI
- kilogram (kg)
Temperature
-
Metric System
- degree Celcius
-
SI
- kelvin (K)
Time
-
Metric System
- second (s)
-
SI
- second (s)
Meter
- one meter is equal to 39.4 inches
- 1 m = 100 cm
- 1 m = 39.4 in.
- 1 m = 1.09 yd
Centimeter
- a smaller unit of length
- commonly used in chemistry
- about equal to the width of your little finger
- 2.54 cm = 1 in.
Volume
- the amount of space a substance occupies
- 1 qt = 946 mL
- 1 L = 1000 mL
- 1 L = 1.06 qt
Liter (L)
- slightly larger than a quart (qt)
- 1 L = 1000 mL
- 1 L = 1.06 qt
Milliliter (mL)
- smaller and more convenient
- commonly used in labs and hospitals
- 1000 mL = 1 L
Mass of an Object
- a measure of the quantity of material it contains
-
SI UNIT
- kilogram (kg)
- used for larger masses, such as body mass
- kilogram (kg)
-
METRIC SYSTEM
- gram (g)
- used for smaller masses
- gram (g)
- 1000 g = 1 kg
- 1 kg = 2.20 lb
- 454 g = 1 lb
Weight
- a measure of the gravitational pull on an object
-
EXAMPLE:
- an astronaut with a mass of 75.0 kg has a weight of 165 lb
Temperature
- tells us how hot or cold something is
-
METRIC SYSTEM
- celsius (℃)
- water freezes at 0℃ and boils at 100℃
- whereas on the Fahrenheit scale, water freezes at 32℉ and boils at 212℉
- celsius (℃)
-
SI UNIT
- kelvin (K)
Time
- measured by second (s) on both systems
Measured Numbers
- the numbers you obtain when you measure a quantity
-
SUCH AS:
- height
- weight
- temperature
Significant Figures
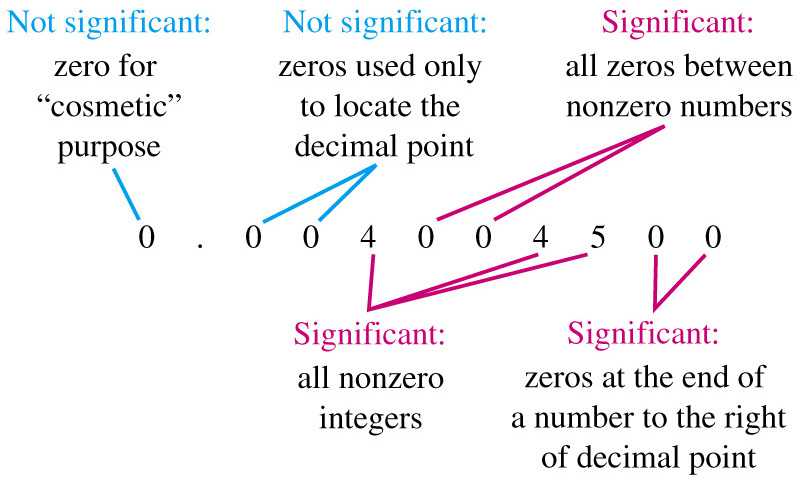
- SIGNIFICANT FIGURE RULES:
- all the digits including the estimated digit
- all nonzero digits and zeros between digits
- zeros at the end of a decimal number
-
A ZERO IS NOT A SIGNIFICANT FIGURE
- at the beginning of a decimal number
- used as a placeholder in a larger number without a decimal point
- not zeros that act as placeholders before digits
Scientific Notation and Significant Zeros

- when one or more zeros in a large number are significant, they are shown clearly by writing the number in scientific notation
Exact Numbers
- numbers obtained by counting items
- not measured
- do not have limited number of significant figures
- do not affect the number of significant figures in a calculated answer
Examples of Some Exact Numbers
- 8 doughnuts
- 2 baseballs
- 5 capsules
- 1 L = 1000 mL
- 1 m = 100 cm
- 1 kg = 1000 g
- 1 ft = 12 in
- 1 qt = 4 cups
- 1 lb = 16 oz
Rules for Rounding Off
- If the first digit to be dropped is 4 or less, then it and all the following digits are simply dropped from the number
- If the first digit to be dropped is 5 or greater, then the last retained digit of the number is increased by 1
Multiplication and Division with Measured Numbers pg. 32
- In multiplication or division, the final answer is written so that it has they same number of significant figures as the measurement with the fewest significant figures
Adding Significant Zeros pg. 32
- When the calculator display contains fewer SFs than needed, add one or more significant zeros to obtain the correct number of significant figures
Addition and Subtraction with SFs pg.32
- In addition or subtraction, the final answer is written so that it has the same number of decimal places as the measurement with the fewest decimal places
Prefix
- can be placed in front of any unit to increase or decrease its size by some factor of 10
-
EXAMPLES:
- milli....milligram (mg)
- micro....microgram (mcg)
Prefixes That Increase the Size of the Unit
- tera (T)
- numerical value: 1,000,000,000,000
- scientific notation: 1012
- equality: 1 Ts = 1 x 1012 s or 1 s = 1 x 10-12 Ts
- giga (G)
- numerical value: 1,000,000,000
- scientific notation: 109
- equality: 1 Gm = 1 x 109 m or 1 m = 1 x 10-12 Gm
- mega (M)
- numerical value: 1,000,000
- scientific notation: 106
- equality: 1 Mg = 1 x 106 g or 1 g = 1 x 10-6 Mg
- kilo (k)
- numerical value: 1,000
- scientific notation: 103
- equality: 1 km = 1 x 103 m or 1 m = 1 x 10-3 km
Prefixes That Decrease the Size of the Unit
- deci (d)
- numerical value: 0.1
- scientific notation: 10-1
- equality: 1 dL = 1 x 10-1 L or 1 L = 10 dL
- centi (c)
- numerical value: 0.01
- scientific notation: 10-2
- equality: 1 cm = 1 x 10-2 m or 1m = 100 cm
- milli (m)
- numerical value: 0.001
- scientific notation: 10-3
- equality: 1 ms = 1 x 10-3 s or 1 s = 1 x 103 ms
- micro (µ*)
- numerical value: 0.000001
- Scientific notation: 10-6
- equality: 1 µg = 1 x 10-6 g or 1 g = 1 x 106 µg
- nano (n)
- numerical value: 0.000000001
- scientific notation: 10-9
- equality: 1 nm = 1 x 10-9 m or 1 m = 1 x 109 nm
- pico (p)
- numerical value: 0.000000000001
- scientific notation: 10-12
- equality: 1 ps = 1 x 10-12 s or 1 s = 1 x 1012 ps
Equalities
- show the relationship between two units that measure the same
quantitiy
- 1 m = 100 cm.... = 1 x 102 cm
- 1 m = 1000 mm... 1 x 103 mm
- 1 cm = 10 mm... 1 x 101 mm
Cubic Centimeter
(abbreviated: cm3 or cc)
- the volume of a cube whose dimension are 1 cm on each side
- has the same volume as a millimeter
- 1 cm3 or cc = 1 mL
Measuring Mass
- 1 kg = 1000 g... = 1 x 103 g
- 1 g = 1000 mg... = 1 x 103 mg
- 1 g = 100 cg... = 1 x 102 cg
- 1 mg = 1000 mcg... = 1 x 103 mcg
Conversion Factors

- any equality written as fraction, with one of the quantities in the numerator and the other in the denominator
Equalities (conversion)
- uses two different units to describe the same measure amount
- written for relationship between units of the metric system, U.S. units, or between metric and U.S. units
-
EXAMPLES:
- 1 m = 1000 mm
- 1 lb = 16 oz
- 2.20 lb = 1 kg
Equalities: Conversion Factors & SF
- the numbers in:
- any equality between two metric units or between two U.S system units are obtained by definition and are exact number
- a definition are exact and are not used to determine SFs
- an equality between metric and U.S units contain one number obtained by measurement and count toward the significant figures
- Exception: The equality 1 in. = 2.54 cm has been defined as an exact relationship, 2.54 is an exact number
Conversion Factors From a Percentage
- a percent factor gives the ratio of the parts to the whole and
uses
- the same unit in the numerator and denominator
- uses the value of 100 and can be written as two factors
Problem Solving Using Unit Conversion
- requires one or more conversion factors to change a given unit to the needed unit
-
problem solving requires indentification of:
- the given quantity units
- the units needed
- conversion factors that connect the given and needed units
- given unit x one or more conversion factors = needed unit
Density

- compares the mass of an object to its volume
Volume Displacement
- A solid
- completely emerged in eater displaces its own volume of water
- has a volume calculated from the volume difference